Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cell Structure Components
Cell Structure Components
Uploaded by
equlleniiOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Cell Structure Components
Cell Structure Components
Uploaded by
equlleniiCopyright:
Available Formats
Cell Structure Components
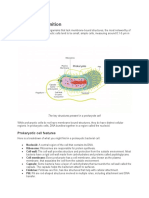
Both eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells share common structural components, including:
Unit membrane: Boundary that defines the cell or organelle.
Protoplasm: The living contents of the cell.
Genetic material: DNA or RNA that carries genetic information.
Ribosomes: Structures involved in protein synthesis.
Life is categorized into three domains: Archaea, Bacteria, and Eukarya. Archaea and Bacteria are
considered prokaryotic, while Eukarya consists of eukaryotic organisms. The presence of a nucleus
distinguishes eukaryotic cells from prokaryotic cells.
Prokaryotic Cells
Examples include bacteria and archaea.
DNA region: DNA is in the nucleoid, not enclosed by a membrane.
Single, circular DNA: Prokaryotes have a single circular DNA, whereas eukaryotes have linear DNA
organized into chromosomes.
Simpler Organization: Lack membrane-bound organelles.
Cell Wall Composition: Bacterial cell walls are made of peptidoglycan.
Organelles: Prokaryotes lack membrane-bound organelles, with the nucleoid and ribosomes being
exceptions.
Eukaryotic Cells
Examples include plants, animals, fungi, and some protozoa.
DNA region: DNA is within the nucleus, enclosed by a nuclear membrane.
Multiple Linear Chromosomes: Eukaryotes have multiple linear chromosomes within the nucleus.
Complex Organization: Contains membrane-bound organelles such as mitochondria, dictyosomes, and
chloroplasts (in plants).
Cell Wall Composition: Plant cell walls are made of cellulose, fungi cell walls are made of chitin.
No Cell Wall in Animals: Animals, despite being eukaryotic, lack a cell wall.
Organelles: Eukaryotes possess membrane-bound organelles such as mitochondria, chloroplasts, and
dictyosomes.
Key pointers of other terms:
• Plant cells have a cell wall made of cellulose.
• Fungi cells have a cell wall made of chitin.
• Bacterial cells have a cell wall made of peptidoglycan.
• Animals (eukaryotes) generally lack a cell wall.
• Ribosomes in both cell types synthesize proteins.
• Proteins act as catalysts, speeding up cellular reactions.
• The phylogenetic tree suggests that life originated from archaeobacteria, evolving into bacteria,
and then eukaryotes.
You might also like
- Prokaryote Definition: Prokaryotic Cell FeaturesDocument5 pagesProkaryote Definition: Prokaryotic Cell FeaturesAli ShanNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotes VS EukaryotesDocument15 pagesProkaryotes VS EukaryotesChool Cydrick B. BascosNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotes VS EukaryotesDocument15 pagesProkaryotes VS EukaryotesGamu GamuNo ratings yet
- All About CellsDocument49 pagesAll About CellsJeanine CristobalNo ratings yet
- Eukaryotes Have A Much More Complex Cell Structure Than ProkaryotesDocument9 pagesEukaryotes Have A Much More Complex Cell Structure Than Prokaryotesnevio.wirtgenNo ratings yet
- Lecture Differences Between Prokaryotes and EukaryotesDocument16 pagesLecture Differences Between Prokaryotes and EukaryotesAyesha MasoodNo ratings yet
- Difference Between Prokaryotes and EukaryoticDocument9 pagesDifference Between Prokaryotes and EukaryoticFadya P.No ratings yet
- Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellDocument56 pagesProkaryotic and Eukaryotic CellKENT GARCIA100% (1)
- The Building Blocks of LifeDocument105 pagesThe Building Blocks of LifePradhees BtechNo ratings yet
- Eukaryotic Cell DefinitionDocument5 pagesEukaryotic Cell DefinitionAnonymous QtQewv0XQhNo ratings yet
- Human CellDocument12 pagesHuman CellCrystal GarciaNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic/Eukaryotic Cell Structure: Dan FreemanDocument15 pagesProkaryotic/Eukaryotic Cell Structure: Dan FreemananneNo ratings yet
- Eukaryote BiologyDocument9 pagesEukaryote BiologyKrizzy EstoceNo ratings yet
- Cells: Michael HodgsonDocument21 pagesCells: Michael HodgsonAntoyia StewartNo ratings yet
- عملي ٢Document4 pagesعملي ٢adelshayea555No ratings yet
- Cell Parts and FunctionsDocument3 pagesCell Parts and FunctionsKyle OwenNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 - Cell TypesDocument16 pagesLesson 3 - Cell TypesArvin Jay LamberteNo ratings yet
- Group 3 Prokaryotic Vs Eukaryotic Cells HandoutsDocument4 pagesGroup 3 Prokaryotic Vs Eukaryotic Cells HandoutsClaire Angelie Ruaya100% (1)
- Prokaryotic VS Eukaryotic CellsDocument5 pagesProkaryotic VS Eukaryotic CellsAngelica FloraNo ratings yet
- HDTD-B-4 - Cell OrganellesDocument43 pagesHDTD-B-4 - Cell OrganellesMariam Qais100% (1)
- Essay Prokaryotic vs. EukaryoticDocument2 pagesEssay Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryoticctramel001No ratings yet
- Microbiology For The Health Sciences: Section II. Introduction To MicroorganismsDocument48 pagesMicrobiology For The Health Sciences: Section II. Introduction To MicroorganismsHiba Abu-jumahNo ratings yet
- Microbiology For The Health Sciences: Section II. Introduction To MicroorganismsDocument48 pagesMicrobiology For The Health Sciences: Section II. Introduction To MicroorganismsHashim Ghazo100% (1)
- Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellDocument19 pagesProkaryotic and Eukaryotic CellReanne MeregildoNo ratings yet
- Lec 2-Cell BiologyDocument48 pagesLec 2-Cell BiologyHowra KiyasdeenNo ratings yet
- Welcome To The Study of Life: Dr. Sajeela AhmedDocument32 pagesWelcome To The Study of Life: Dr. Sajeela AhmedMohammad NaqashNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotes and EukaryotesDocument21 pagesProkaryotes and EukaryotesJeff Hambre100% (2)
- Prokaryotic CellsDocument2 pagesProkaryotic CellsBerch MelendezNo ratings yet
- LESSON 3 - Prokaryotid Vs Eukaryotic CellsDocument41 pagesLESSON 3 - Prokaryotid Vs Eukaryotic CellsHyacinth RaeNo ratings yet
- Cell (Biology) : From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument15 pagesCell (Biology) : From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaShabbir Hussain MaloobhaiNo ratings yet
- Cell Types: Prokaryotes and EukaryotesDocument4 pagesCell Types: Prokaryotes and Eukaryotesمصطفى رسول هاديNo ratings yet
- Cell OrganizationDocument6 pagesCell OrganizationKaarthigan RamaiahNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic CellDocument4 pagesProkaryotic Cellkrista mae logronoNo ratings yet
- ZH Core IV - Cell BiologyDocument95 pagesZH Core IV - Cell Biologysahib100% (1)
- Cell (Biology) : From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument14 pagesCell (Biology) : From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediarycasiquinNo ratings yet
- Lecture1 CellDocument8 pagesLecture1 CellbaderNo ratings yet
- Unit Mahluk Hidup - Penyusun Mahluk HidupDocument56 pagesUnit Mahluk Hidup - Penyusun Mahluk HidupYahya RhamadanNo ratings yet
- Arindam Mondal: School of Bio ScienceDocument39 pagesArindam Mondal: School of Bio ScienceSohini RoyNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Biochemistry: by DR - Zaizafoon NabeelDocument34 pagesIntroduction To Biochemistry: by DR - Zaizafoon Nabeelabdinasir aliNo ratings yet
- Cell (Biology) : Cells in Different Phases of The Cell CycleDocument14 pagesCell (Biology) : Cells in Different Phases of The Cell CycleroavNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsDocument21 pagesProkaryotic and Eukaryotic CellskenNo ratings yet
- Cell StructuresDocument25 pagesCell StructuresAminul Islam Arafat 2132536642No ratings yet
- UOI Science Journal 3Document2 pagesUOI Science Journal 3reemagotewala81No ratings yet
- The Living CellDocument53 pagesThe Living CellDaniele Joseph HizonNo ratings yet
- 8 Cell The Unit of LifeDocument5 pages8 Cell The Unit of Lifebikram keshari pradhanNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure and FunctionDocument33 pagesCell Structure and FunctionFahim Abid100% (1)
- ProkariatesDocument24 pagesProkariatesteja prasadNo ratings yet
- Differences Between Prokaryotic & Eukaryotic Cells PresentationDocument24 pagesDifferences Between Prokaryotic & Eukaryotic Cells PresentationGeoffrey100% (1)
- Robert Hooke (1665) - Who Named The Biological Unit Cell Cell Theory 1839 - byDocument11 pagesRobert Hooke (1665) - Who Named The Biological Unit Cell Cell Theory 1839 - byKamlesh RatnamNo ratings yet
- Biochem Lecture 2Document3 pagesBiochem Lecture 2Samier AlihuddinNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 - Biology NotesDocument22 pagesUnit 1 - Biology Noteshuman tie lineNo ratings yet
- Cells As The Basis of Life 1Document40 pagesCells As The Basis of Life 1Singh Gurleen100% (1)
- Biochemistry & Genetics: II SHS 109: Resource Person: DR Tanveer Akbar Reference TextDocument54 pagesBiochemistry & Genetics: II SHS 109: Resource Person: DR Tanveer Akbar Reference TexttNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1-Introduction To The CellDocument18 pagesLecture 1-Introduction To The CellThuto SmithNo ratings yet
- Environmental Microbiology UNIT 1Document43 pagesEnvironmental Microbiology UNIT 1Esai Kanaga YadavNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 - 3Document32 pagesUnit 1 - 3Sunita SharmaNo ratings yet
- L.3 - The CellDocument3 pagesL.3 - The CellJari JariNo ratings yet
- Cells and Cell StructureDocument3 pagesCells and Cell Structureapi-238197463No ratings yet
- Reviewer For Science 11Document7 pagesReviewer For Science 11Bea Hannah FarrenNo ratings yet