Professional Documents
Culture Documents
3 Gastrointestinal Intubations
Uploaded by
megbriansularte0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views19 pagesGastrostomy, PEG, and nasogastric tubes can be used to deliver food and medications directly to the stomach or small intestine through openings in the abdominal wall or nose. Various types of tubes are inserted through different routes depending on factors like the patient's condition and how long the tube will be needed. Nurses are responsible for properly placing, maintaining, and caring for enteral tubes to ensure safe and effective delivery of feedings and medications.
Original Description:
Thank you
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentGastrostomy, PEG, and nasogastric tubes can be used to deliver food and medications directly to the stomach or small intestine through openings in the abdominal wall or nose. Various types of tubes are inserted through different routes depending on factors like the patient's condition and how long the tube will be needed. Nurses are responsible for properly placing, maintaining, and caring for enteral tubes to ensure safe and effective delivery of feedings and medications.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views19 pages3 Gastrointestinal Intubations
Uploaded by
megbriansularteGastrostomy, PEG, and nasogastric tubes can be used to deliver food and medications directly to the stomach or small intestine through openings in the abdominal wall or nose. Various types of tubes are inserted through different routes depending on factors like the patient's condition and how long the tube will be needed. Nurses are responsible for properly placing, maintaining, and caring for enteral tubes to ensure safe and effective delivery of feedings and medications.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 19
Gastrostomy
• Surgical creation of a gastric fistula through the abdominal
wall, necessary in some cases of cicatricial stricture of the
esophagus for the purpose of introducing food into the
stomach.
Percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy (PEG)
• A feeding ostomy. PEG tubes are inserted through the
esophagus into the stomach with the aid of an endoscope
and then pulled through a stab wound made in the
abdominal wall.
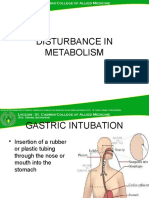
Nasogastric
• the nostril to the nasopharynx and to the stomach
Gastrointestinal Tubes
• Can be inserted via
– Nose
– Stomach
• Many types can be inserted by nurses, but some
of the larger, longer or multiple lumen tubes must
be inserted by physicians or nurses with advanced
training
Enteral Access devices
• Access can be achieved via various routes
– Nasogastric = inserted thru 1 of nostrils down
nasopharnyx to alimentary tract (may also go mouth
down but causes gagging++ and discomfort, more often
in premies)
– Nasoenteric inserted same as Nasogastric but extends
down into upper small intestine (used with those with
high risk of aspiration)
– Gastrostomy, Jejunostomy = for longer term and placed
via placement thru abd wall into stomach (gastrostomy)
or into jujumen (Jejunostomy)
NG tubes
• Used with
– Pts with intact gag & cough reflexes
– Pts with adequate gastric emptying
– Short term use
Inserting a NG tube
• If rubber tube used, place on ice for 5-10 mins to stiffen
tube
• Make sure guide wire if present is secured in position
• Measure distance (NEX)
• Use only water soluble lubricant
• Have pt sit upright, head back
• Once tube at throat (gag) have client tilt head forward
and swallow
• NEVER, NEVER, EVER FORCE A TUBE DOWN
Obtaining the NEX
(nose, earlobe and
xiphoid)
Some tubes may be
pre-measured but
this may not
correlated exactly
with the
measurement
obtained
TO CONFIRM PLACEMENT OF NG
• Placement most reliably confirmed by x-ray
• Can also aspirate for stomach contents or auscultate
air insufflation
1. Aspirate for stomach contents = attach syringe to
tube and apply gentle pressure. If contents return,
tube is in place
2. Air insufflation = attach syringe, place stethoscope
over pt’s epigastric region. Inject about 15-20ml of
air and listen for “whoosh”
3. Ask pt to talk = if cannot talk, tube may be coiled in
throat or passed through vocal cords
Pt with NG tube
• Will require
– Inspect nose for discharge and irritation
– Clean nostril and tube
– Apply water soluble lubricant to nostril if area dry,
crusted
– Frequent mouth care (q2h) as client will be NPO
NG problem solving
• Pain or vomiting after insertion = indicates tube is
obstructed or incorrectly placed
• Not draining = may be obstructed or needs to
repositioned then checked again for placement
• If pt displaying signs of distress (gasping, coughing,
cyanotic) remove tube immediately
Nurses responsibility
• Assess gastric contents
– Color
– Consistency
– Odor
– Amount
• Irrigate tube before and after meds/feeds
• Check GI function by auscultation for bowel sounds
Enteral Feeding & Meds
• Long Term Support accomplished by creating a an opening
into:
– Gastrostomy (opening into stomach)
– Jejunostomy (opening into jejunum)
• Methods of feeding includes:
– PEG (Percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy)
– Surgical or laproscopically placed gastrostomy tube
• More & more PEG’s are popular as can be safely inserted &
removed at bedside or in OPD
To insert requires (by a physician)
– local anesthesia,
– passage of endoscope into stomach,
– a small incision or stab wound thru the skin of the
abdomen
– pushing a cannula thru the incision
– insertion of guide wire thru cannula
– introduction & placement of PEG
Before feeds with PEG’s or NG
• NG placement should be confirmed:
– After insertion
– Before beginning meds or feeds
– At regular interval during a continuous feed
• With NG’s and New PEG’s anticipate:
– Measuring of residual before each feed
– Measuring residual done to evaluate absorption of last
feed (ie. Is there undigested formula from a previous
feed)
If residual is more than last infusion or 150 ml,
hold feeding for 1 hour and recheck.
For continuous feeds, check residual q4-6 hours
• Assess bowel sounds prior to each feeding or for
continuous feeds, q4-8h
• Monitor for abdominal distention (would indicate
intolerance to previous feed)
• Monitor for diarrhea, constipation or flatulence (lack
of bulk may cause constipation. Hypertonic or
concentration of formula may cause diarrhea or
flatulence)
Nursing care
• Elevate head at least 30 degrees during feed and 1 hr
following
• Tube must be flushed before and after feeds, med admin or
aspiration for patency
• Delivery sets must be changed q 12-24hrs or according to
policy
• Opened cans must be stored according to manufacturer’s
directions
• Clean skin and stoma area at least daily, should be qshift
• Mouth care q2-4 hours
You might also like
- Clinical Nursing Manual PDFDocument93 pagesClinical Nursing Manual PDFVatau FlorinNo ratings yet
- Gavage, Enteral Feeding or Tube Feeding. Placement May Be Temporary For TheDocument5 pagesGavage, Enteral Feeding or Tube Feeding. Placement May Be Temporary For TheWillen May Delopere Lomarda100% (1)
- Nasogastric Tube: - Insertion - FeedingDocument61 pagesNasogastric Tube: - Insertion - FeedingJustine Cagatan75% (4)
- Promoting Nutrition (Enteral Nutrition)Document51 pagesPromoting Nutrition (Enteral Nutrition)Yayin Pestaño100% (1)
- GASTROSTOMYDocument8 pagesGASTROSTOMYRio Gonzales100% (1)
- Gastrostomy and JejunostomyDocument43 pagesGastrostomy and JejunostomyLeslie Anne Alcibar TababaNo ratings yet
- NGT FeedingDocument8 pagesNGT FeedingSheng GosepNo ratings yet
- Therapeutic DietsDocument34 pagesTherapeutic DietsBanthracis67% (3)
- Gastric LavageDocument19 pagesGastric LavageAnita Santiago Soguilon100% (1)
- Nasogastric Tube Insertion, Feeding and RemovalDocument13 pagesNasogastric Tube Insertion, Feeding and RemovalJacqueline de Asis100% (2)
- Nasogastric Tube Insertion 2006Document43 pagesNasogastric Tube Insertion 2006Fira W100% (1)
- Basic Nursing ProceduresDocument9 pagesBasic Nursing Proceduresbernadette_olaveNo ratings yet
- D - 10answer KeyDocument16 pagesD - 10answer KeyJune DumdumayaNo ratings yet
- Dysphagia, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandDysphagia, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- NGT InsertionDocument10 pagesNGT Insertionapi-3722454100% (3)
- Final Questionnaires 123Document2 pagesFinal Questionnaires 123Kristel Jane QuitoNo ratings yet
- Return Residual Fluid To Stomach Via Tube and Proceed To FeedingDocument7 pagesReturn Residual Fluid To Stomach Via Tube and Proceed To FeedingMhae De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Nasogastric Tube InsertionDocument18 pagesNasogastric Tube InsertionSandya PallapotuNo ratings yet
- Rotation Plan For Ward DutyDocument9 pagesRotation Plan For Ward DutyMarj Herrera0% (1)
- Elderly Care 101-NGT and PEGDocument92 pagesElderly Care 101-NGT and PEGBecky GalanoNo ratings yet
- PEG Tube Feeding or Care CompleteDocument7 pagesPEG Tube Feeding or Care CompleteMJ LomuntadNo ratings yet
- Nasogastric Tube FeedingDocument7 pagesNasogastric Tube FeedingVina Empiales100% (1)
- NutritionDocument53 pagesNutritionalelichengNo ratings yet
- GI Ch.44-47Document40 pagesGI Ch.44-47W11795800% (1)
- 68w Health CareDocument598 pages68w Health CareRaluca Buzatu100% (1)
- G.I QuestionsDocument32 pagesG.I QuestionsNic Korapat100% (8)
- Romsons-All-Product CATALOG PDFDocument53 pagesRomsons-All-Product CATALOG PDFrendysamanosuke71% (7)
- Sample ExamDocument13 pagesSample ExamJenny Mendoza VillagonzaNo ratings yet
- NUR 204 2019 Inserting A Nasogastric TubeDocument56 pagesNUR 204 2019 Inserting A Nasogastric TubeHanan DaghashNo ratings yet
- NGT Feeding ChecklistDocument1 pageNGT Feeding ChecklistJoycee BoNo ratings yet
- Care of Unconscious PatientDocument5 pagesCare of Unconscious PatientRuchika Kaushal67% (3)
- .archNG - Parenteral NutritionDocument77 pages.archNG - Parenteral NutritionBidhya GuptaNo ratings yet
- Gastrostomy Feeding ProcedureDocument5 pagesGastrostomy Feeding ProcedureRohini RaiNo ratings yet
- NGTDocument27 pagesNGTMark Christian M. GonzagaNo ratings yet
- NGT Insertion 2022Document41 pagesNGT Insertion 2022Krishna Faith P. DelaraNo ratings yet
- NG Tube IntubationDocument40 pagesNG Tube IntubationVed BratNo ratings yet
- NG Tube InsertionDocument37 pagesNG Tube InsertionSarah BirechNo ratings yet
- Types of Feeding-GastrostomyDocument8 pagesTypes of Feeding-GastrostomyElda KuizonNo ratings yet
- Gastrostomy, Duodenostomy and Jejunostomy Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument5 pagesGastrostomy, Duodenostomy and Jejunostomy Nursing ResponsibilitiesRocco WalksNo ratings yet
- Nasogastric Intubation: DR - Efman.E.U.Manawan Mkes.,Spb-KbdDocument32 pagesNasogastric Intubation: DR - Efman.E.U.Manawan Mkes.,Spb-KbdBilly PeterNo ratings yet
- NGTDocument36 pagesNGTAstrid Bernadette Ulina PurbaNo ratings yet
- Ncm116 Skills LabDocument17 pagesNcm116 Skills LabMarie Isabelle HerveraNo ratings yet
- Nasogastric Tubes: NOAA Diving Medical Technician 2015Document30 pagesNasogastric Tubes: NOAA Diving Medical Technician 2015Silvia Rossa MuisNo ratings yet
- Nursing Skills: Enteral Nutrition / NGTDocument6 pagesNursing Skills: Enteral Nutrition / NGTJames Bryan ⎝⏠⏝⏝⏠⎠ NoboraNo ratings yet
- Care To The Digestive SystemDocument16 pagesCare To The Digestive SystemSONGA AmriNo ratings yet
- Nasogastric Tube Insertion AND Feeding: Mrs. Pramodini R. KhobragadeDocument35 pagesNasogastric Tube Insertion AND Feeding: Mrs. Pramodini R. Khobragadeomar kmr97No ratings yet
- NGT FeedingDocument19 pagesNGT FeedingzhaimeangirlNo ratings yet
- NGT Insertion: Group 2 Guerrero, Gumatay, Lim, Lopez, Mallabo, Miñano, Nario, Olores, Paaño, Pajutan, Paz, PerezDocument19 pagesNGT Insertion: Group 2 Guerrero, Gumatay, Lim, Lopez, Mallabo, Miñano, Nario, Olores, Paaño, Pajutan, Paz, PerezHarlyn MagsinoNo ratings yet
- NG Tube Lictures 2023Document22 pagesNG Tube Lictures 2023ALi NursingNo ratings yet
- Naspo Gastric Tube Feeding FinalDocument32 pagesNaspo Gastric Tube Feeding FinalNezuko0% (1)
- Day 5 Lecture - GI and NutritionDocument65 pagesDay 5 Lecture - GI and NutritionRemej SilutgamNo ratings yet
- Enteral FeedingDocument11 pagesEnteral Feedingنعمة حسنىNo ratings yet
- Providing Special CareDocument23 pagesProviding Special CareJan LagriaNo ratings yet
- Module 3 Nursing Skills Procedure On GI, Endo-Metab Concept (A)Document18 pagesModule 3 Nursing Skills Procedure On GI, Endo-Metab Concept (A)Nashebah A. BatuganNo ratings yet
- Og NGDocument22 pagesOg NGSandya PallapotuNo ratings yet
- Gastrointestinal Intubation: Nasogastric TubesDocument29 pagesGastrointestinal Intubation: Nasogastric TubesAgastya JanardhanaNo ratings yet
- Common Complication: What Is It?Document5 pagesCommon Complication: What Is It?khalidicuNo ratings yet
- Feeding by Nasogastric TubesDocument3 pagesFeeding by Nasogastric TubesLheidaniel MMM.No ratings yet
- Objectives: at The End of The Discussion The Students Will Be Able ToDocument6 pagesObjectives: at The End of The Discussion The Students Will Be Able ToMichael Angelo SeñaNo ratings yet
- NGTDocument4 pagesNGTRuthie BangteganNo ratings yet
- Enteral NutritionDocument18 pagesEnteral Nutritiontwy113No ratings yet
- NUTRI LEC CalaraDocument6 pagesNUTRI LEC CalaracalarasheanNo ratings yet
- Nasogastric NG Tube PlacementDocument10 pagesNasogastric NG Tube PlacementA.J PolyNo ratings yet
- NGT PresentationDocument23 pagesNGT PresentationniyigokNo ratings yet
- Gastrointestinal Treatment Modalties 1Document28 pagesGastrointestinal Treatment Modalties 1AndreNo ratings yet
- Nasogastric Tube Insertion PreparedDocument30 pagesNasogastric Tube Insertion PreparedicameilisayofianaNo ratings yet
- Nasogastric Intubation: DR - Efman.E.U.Manawan Mkes.,Spb-KbdDocument32 pagesNasogastric Intubation: DR - Efman.E.U.Manawan Mkes.,Spb-KbdNur Ilmi SofiahNo ratings yet
- Nasogastric IntubationDocument3 pagesNasogastric IntubationUmbra MeaNo ratings yet
- Inserting A Nasogastric TubeDocument38 pagesInserting A Nasogastric TubeMicah Alexis CandelarioNo ratings yet
- NGT Feeding Discussion InotDocument2 pagesNGT Feeding Discussion InotRhenelyn Delos ReyesNo ratings yet
- Ccu NotesDocument76 pagesCcu NotesAr PeeNo ratings yet
- Nasogastric IntubationDocument4 pagesNasogastric IntubationDaphnie Mikaela Belarmino LayuganNo ratings yet
- If they could talk about walking again: Canine Cruciate Surgery Rehabilitation Program: A 10 week detailed program of specific approaches, exercises, massage, and restoring balance to get the best results after your pet has undergone surgery for cruciate ligament repair. Tracking sheets for each week.From EverandIf they could talk about walking again: Canine Cruciate Surgery Rehabilitation Program: A 10 week detailed program of specific approaches, exercises, massage, and restoring balance to get the best results after your pet has undergone surgery for cruciate ligament repair. Tracking sheets for each week.No ratings yet
- Rules and Directions for the Employment of Injections in Various DiseasesFrom EverandRules and Directions for the Employment of Injections in Various DiseasesNo ratings yet
- PRACTICE TEST 1 - SECE StudentDocument17 pagesPRACTICE TEST 1 - SECE StudentAlex OlivarNo ratings yet
- NGT Peritoneal LavageDocument12 pagesNGT Peritoneal LavageJeffrey Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Nursing Review Bullets HighlightsDocument65 pagesNursing Review Bullets HighlightsEuanne OrellanoNo ratings yet
- NGTDocument2 pagesNGTMohamad AbdelkhalikNo ratings yet
- Insertion of A Nasogastric TubeDocument3 pagesInsertion of A Nasogastric TubeJames Andre P. MoralesNo ratings yet
- A Guide To Emergency Departments Nursing Documentation 2020Document67 pagesA Guide To Emergency Departments Nursing Documentation 2020Mary Christiane alvendiaNo ratings yet
- Petrus Nnolim CVDocument5 pagesPetrus Nnolim CVagni.nnolimNo ratings yet
- NP IiiDocument9 pagesNP IiiVia LatrasNo ratings yet
- Worksheets - Isbar Week 4 x1Document3 pagesWorksheets - Isbar Week 4 x1api-631170779No ratings yet
- Enteral and Parenteral Nutrition Support: Chapter Sections and Learning Objectives (Los)Document28 pagesEnteral and Parenteral Nutrition Support: Chapter Sections and Learning Objectives (Los)Hasby RiesandyNo ratings yet
- Learning Activity N3A & N3BDocument3 pagesLearning Activity N3A & N3BMikaela JosonNo ratings yet
- Tube FeedingDocument47 pagesTube FeedingArlyn Mendenilla0% (1)
- Act2 - Additional Info and QuestionsDocument4 pagesAct2 - Additional Info and QuestionsMika SaldanaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Skills ChecklistDocument7 pagesNursing Skills Checklistapi-353970372No ratings yet
- مزاولةDocument226 pagesمزاولةyaraikhlayelNo ratings yet