0% found this document useful (0 votes)
51 views27 pagesGout Treatment: Colchicine & Medications
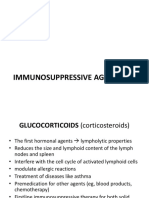
Gout is an inflammatory arthritis caused by elevated uric acid levels. It causes acute joint pain. Colchicine relieves gout pain and inflammation by preventing neutrophil migration and inhibiting tubulin polymerization. It is absorbed quickly after oral administration. Common side effects include diarrhea and nausea. Allopurinol and probenecid lower uric acid levels by inhibiting uric acid production or increasing urinary excretion, respectively. Both can cause rashes and blood disorders as side effects.
Uploaded by
ElleCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
51 views27 pagesGout Treatment: Colchicine & Medications
Gout is an inflammatory arthritis caused by elevated uric acid levels. It causes acute joint pain. Colchicine relieves gout pain and inflammation by preventing neutrophil migration and inhibiting tubulin polymerization. It is absorbed quickly after oral administration. Common side effects include diarrhea and nausea. Allopurinol and probenecid lower uric acid levels by inhibiting uric acid production or increasing urinary excretion, respectively. Both can cause rashes and blood disorders as side effects.
Uploaded by
ElleCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd