Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Immuno Far Mako Log I
Uploaded by
Mia Rahmawati0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
45 views12 pagesThe document summarizes several classes of immunosuppressive agents, including glucocorticoids, calcineurin inhibitors cyclosporine and tacrolimus, mTOR inhibitors such as sirolimus, and mycophenolate mofetil. It describes their mechanisms of action, uses for conditions like organ transplantation and autoimmune disorders, routes of administration, metabolism and toxicities.
Original Description:
The first hormonal agents lympholytic properties
Reduces the size and lymphoid content of the lymph nodes and spleen
Interfere with the cell cycle of activated lymphoid cells
modulate allergic reactions
Treatment of diseases like asthma
Premedication for other agents (eg, blood products, chemotherapy)
Firstline immunosuppressive therapy for both solid organ and hematopoietic stem cell transplant
Original Title
Immuno Far Mako Log i
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document summarizes several classes of immunosuppressive agents, including glucocorticoids, calcineurin inhibitors cyclosporine and tacrolimus, mTOR inhibitors such as sirolimus, and mycophenolate mofetil. It describes their mechanisms of action, uses for conditions like organ transplantation and autoimmune disorders, routes of administration, metabolism and toxicities.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
45 views12 pagesImmuno Far Mako Log I
Uploaded by
Mia RahmawatiThe document summarizes several classes of immunosuppressive agents, including glucocorticoids, calcineurin inhibitors cyclosporine and tacrolimus, mTOR inhibitors such as sirolimus, and mycophenolate mofetil. It describes their mechanisms of action, uses for conditions like organ transplantation and autoimmune disorders, routes of administration, metabolism and toxicities.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 12
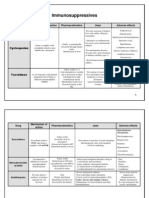
IMMUNOSUPPRESSIVE AGENTS
GLUCOCORTICOIDS (corticosteroids)
• The first hormonal agents lympholytic properties
• Reduces the size and lymphoid content of the lymph
nodes and spleen
• Interfere with the cell cycle of activated lymphoid cells
• modulate allergic reactions
• Treatment of diseases like asthma
• Premedication for other agents (eg, blood products,
chemotherapy)
• Firstline immunosuppressive therapy for both solid
organ and hematopoietic stem cell transplant
CALCINEURIN INHIBITORS:
Cyclosporine
• An immunosuppressive agent with efficacy in human
organ transplantation
• binds to cyclophilin inhibits the gene
transcription of IL-2, IL-3, IFN-γ, and other factors
produced by antigen-stimulated T cells
• Intravenously or orally, though it is slowly and
incompletely absorbed (20–50%)
• Metabolized by the P450 3A enzyme
Cyclosporine (2)
• Toxicities : nephrotoxicity, hyperten- sion,
hyperglycemia, liver dysfunction, hyperkalemia,
altered mental status, seizures, and hirsutism
• May be used alone or in combination
• For autoimmune disorders: uveitis, rheumatoid
arthritis, psoriasis, and asthma.
CALCINEURIN INHIBITORS:
Tacrolimus
• An immunosuppressant macrolide antibiotic
produced by Streptomyces tsukubaensis
• Binds to FK-binding protein (FKBP)
• 10–100 times more potent than cyclosporine in
inhibiting immune responses
• For organ and stem cell transplantation
• Orally or intravenously
• Metabolized primarily by P450 enzymes in the liver
Tacrolimus (2)
• Toxic effects : nephrotoxicity, neurotoxicity,
hyperglycemia, hypertension, hyper- kalemia, and
gastrointestinal complaints.
• Tacrolimus ointment :therapy of atopic dermatitis
and psoriasis
Mechanism of action of cyclosporine and tacrolimus
MAMMALIAN TARGET OF RAPAMYCIN (mTOR)
INHIBITORS
• Sirolimus (rapamycin) as well as its analogs (called
“rapalogs”) such as everolimus and temsirolimus
• An immunosuppressant macrolide antibiotic
produced by Streptomyces hygroscopicus
• Effectively alone and in combination to prevent
rejection of solid organ allografts
• Sirolimus is available as an oral drug
• Topical sirolimus is also used in some dermatologic
disorder
• Toxicities : myelosuppression (especially
thrombocytopenia), hepatotoxicity, diarrhea,
hypertriglyceridemia, pneumonitis, and headache
Mechanism of action of sirolimus
MYCOPHENOLATE MOFETIL
• Prodrug: is hydrolyzed to mycophenolic acid
• Isolated from the mold Penicillium glaucus
• Available in both oral and intravenous forms
• For solid organ transplant patients for refractory
rejection
• Toxicities: gastrointestinal disturbances (nausea and
vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal pain) headache,
hypertension, and reversible myelosuppression
(primarily neutropenia)
Mechanisme of action mycophenolate mofetil
You might also like
- Immunosuppressive PharmacologyDocument54 pagesImmunosuppressive PharmacologyCARSON 539No ratings yet
- Immunosuppresantmbbs 190608061036Document115 pagesImmunosuppresantmbbs 190608061036syarintaadeninaNo ratings yet
- Immunomodulator Drugs2Document23 pagesImmunomodulator Drugs2Ankita TatheNo ratings yet
- Immuno Modulator SDocument62 pagesImmuno Modulator SAntony Prakash RajNo ratings yet
- Immunomodulator 2014Document56 pagesImmunomodulator 2014LeilybadryaNo ratings yet
- Immunomodulator: Dr. Hj. Rika Yuliwulandari, PHDDocument55 pagesImmunomodulator: Dr. Hj. Rika Yuliwulandari, PHDAnonymous 3ktnNjNo ratings yet
- ImmunopharmacologyDocument19 pagesImmunopharmacologyMaaz Uddin Siddiqui100% (1)
- S 25 Staud ImmunomodulatorsDocument41 pagesS 25 Staud ImmunomodulatorsCarlo MaxiaNo ratings yet
- Immunopharmacology ImmunosupressantsDocument15 pagesImmunopharmacology ImmunosupressantsPraज्ञा GharpankarNo ratings yet
- Immunosuppressants Prof. Alhaider, 1431 HDocument45 pagesImmunosuppressants Prof. Alhaider, 1431 HMourian AmanNo ratings yet
- S-Immunomodulator DrugsDocument48 pagesS-Immunomodulator DrugsFaishal100% (2)
- Immunomodulators: Ma. Stephanie Fay S. Cagayan, MDDocument67 pagesImmunomodulators: Ma. Stephanie Fay S. Cagayan, MDFaye Cagayan100% (1)
- Immunosuppressants: Pharmacology TeamDocument26 pagesImmunosuppressants: Pharmacology TeamZaina MasriNo ratings yet
- IMMUNOMODULATORSDocument44 pagesIMMUNOMODULATORSMaria khurshidNo ratings yet
- Immuno PharmacologyDocument39 pagesImmuno PharmacologyGd SuarantaNo ratings yet
- Prof. - Sanjay - Khattri - Anti - Rheumatoid - DrugsDocument29 pagesProf. - Sanjay - Khattri - Anti - Rheumatoid - DrugsBe GameNo ratings yet
- Immunosuppressive AgentsDocument62 pagesImmunosuppressive AgentsApurba Sarker ApuNo ratings yet
- Immunosuppressive DrugsDocument11 pagesImmunosuppressive DrugsAubrey GadorNo ratings yet
- Immune System 14Document61 pagesImmune System 14Лариса ТкачеваNo ratings yet
- Immuno-Suppressants: Dr. PrasadDocument21 pagesImmuno-Suppressants: Dr. PrasadMuskaan ZaharaNo ratings yet
- Immunosuppressants NotesDocument20 pagesImmunosuppressants NotesmadcalNo ratings yet
- Immunomodulators: Dr. Kaushik Mukhopadhyay Assistant Professor, Dept. of Pharmacology Esi-PgimsrDocument31 pagesImmunomodulators: Dr. Kaushik Mukhopadhyay Assistant Professor, Dept. of Pharmacology Esi-PgimsrsyarintaadeninaNo ratings yet
- Immunomodulators: - Nirali Thakkar (From SMT S.M.Shah Pharmacy College)Document23 pagesImmunomodulators: - Nirali Thakkar (From SMT S.M.Shah Pharmacy College)Suvojit BasakNo ratings yet
- Drug TransplantationDocument36 pagesDrug Transplantationsajad abasewNo ratings yet
- Surgery 06 - Transplantation - 27th April 2023Document110 pagesSurgery 06 - Transplantation - 27th April 2023mannkheni209No ratings yet
- Immunosuppressant DrugsDocument28 pagesImmunosuppressant DrugsimnasNo ratings yet
- Anticancer DrugsDocument117 pagesAnticancer DrugsKishore Chandra Korada100% (2)
- Immunosuppressive AgentsDocument36 pagesImmunosuppressive AgentsFlorensa Teolina NdruruNo ratings yet
- Immunotherapy: Prof Anura WeerasingheDocument17 pagesImmunotherapy: Prof Anura WeerasingherikarzNo ratings yet
- ERYTHROMYCINDocument22 pagesERYTHROMYCINhiraNo ratings yet
- Antifungal - Anticancer 21Document83 pagesAntifungal - Anticancer 21DR AbidNo ratings yet
- Inhibitori KalcineurinaDocument8 pagesInhibitori KalcineurinaVedran PlećašNo ratings yet
- Immunosuppressant DrugsDocument6 pagesImmunosuppressant DrugsShoaib MohiuddinNo ratings yet
- Immunopharmacology: Ma. Janetth B. Serrano, M.D., DPBADocument33 pagesImmunopharmacology: Ma. Janetth B. Serrano, M.D., DPBAJendrianiNo ratings yet
- ImmunomodulatorsDocument8 pagesImmunomodulatorsfaisalnadeem100% (1)
- AntiNeo SEDocument93 pagesAntiNeo SEJerome BentleyNo ratings yet
- Powerpoint For Marking PharmacologyDocument25 pagesPowerpoint For Marking PharmacologyKennedy ShelemaniNo ratings yet
- ChloramphenicolDocument20 pagesChloramphenicolPROF DR SHAHMURAD100% (2)
- CologyDocument10 pagesCologySuvojit BasakNo ratings yet
- 1 ImmunopharmDocument63 pages1 ImmunopharmDr.TamilvelanNo ratings yet
- Immunosuppressant DrugsDocument87 pagesImmunosuppressant DrugsNagu KopparapuNo ratings yet
- MedSurg Medications & TablesDocument71 pagesMedSurg Medications & TablesSarah PlunkettNo ratings yet
- Burchum & Rosenthal: Lehne's Pharmacology For Nursing Care, 9th EditionDocument2 pagesBurchum & Rosenthal: Lehne's Pharmacology For Nursing Care, 9th Editionhockeyman1584No ratings yet
- NCM 106 Immunosuppresants 1 1Document11 pagesNCM 106 Immunosuppresants 1 1Mariella EspañaNo ratings yet
- ImmunosuppressantsDocument18 pagesImmunosuppressantsomar khanNo ratings yet
- IMMUNOMODULATORS (EDocFind - Com)Document67 pagesIMMUNOMODULATORS (EDocFind - Com)sac00772006No ratings yet
- Tetra, Makrolid, AminoglikosidDocument30 pagesTetra, Makrolid, AminoglikosidSarah AvecienaNo ratings yet
- Principles of Antimicrobial Therapy Part 1Document83 pagesPrinciples of Antimicrobial Therapy Part 1Carl Elexer Cuyugan Ano100% (1)
- 1 - Immuno Tables1Document4 pages1 - Immuno Tables1Urugonda VenumadhavNo ratings yet
- IMMUNOSUPPRESANTSDocument13 pagesIMMUNOSUPPRESANTSasriNo ratings yet
- Plasma Proteins Prots&AA Chem Lect (28!10!16) - 1Document43 pagesPlasma Proteins Prots&AA Chem Lect (28!10!16) - 1Zoraiz AhmadNo ratings yet
- Cancer ChemotherapyDocument103 pagesCancer ChemotherapyTrang MaiNo ratings yet
- Cancer CT DrugsDocument29 pagesCancer CT DrugsPinanto IrwandyNo ratings yet
- 12 MalariaDocument61 pages12 MalariaMewael TesfamichaelNo ratings yet
- Female Hormonal TherapyDocument38 pagesFemale Hormonal TherapySA NodeNo ratings yet
- Macrolides and ChloramphenicolDocument28 pagesMacrolides and ChloramphenicolShahid IqbalNo ratings yet
- Antifungal Drugs: - Polyene Antibiotics: Amphotericin B, Nystatin - Antimetabolites: 5-Fluorocytosine - AzolesDocument18 pagesAntifungal Drugs: - Polyene Antibiotics: Amphotericin B, Nystatin - Antimetabolites: 5-Fluorocytosine - AzolesgopscharanNo ratings yet
- Naplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesFrom EverandNaplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- APPSC GR I Initial Key Paper IIDocument52 pagesAPPSC GR I Initial Key Paper IIdarimaduguNo ratings yet
- Week 1 Lab #2 - Microscopy & Microscopic Examination of Living MicroorganismsDocument53 pagesWeek 1 Lab #2 - Microscopy & Microscopic Examination of Living MicroorganismsNgoc PhamNo ratings yet
- DWDMDocument41 pagesDWDMKarthik KompelliNo ratings yet
- FWN Magazine 2018 - Leonor VintervollDocument48 pagesFWN Magazine 2018 - Leonor VintervollFilipina Women's NetworkNo ratings yet
- MBF100 Subject OutlineDocument2 pagesMBF100 Subject OutlineMARUTI JEWELSNo ratings yet
- Ojt HRMDocument7 pagesOjt HRMArlyn Joy NacinoNo ratings yet
- Med Error PaperDocument4 pagesMed Error Paperapi-314062228100% (1)
- 127 Bba-204Document3 pages127 Bba-204Ghanshyam SharmaNo ratings yet
- Filtomat M300Document4 pagesFiltomat M300Sasa Jadrovski100% (1)
- rOCKY Dem Manual (010-057)Document48 pagesrOCKY Dem Manual (010-057)eduardo huancaNo ratings yet
- Antonov 225 - The Largest - Airliner in The WorldDocument63 pagesAntonov 225 - The Largest - Airliner in The WorldFridayFunStuffNo ratings yet
- Making Sense of The Future of Libraries: Dan Dorner, Jennifer Campbell-Meier and Iva SetoDocument14 pagesMaking Sense of The Future of Libraries: Dan Dorner, Jennifer Campbell-Meier and Iva SetoBiblioteca IICENo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Cot1Document9 pagesLesson Plan Cot1Paglinawan Al KimNo ratings yet
- Trading Book - AGDocument7 pagesTrading Book - AGAnilkumarGopinathanNairNo ratings yet
- Unknown 31Document40 pagesUnknown 31Tina TinaNo ratings yet
- Far 2 Quiz 03212024Document6 pagesFar 2 Quiz 03212024red118831No ratings yet
- Strategi Meningkatkan Kapasitas Penangkar Benih Padi Sawah (Oriza Sativa L) Dengan Optimalisasi Peran Kelompok TaniDocument24 pagesStrategi Meningkatkan Kapasitas Penangkar Benih Padi Sawah (Oriza Sativa L) Dengan Optimalisasi Peran Kelompok TaniHilmyTafantoNo ratings yet
- Dimitris Achlioptas Ucsc Bsoe Baskin School of EngineeringDocument22 pagesDimitris Achlioptas Ucsc Bsoe Baskin School of EngineeringUCSC Students100% (1)
- Case Study StarbucksDocument2 pagesCase Study StarbucksSonal Agarwal100% (2)
- 1.2.2.5 Packet Tracer - Connecting Devices To Build IoTDocument4 pages1.2.2.5 Packet Tracer - Connecting Devices To Build IoTyayasan dharamabharataNo ratings yet
- E-Cat35xt014 Xtro PhantomsDocument32 pagesE-Cat35xt014 Xtro PhantomsKari Wilfong100% (5)
- Indiana Property Tax Benefits: (This Form Must Be Printed On Gold or Yellow Paper)Document2 pagesIndiana Property Tax Benefits: (This Form Must Be Printed On Gold or Yellow Paper)abramsdcNo ratings yet
- MPH EocDocument8 pagesMPH EocGalaleldin AliNo ratings yet
- Plant Gardening AerationDocument4 pagesPlant Gardening Aerationut.testbox7243No ratings yet
- W1 - V1 MultipleWorksheets SolnDocument3 pagesW1 - V1 MultipleWorksheets SolnAKHIL RAJ SNo ratings yet
- 11-Potential Use of Volcanic Pumice As A Construction Materialhossain2004Document7 pages11-Potential Use of Volcanic Pumice As A Construction Materialhossain2004afzal taiNo ratings yet
- Legends & Lairs - Giant LoreDocument66 pagesLegends & Lairs - Giant LoreGary DowellNo ratings yet
- Stadium and Club Tours - Senior Tour GuideDocument4 pagesStadium and Club Tours - Senior Tour GuidebizmbuuNo ratings yet
- Software Requirements SpecificationDocument9 pagesSoftware Requirements SpecificationSu-kEm Tech LabNo ratings yet
- Eat Something DifferentDocument3 pagesEat Something Differentsrajendr200100% (1)