Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Conclusions
Uploaded by
Ravi Sankar0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views2 pagesHeavy metals originate in municipal solid waste from various sources like batteries, electronics, paint chips and more. These metals can contaminate the compostable organic waste. In 2013 in the US, recycling and composting rates were only 34.3% despite Americans generating 254 million tons of total waste. Waste incinerators emit more carbon dioxide per unit of electricity than coal plants, making waste a poor fuel source for power generation.
Original Description:
conclusions
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentHeavy metals originate in municipal solid waste from various sources like batteries, electronics, paint chips and more. These metals can contaminate the compostable organic waste. In 2013 in the US, recycling and composting rates were only 34.3% despite Americans generating 254 million tons of total waste. Waste incinerators emit more carbon dioxide per unit of electricity than coal plants, making waste a poor fuel source for power generation.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views2 pagesConclusions
Uploaded by
Ravi SankarHeavy metals originate in municipal solid waste from various sources like batteries, electronics, paint chips and more. These metals can contaminate the compostable organic waste. In 2013 in the US, recycling and composting rates were only 34.3% despite Americans generating 254 million tons of total waste. Waste incinerators emit more carbon dioxide per unit of electricity than coal plants, making waste a poor fuel source for power generation.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
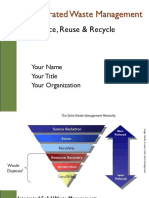
Heavy metals in Municipal Solid Waste
• Heavy metals originate mostly in non source-separated municipal
solid wastes from a verity of sources: batteries, electronic appliances,
newspapers, paint chips, foils, motor oils and plastics that can all
introduce metal contaminant into the compostable organic fraction
(Hamdi et al., 2003) – Heavy metal distribution in soil and plant in
municipal solid waste compost amended plots, F. Ayari; H. Hamdi;
N.Jedidi; N.Gharbi; R.Kossai, Int. J. Environ Sci. Tech, 2010.
Waste to Energy plant scenario in USA
• In 2013, Americans generated about 254 million tons of trash and
recycled and composted about 87 million tons of this material,
equivalent to a 34.3 percent recycling rate. On average, we recycled
and composted 1.51 pounds of our individual waste generation of
4.40 pounds per person per day. – Recycling rate is only 34.3% in the
year 2013.
• U.S. EPA estimates incinerators emit more CO2 per unit of electricity
(2,988 lbs/MWH) than coal-fired power plants (2,249 lbs/MWH), This
makes waste a very poor fuel source for power generation.44 A
report by Eco-Cycle points to the Intergovernmental Panel of Climate
Change’s (“IPCC”) CO2 reporting requirements that include both
biogenic and non-biogenic greenhouse gas emissions when
comparing electricity generation sources
You might also like
- Jay ProjectDocument29 pagesJay ProjectJay ChouguleNo ratings yet
- A Short Review On Solid Waste Generations Recycling Andmanagement in The Present Scenario of IndiaDocument7 pagesA Short Review On Solid Waste Generations Recycling Andmanagement in The Present Scenario of IndiaNeeraj ChaubeyNo ratings yet
- E-Waste PresentationDocument31 pagesE-Waste PresentationSimran Singh100% (4)
- Assessment of Heavy Metal Contamination in Soil Due To Leachate Migration From An Open Dumping SiteDocument13 pagesAssessment of Heavy Metal Contamination in Soil Due To Leachate Migration From An Open Dumping SiteEustache NIJEJENo ratings yet
- Submitted To:-Submitted byDocument9 pagesSubmitted To:-Submitted byAastha JoshiNo ratings yet
- A Review of The Recycling of Non-Metallic Fractions of Printed Circuit BoardsDocument11 pagesA Review of The Recycling of Non-Metallic Fractions of Printed Circuit BoardsJon Bisu DebnathNo ratings yet
- ConcreteDocument56 pagesConcreteइंजि कौस्तुभ पवार100% (1)
- Solid WasteDocument12 pagesSolid WasteMoayedJaberNo ratings yet
- MSW esW5myIzvn PDFDocument38 pagesMSW esW5myIzvn PDFKavya ModiNo ratings yet
- Internship ReportDocument11 pagesInternship ReportgeorgeNo ratings yet
- What Does It Mean? 2 Kinds of Waste: Biodegradable NonbiodegradableDocument18 pagesWhat Does It Mean? 2 Kinds of Waste: Biodegradable NonbiodegradableMoazzam HayatNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Heavy Metals Content in Soils and Plants Around Waste Dumpsites in Uyo Metropolis, Akwa Ibom StateDocument12 pagesAssessment of Heavy Metals Content in Soils and Plants Around Waste Dumpsites in Uyo Metropolis, Akwa Ibom StatetheijesNo ratings yet
- Development of A Polythene Recycling Machine From Locally Sourced MaterialsDocument5 pagesDevelopment of A Polythene Recycling Machine From Locally Sourced MaterialsjackullyNo ratings yet
- Waste ManagementDocument31 pagesWaste ManagementBravo HeroNo ratings yet
- Ewaste ContentDocument18 pagesEwaste ContentRajas WadivkarNo ratings yet
- Factors Affecting The Generation of Solid Waste: Assignment TopicDocument4 pagesFactors Affecting The Generation of Solid Waste: Assignment TopicImran AwanNo ratings yet
- Dealing With Ewaste For Industry, Enviromental Protection and SustainabilityDocument16 pagesDealing With Ewaste For Industry, Enviromental Protection and SustainabilityJake SuttonNo ratings yet
- Recovery of Precious Metals From Electronic WasteDocument43 pagesRecovery of Precious Metals From Electronic WasteHemant Gaule100% (1)
- Amount of Electronic Waste WorldwideDocument2 pagesAmount of Electronic Waste WorldwideNoor Uddin SakifNo ratings yet
- Effect of Heavey Metal Contaminationin The SoilDocument15 pagesEffect of Heavey Metal Contaminationin The SoilgebregideyNo ratings yet
- Ewaste 2023 BookchapterDocument1 pageEwaste 2023 BookchapterDivyansh VermaNo ratings yet
- Statistics Division: United NationsDocument32 pagesStatistics Division: United NationsVaibhav RohraNo ratings yet
- Environment Law AssignmentDocument49 pagesEnvironment Law AssignmentGouri SureshNo ratings yet
- Electronic Waste Management in IndiaDocument11 pagesElectronic Waste Management in IndiaJegadeeswaran SivagnanamNo ratings yet
- Ewaste Recycling FactsDocument4 pagesEwaste Recycling FactsBotagoz KaukenovaNo ratings yet
- World's Largest Science, Technology & Medicine Open Access Book PublisherDocument39 pagesWorld's Largest Science, Technology & Medicine Open Access Book PublisherMelchor MesalinaNo ratings yet
- Types of Waste: Waste Any Unwanted Item or Substance Resulting FromDocument21 pagesTypes of Waste: Waste Any Unwanted Item or Substance Resulting Fromashraf refaatNo ratings yet
- Business PlanDocument44 pagesBusiness PlanAnubhav Sood50% (2)
- Introduction To Solid Waste ManagementDocument49 pagesIntroduction To Solid Waste ManagementDudinciNo ratings yet
- Summary of Key ConceptsDocument3 pagesSummary of Key ConceptssupercleoNo ratings yet
- Solid Waste ManagementDocument26 pagesSolid Waste ManagementSanjeev KumarNo ratings yet
- SampleDocument11 pagesSamplevssubrahmaniyan0No ratings yet
- Solid Waste ManagementDocument69 pagesSolid Waste ManagementShane RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Fec IvDocument55 pagesFec Ivgauravkr060606No ratings yet
- Final Solid WasteDocument58 pagesFinal Solid Wastedigvijay909100% (3)
- A Review On Electric and Electronic Waste Material Management in 21st CenturyDocument1 pageA Review On Electric and Electronic Waste Material Management in 21st CenturyDivyansh VermaNo ratings yet
- Scrap Metal Recycling Industry ArticleDocument6 pagesScrap Metal Recycling Industry ArticleRidhi AroraNo ratings yet
- The International Journal of Engineering and Science (The IJES)Document8 pagesThe International Journal of Engineering and Science (The IJES)theijesNo ratings yet
- Electronic Waste: ProblemsDocument4 pagesElectronic Waste: ProblemsManish KumarNo ratings yet
- E Waste Management SeminarDocument20 pagesE Waste Management SeminarAbhinav.44No ratings yet
- Solid Waste Guided NotesDocument2 pagesSolid Waste Guided Notesapi-268533145No ratings yet
- Environmental Impacts of Energy From Biomass Unit 4Document7 pagesEnvironmental Impacts of Energy From Biomass Unit 4Rafia Rayana btbcNo ratings yet
- The Impact of Electronic Waste On The WorldDocument4 pagesThe Impact of Electronic Waste On The WorldViviNo ratings yet
- The Problem of Solid Waste ManagementDocument6 pagesThe Problem of Solid Waste ManagementOwen Lamidi AndenyangNo ratings yet
- CH 19 PPT Wastes and RecyclingDocument19 pagesCH 19 PPT Wastes and Recyclingapi-244168124No ratings yet
- E WasteDocument42 pagesE Wastesky100% (4)
- What Is Land PolutionDocument4 pagesWhat Is Land PolutionUtari Ika CahyaniNo ratings yet
- Design and Fabrication of A Furnace For PDFDocument12 pagesDesign and Fabrication of A Furnace For PDFHarshad Pawar PatilNo ratings yet
- Class 22 - Urbanization and Solid WasteDocument30 pagesClass 22 - Urbanization and Solid WastePaul O'ConnorNo ratings yet
- Electronic Waste Recyclinga Review of U.S. Infrastructure and Technology OptionsDocument33 pagesElectronic Waste Recyclinga Review of U.S. Infrastructure and Technology OptionsYesenia Najarro VarelaNo ratings yet
- Expose D AnglaisDocument7 pagesExpose D AnglaisBouba SmithNo ratings yet
- Marine Pollution Questions & AnswersDocument16 pagesMarine Pollution Questions & AnswersBasem Tam100% (2)
- #Environmental Final PaperDocument7 pages#Environmental Final PaperOwen ElliottNo ratings yet
- Progress in Biomass Conversion: Volume IFrom EverandProgress in Biomass Conversion: Volume IKyosti V. SarkanenNo ratings yet
- Sun, Wind and Desert: MENA, the upcoming Clean Energy World ChampionFrom EverandSun, Wind and Desert: MENA, the upcoming Clean Energy World ChampionNo ratings yet
- “Clean” Energy Exploitations: Helping Citizens Understand the Environmental and Humanity Abuses That Support “Clean” EnergyFrom Everand“Clean” Energy Exploitations: Helping Citizens Understand the Environmental and Humanity Abuses That Support “Clean” EnergyNo ratings yet
- Solid Wastes ManagementFrom EverandSolid Wastes ManagementStephen BurnleyNo ratings yet
- Solutions Manual to accompany Engineering Materials ScienceFrom EverandSolutions Manual to accompany Engineering Materials ScienceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Clean Electricity Through Advanced Coal Technologies: Handbook of Pollution Prevention and Cleaner ProductionFrom EverandClean Electricity Through Advanced Coal Technologies: Handbook of Pollution Prevention and Cleaner ProductionNo ratings yet
- Inequalities, Inequities, Environmental Justice in Waste Management and HealthDocument6 pagesInequalities, Inequities, Environmental Justice in Waste Management and HealthRavi SankarNo ratings yet
- Waste in USADocument6 pagesWaste in USARavi Sankar100% (1)
- Integrated Waste Management: Reduce, Reuse & RecycleDocument17 pagesIntegrated Waste Management: Reduce, Reuse & RecycleRavi SankarNo ratings yet
- The History of Energy Recovery From Combustion: Clean Air Act (CAA)Document3 pagesThe History of Energy Recovery From Combustion: Clean Air Act (CAA)Ravi SankarNo ratings yet
- Nonwaste Fuels RulesDocument6 pagesNonwaste Fuels RulesRavi SankarNo ratings yet
- Compliance of Boiler Standards and Industrial Safety in Indian SubcontinentDocument8 pagesCompliance of Boiler Standards and Industrial Safety in Indian SubcontinentRavi SankarNo ratings yet
- Municipal Solid Waste: Related LinksDocument4 pagesMunicipal Solid Waste: Related LinksRavi SankarNo ratings yet
- Since The 1880sDocument5 pagesSince The 1880sRavi SankarNo ratings yet