Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Toxoplasma Gondii-2
Uploaded by
Ayu Zakiyah0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views10 pagesToxoplasma gondii is a protozoan parasite first described in 1908 that can infect nearly all warm-blooded animals and humans. It is one of the most common parasites globally. T. gondii has three infectious stages - the rapidly dividing tachyzoite stage found during acute infection, the slow-growing tissue cyst (bradyzoite) stage found in chronic infection, and the oocyst stage found only in the intestine of felines. The parasite has a complex life cycle involving sexual reproduction in felines and asexual reproduction in warm-blooded hosts. While most human infections are asymptomatic, it can cause severe disease in immunocompromised individuals or congenital infection if a woman is
Original Description:
PARASITOLOGI
Original Title
Toxoplasma_gondii-2-
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentToxoplasma gondii is a protozoan parasite first described in 1908 that can infect nearly all warm-blooded animals and humans. It is one of the most common parasites globally. T. gondii has three infectious stages - the rapidly dividing tachyzoite stage found during acute infection, the slow-growing tissue cyst (bradyzoite) stage found in chronic infection, and the oocyst stage found only in the intestine of felines. The parasite has a complex life cycle involving sexual reproduction in felines and asexual reproduction in warm-blooded hosts. While most human infections are asymptomatic, it can cause severe disease in immunocompromised individuals or congenital infection if a woman is
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views10 pagesToxoplasma Gondii-2
Uploaded by
Ayu ZakiyahToxoplasma gondii is a protozoan parasite first described in 1908 that can infect nearly all warm-blooded animals and humans. It is one of the most common parasites globally. T. gondii has three infectious stages - the rapidly dividing tachyzoite stage found during acute infection, the slow-growing tissue cyst (bradyzoite) stage found in chronic infection, and the oocyst stage found only in the intestine of felines. The parasite has a complex life cycle involving sexual reproduction in felines and asexual reproduction in warm-blooded hosts. While most human infections are asymptomatic, it can cause severe disease in immunocompromised individuals or congenital infection if a woman is
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 10
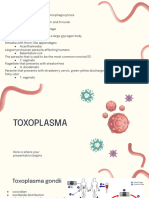
Toxoplasma gondii
History & Distribution
• First described in 1908 by Charles Nicolle and
Louis Herbert Manceaux in small North
American rodent called “gundi”
(Ctenodactylus gondii)
• Its importance as a human pathogen was
recognized much later when Janku (1923)
observed the cyst in the retina of a child with
hydrocephalus and micro-opthalmia
• The name Toxoplasma is derived from the
Greek word “Toxon” meaning arc or brow
referring to thecurved shape of the
trophozoite.
• Toxoplasma is now recognized as the most
common protozoan parasite globally, with the
widest range of hosts spread over 200 species
of birds, reptiles, and mammals including
human
Morphology
• Trophozoites (tachyzoites)
– Crescent shaped with one end pointed and the
other end rounded
– 3-7 µm in length. Nucleus is ovoid and is situated
at the blunt end of the parasite
– stains well with Giemsa stain
– Rapidly proliferating
• Tissue cyst (bradyzoites)
– Found during chronic stage in the brain (most
common site), skeletal muscles, various other
organs
– the cyst is round or oval, 10-20 µm and contains
numerous bradyzoites. Cyst remain viable in tissue
for several years
– In immunodeficient host, they may leading to
clinical disease
• Oocyst
– Develop only in definitive host (in the intestine of
cats and other felines but not in human)
– Oval, 10-12 µm diameter, thick resistant wall
– Formed by sexual reproduction (gametogony)
– Cats shed millions of oocysts per day in feces for
about 2 weeks during primary infection
– Undergo sporulation in the soil (sporulated oocyst
is infective stage)
– Very resistant to environmental conditions and
can remain infective in soil for about a year
Life cycle
Pathogenity
• One of the major fatal complications in AIDS
• Most human infections are asymptomatic
• Clinical toxoplasmosis may be congenital
(transmitted transplacentally from mother to
fetus) or acquired
Laboratory diagnosis
• Microscopy
– Tachyzoites and tissue cyst can be detected in
various specimens like blood, sputum, bone
marrow aspirate, cerebrospinal fluid, spleen and
brain
– Stain by Giemsa, PAS or GMS
– Tachyzoites appear as crescent-shaped structure
with blue cytoplasm and dark nucleus
• Animal inoculation
• Serodiagnosis
• Molecular
• Imaging
You might also like
- Toxoplasma GondiiDocument40 pagesToxoplasma GondiiNeelam Joshi100% (2)
- Miscellaneous Sporozoa and Microspora: Toxoplasma GondiiDocument10 pagesMiscellaneous Sporozoa and Microspora: Toxoplasma Gondiizahraakhalaf765No ratings yet
- Toxoplasma Pneumocystis Microsporidia BabesiaDocument40 pagesToxoplasma Pneumocystis Microsporidia BabesiadhaineyNo ratings yet
- Toxoplasmosis and Pregnancy: Parasitology Laboratorium Medical Faculty Jember UniversityDocument53 pagesToxoplasmosis and Pregnancy: Parasitology Laboratorium Medical Faculty Jember UniversityEnggar GumelarNo ratings yet
- Echinococcus: Santosh Kumar Yadav M.Sc. Clinical Microbiology Iom, TuthDocument40 pagesEchinococcus: Santosh Kumar Yadav M.Sc. Clinical Microbiology Iom, TuthMeenakshisundaram CNo ratings yet
- Dickens Study GuideDocument18 pagesDickens Study GuideBrad MooreNo ratings yet
- Phylum Class Order Genera: Apicomplexa Haematozoa Haemosporida Plasmodium Piroplasmida Coccidia EimeriidaDocument39 pagesPhylum Class Order Genera: Apicomplexa Haematozoa Haemosporida Plasmodium Piroplasmida Coccidia EimeriidaMegbaruNo ratings yet
- Protozoan Parasites: Gwy-Am Shin Office: Suite 2335, 4225 Roosevelt Phone: 206-543-9026 Email: Gwyam@u.washington - EduDocument35 pagesProtozoan Parasites: Gwy-Am Shin Office: Suite 2335, 4225 Roosevelt Phone: 206-543-9026 Email: Gwyam@u.washington - EduHazhar OmerNo ratings yet
- Chronic Active Toxoplasmosis PDFDocument15 pagesChronic Active Toxoplasmosis PDFHugo AzzolinaNo ratings yet
- Protozoal Infections 29 April 2013Document87 pagesProtozoal Infections 29 April 2013Nive KojNo ratings yet
- Toxo For 2Document13 pagesToxo For 2abel semuNo ratings yet
- Pathogens in The Environment: - Viruses and Prions - Bacteria and Rickettsiae - Fungi and Algae - Protozoans - HelminthsDocument34 pagesPathogens in The Environment: - Viruses and Prions - Bacteria and Rickettsiae - Fungi and Algae - Protozoans - HelminthsEnaANo ratings yet
- M2. TISSUE and INTESTINAL COCCIDIADocument3 pagesM2. TISSUE and INTESTINAL COCCIDIAocampoangelabeatrizebNo ratings yet
- Taenia SoliumDocument8 pagesTaenia SoliumJoshua Bien FuentesNo ratings yet
- Toxoplasmosis Class SMV 2023Document67 pagesToxoplasmosis Class SMV 2023SayonaraMeloNo ratings yet
- Protozoans ParasitesDocument29 pagesProtozoans Parasitespotatopurple009No ratings yet
- Para Lec 4Document24 pagesPara Lec 4stpaulafamilyNo ratings yet
- CDC - DPDX - ToxoplasmosisDocument7 pagesCDC - DPDX - ToxoplasmosisaginaNo ratings yet
- Toxoplasmosis - Page 1Document2 pagesToxoplasmosis - Page 1Ralph Charles Whitley, Sr.No ratings yet
- Proto Lec4Document29 pagesProto Lec4Syed Hammad UllahNo ratings yet
- PARASITOLOGY - Toxoplasma, SarcocystisDocument29 pagesPARASITOLOGY - Toxoplasma, Sarcocystistanishapatel1005No ratings yet
- Toxoplasma GondiiDocument29 pagesToxoplasma GondiiNagalingaNo ratings yet
- 39 HelminthiasisDocument87 pages39 HelminthiasisArlini Nurul YuliantiNo ratings yet
- EchinococcosisDocument52 pagesEchinococcosisZezo TarekNo ratings yet
- Jha CS, Sinha R, Sen S, Jha H. Intraoral Hydatid Cyst: A Review. J Oral Med, Oral SurgDocument29 pagesJha CS, Sinha R, Sen S, Jha H. Intraoral Hydatid Cyst: A Review. J Oral Med, Oral SurgDR.YASIR SHAFEEQ MohiyuddinNo ratings yet
- Parasitology - CestodesDocument23 pagesParasitology - CestodesJeth Roque GalleneroNo ratings yet
- Week 15Document4 pagesWeek 15DELOS SANTOS JESSIECAHNo ratings yet
- Page Three 100509ToxoplasmaGondiinfectsMostSpeciesPage3Document2 pagesPage Three 100509ToxoplasmaGondiinfectsMostSpeciesPage3Ralph Charles Whitley, Sr.No ratings yet
- Echinococcus SP.: ClassificationDocument6 pagesEchinococcus SP.: ClassificationLucia VillacrizNo ratings yet
- Submitted By: Group 6 MT 3BDocument49 pagesSubmitted By: Group 6 MT 3BChristine Joy TanglaoNo ratings yet
- Cestode NotesDocument26 pagesCestode NotesJOSEPH NDERITUNo ratings yet
- Pha6114 CestodesDocument34 pagesPha6114 CestodesLisaNo ratings yet
- (I2M Week 6-7) Multicellular PathogensDocument40 pages(I2M Week 6-7) Multicellular PathogensellaNo ratings yet
- ParasitologyDocument29 pagesParasitologyPC NNo ratings yet
- Fungal Mycosis and Other InfectionsDocument34 pagesFungal Mycosis and Other InfectionsRajeev PotadarNo ratings yet
- Worksheet in Bio 102: Microbiology and Parasitology (WEEK 17)Document3 pagesWorksheet in Bio 102: Microbiology and Parasitology (WEEK 17)DELOS SANTOS JESSIECAHNo ratings yet
- Medical Parasitology Part 3 Fourth LectureDocument18 pagesMedical Parasitology Part 3 Fourth LectureIbraheem YesharNo ratings yet
- Echniococcus Granulosis: Submitted By: Arushi Patiyal B.Sc. (Hons) Microbiology 3 YearDocument41 pagesEchniococcus Granulosis: Submitted By: Arushi Patiyal B.Sc. (Hons) Microbiology 3 YearArushi PatiyalNo ratings yet
- Bakteri ClostridiumDocument39 pagesBakteri ClostridiumEuuzNo ratings yet
- Hydatid CystDocument50 pagesHydatid CystShashidhara Puttaraj100% (1)
- Toxoplas MA: Mohd Faris Bin Mohd PUADI (M132001834)Document18 pagesToxoplas MA: Mohd Faris Bin Mohd PUADI (M132001834)Mohd Faris PuadiNo ratings yet
- Fungi & Systemic MycosesDocument49 pagesFungi & Systemic MycosesAmal ShereefNo ratings yet
- Medical Parasitology PDFDocument33 pagesMedical Parasitology PDFRohan100% (1)
- Medical ParasitologyDocument33 pagesMedical ParasitologyAlexander Luie Jhames SaritaNo ratings yet
- Hydatid Disease (Hydatidosis) ,-19-20Document8 pagesHydatid Disease (Hydatidosis) ,-19-20Djdjjd SiisusNo ratings yet
- Para Handout - Coccidia - ToxoplasmaDocument15 pagesPara Handout - Coccidia - ToxoplasmaDerick SemNo ratings yet
- Toxoplasmosis2019 PDFDocument69 pagesToxoplasmosis2019 PDFDavid Felipe Cardona GuarinNo ratings yet
- ToxoplasmosisDocument27 pagesToxoplasmosisKnjigeNo ratings yet
- Trypanosoma CruziDocument38 pagesTrypanosoma CruziChipego ChiyaamaNo ratings yet
- Echinococcus GranulossusDocument23 pagesEchinococcus GranulossusDorothyNo ratings yet
- Chaga's and TaxoplasmosisDocument4 pagesChaga's and TaxoplasmosisIvan Tangliben100% (1)
- Parasitology Lecture 6 - CoccidiaDocument4 pagesParasitology Lecture 6 - Coccidiamiguel cuevasNo ratings yet
- Cyclophyllidean CestodesDocument92 pagesCyclophyllidean CestodesPauline AñesNo ratings yet
- Fungi & Systemic MycosesDocument42 pagesFungi & Systemic MycosesariffdrNo ratings yet
- Parasites ..Practical 2Document98 pagesParasites ..Practical 2Radhwan Hameed Asad100% (1)
- Cestoda Nematoda Trematoda 2018 - IDocument37 pagesCestoda Nematoda Trematoda 2018 - IAnonymous OWCJUT1100% (1)
- Advanced Medical ParasitologyDocument6 pagesAdvanced Medical ParasitologyDjdjjd SiisusNo ratings yet
- Biology Parasitology Revision NotesDocument29 pagesBiology Parasitology Revision NotesUsman Ali KhanNo ratings yet
- Life Cycle, Pathogenicity, Causes, Symptoms and Control of LeishmaniaDocument24 pagesLife Cycle, Pathogenicity, Causes, Symptoms and Control of LeishmaniaAditi TanwarNo ratings yet