Professional Documents
Culture Documents
IPC Cycle Cow-Ip-Cycle
Uploaded by
Arsalan M0%(1)0% found this document useful (1 vote)
265 views26 pagesIpc of cow
Original Title
IPC Cycle Cow-ip-cycle
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentIpc of cow
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0%(1)0% found this document useful (1 vote)
265 views26 pagesIPC Cycle Cow-Ip-Cycle
Uploaded by
Arsalan MIpc of cow
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 26
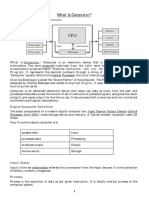
Information Processing Cycle
What is the Information
Processing Cycle?
These are the steps that are taken to
convert raw facts, which is data, into
information. It starts with data
collection.
The 4 basic operations of the
information processing cycle are input,
processing, output, storage and/or
distribution.
A computer is the machine that
performs the cycle.
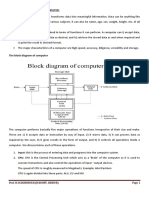
1. Input:
In this phase the computer receives
data from input source by user or a
program. An input source by user can
be an input device like keyboard,
mouse, microphone etc.
2. Processing:
After receiving data, here the computer
performs actions on the data like
mathematical operations or logical
comparisons etc. as per being
instructed by user or a program.
3. Output:
After processing the data computer
has generated information that now
can be sent to output. Output can be
sent for display in monitor, or to printer
or speaker as sound etc. It is also as
per required by the user or program.
4. Storage:
Again, after processing the data, computer can
also store the data into an storage device for
future use.
Phase output and storage, are optional. Both of
them can be required and vice-versa, as the
generated information can also be directly used
by another processing cycle where this
generated information will be treated as data to
be processed.
IP Cycle:
Start with a cow:
The cow is at the
beginning of the IP
Cycle.
This is the
origination- Putting
through thoughts
into words.
This is dealing with
raw data or facts
that have been
collected already.
Production:
Eating is just a
natural part of life
for cows.
This the production
part of the
information
processing cycle.
Production-Keying
the originators text
into the computer.
Process:
Milk is used for
many different kinds
of good foods.
This action of
milking the cow can
be considered part
of the process-
editing,
proofreading and
revisions.
Output:
After milking the cows,
farmers have to get the
milk ready to transport
to the manufacturer.
This is the Output part
of the IP Cycle.
Output- printing out the
document (hardcopy)
of reading it from the
screen (softcopy)
Storage:
Once the manufacturer
has the milk, the milk
has to be pasteurized.
This is can be
considered the storage
part of the cycle.
Storage-saving the
document on a USB or
filing it in a filing
cabinet.
Replication:
Once the milk is
pasteurized it can
be made into many
different kinds of
milk products.
This is like
Replication- making
copies of the
document.
Distribution:
Finally, the products
are sent to retail
stores so that we
can buy them.
This is Distribution-
getting the finished
documents to the
receiver by hand or
electronically (fax or
email).
Your Analogy!
Your assignment now is to come up
with your own Information Processing
Cycle analogy.
You must be creative with your
analogies.
They must include: Origination,
Production, Process, Output, Storage,
Replication, and Distribution.
Analogy Cont’d:
You can use any object, animal or food
for your analogies.
Here are some examples:
– Dishwasher
– Car
– Sandwiches
– Washing Machine
Analogy Cont’d:
You can work in pairs or you can do this on
your own.
Remember to keep the analogies clean and
appropriate!.
As well, you must show the connection
between your analogy and the actual
Information Processing Cycle.
Remember to Include:
Origination- the raw data or facts
Production- keying the data into the
computer
Process- editing and proofreading
Output- printing out the document
Storage- saving the document
Replication- making copies
Distribution- emailing finished product
Application software program
An application is any program, or
group of programs, that is designed for
the end user.
Applications software (also called end-
user programs) include such things as
database programs, word processors,
Web browsers and spreadsheets.
Examples of Application
Software
The most common application
software programs are used by
millions every day and include:
Microsoft suite of products (Office,
Excel, Word, PowerPoint, Outlook,
etc.) Internet browsers like Firefox,
Safari, and Chrome.
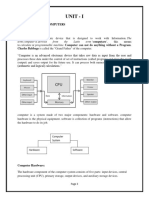
Application software diagram
applications sit on top of systems
software because they are unable to run
without the operating system and system
utilities.
Systems software consists of low-level
programs that interact with the computer
at a very basic level. This includes
operating systems, compilers, and utilities
for managing computer resources.
different types of application
software
Depending on the level of language used there
are different types of application software:
1) Word processing 5) Communication
software. ... Software. ...
2) Spreadsheet 6) Presentation
Software. ... Software. ...
3) Desktop Publishing 7) Internet
Software. ... Browsers. ...
4) Database Software. 8) Email Programs.
...
You might also like
- Computer Vision with Maker Tech: Detecting People With a Raspberry Pi, a Thermal Camera, and Machine LearningFrom EverandComputer Vision with Maker Tech: Detecting People With a Raspberry Pi, a Thermal Camera, and Machine LearningNo ratings yet
- Computer Science Computer Science: Unit Unit-1Document78 pagesComputer Science Computer Science: Unit Unit-1Srijan ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- COMPUTER FUNDAMENTS LectureDocument18 pagesCOMPUTER FUNDAMENTS LectureDanilo Belialba Jr.No ratings yet
- L2 - Machine Learning ProcessDocument17 pagesL2 - Machine Learning ProcessKinya KageniNo ratings yet
- L2 - Machine Learning ProcessDocument17 pagesL2 - Machine Learning ProcessKinya KageniNo ratings yet
- Hands-on Scikit-Learn for Machine Learning Applications: Data Science Fundamentals with PythonFrom EverandHands-on Scikit-Learn for Machine Learning Applications: Data Science Fundamentals with PythonNo ratings yet
- Data Processing, Security, AntivirusDocument9 pagesData Processing, Security, AntivirusOgbo IsuNo ratings yet
- Chapter I Introduction To ComputerDocument10 pagesChapter I Introduction To ComputerJasmine Nicole OsallaNo ratings yet
- Input-Output ModelDocument54 pagesInput-Output ModelVishal AgnihotriNo ratings yet
- Eclipse TEA Revealed: Building Plug-ins and Creating Extensions for EclipseFrom EverandEclipse TEA Revealed: Building Plug-ins and Creating Extensions for EclipseNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Computers: ObjectivesDocument10 pagesIntroduction To Computers: ObjectivesNeoNo ratings yet
- Isabela State University: I. MODULE 2 - Evolution of Computing IIDocument16 pagesIsabela State University: I. MODULE 2 - Evolution of Computing IIKaren joy BajoNo ratings yet
- UNIT 3: Computer Usage For Nurse Informaticists Chapter 4: Introduction To Software (Week 6) Intended Learning Outcomes (ILO)Document28 pagesUNIT 3: Computer Usage For Nurse Informaticists Chapter 4: Introduction To Software (Week 6) Intended Learning Outcomes (ILO)John Van Dave TaturoNo ratings yet
- Basics of ComputersDocument52 pagesBasics of ComputersAlfred SalazarNo ratings yet
- E CommerceDocument24 pagesE CommerceChamoadh DissanayakeNo ratings yet
- What Is A Computer?: - Modern Computers Are Electronic and Digital Devices ThatDocument15 pagesWhat Is A Computer?: - Modern Computers Are Electronic and Digital Devices ThatEric MarilagNo ratings yet
- Basics of Computers - IntroDocument14 pagesBasics of Computers - IntrosaraNo ratings yet
- 7 Computer Skills You Must Have to Survive & Prosper in Today's World ("Computer Skills for Financial Independence")From Everand7 Computer Skills You Must Have to Survive & Prosper in Today's World ("Computer Skills for Financial Independence")Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- ReviewerDocument6 pagesReviewerClaudine Jo B. TalabocNo ratings yet
- FOURTHDocument7 pagesFOURTHavinmanzanoNo ratings yet
- Basics of Computers - Quick Guide - TutorialspointDocument50 pagesBasics of Computers - Quick Guide - TutorialspointJames MukhwanaNo ratings yet
- What is a Computer? - Concise overview of computer definition, characteristics, and data processing cycleDocument4 pagesWhat is a Computer? - Concise overview of computer definition, characteristics, and data processing cycleJhonjosua GonoNo ratings yet
- Unit 1: Computer FundamentalsDocument8 pagesUnit 1: Computer FundamentalsShivNo ratings yet
- TLE 7-8 ICT-CSS Q1 - M2 For Printing-1Document17 pagesTLE 7-8 ICT-CSS Q1 - M2 For Printing-1anielyn.libangNo ratings yet
- Basics of Computers - Quick GuideDocument47 pagesBasics of Computers - Quick GuideChinmoyee BiswasNo ratings yet
- Intro To Info TechDocument33 pagesIntro To Info TechGrezel NiceNo ratings yet
- Define Computer PDFDocument54 pagesDefine Computer PDFamitukumar88% (8)
- New Rich Text Docnew Decument UmentDocument5 pagesNew Rich Text Docnew Decument UmentUnimart DhanmondiNo ratings yet
- Uses of ComputersDocument22 pagesUses of Computersa yuNo ratings yet
- Mis & E Business: Basic Concept of Computers, History of MIS and Concepts of DatabaseDocument8 pagesMis & E Business: Basic Concept of Computers, History of MIS and Concepts of DatabasefakhrulNo ratings yet
- Computer Notes PDFDocument49 pagesComputer Notes PDFLorbie Castañeda FrigillanoNo ratings yet
- Raspberry Pi: 40 Outstanding Raspberry Pi Tips and Tricks for Absolute BeginnersFrom EverandRaspberry Pi: 40 Outstanding Raspberry Pi Tips and Tricks for Absolute BeginnersNo ratings yet
- Basics of Computers Quick GuideDocument51 pagesBasics of Computers Quick GuideHugfhehsNo ratings yet
- L1-OVERVIEW OF COMPUTERS 165 177 Computer ScienceDocument16 pagesL1-OVERVIEW OF COMPUTERS 165 177 Computer ScienceBetty Njeri MbuguaNo ratings yet
- FundamentalsDocument150 pagesFundamentalsamrshouib27No ratings yet
- Infodigicom 0Document19 pagesInfodigicom 0Aryan SampatNo ratings yet
- ICS 2174 Intro To Computer Science 2023Document28 pagesICS 2174 Intro To Computer Science 2023emmanuelmututa25No ratings yet
- 1.introduction To Digital ComputerDocument7 pages1.introduction To Digital ComputerMangesh Deshmukh100% (1)
- 2nd Sem - C-Programming (Module I-III)Document78 pages2nd Sem - C-Programming (Module I-III)Partha Sarathi BeheraNo ratings yet
- Introduction to the World of ComputersDocument57 pagesIntroduction to the World of ComputersLaxman KumarNo ratings yet
- IT School Module on InformaticsDocument26 pagesIT School Module on InformaticsJORINA PUMIHICNo ratings yet
- IT Applications in Business UNIT I NOTESDocument50 pagesIT Applications in Business UNIT I NOTESTanmay AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Basic Components of ComputerDocument22 pagesBasic Components of Computerocamp2007No ratings yet
- computer_introduction Unit1Document7 pagescomputer_introduction Unit1mailtoprateekk30No ratings yet
- 02 ProcessesDocument36 pages02 Processesdas_pranjalNo ratings yet
- Computer Fundamentals FinalDocument15 pagesComputer Fundamentals FinalanilperfectNo ratings yet
- Sic T 1 OriginalDocument53 pagesSic T 1 Originaladcbvm operatorNo ratings yet
- Basic of ComputerDocument19 pagesBasic of Computersailisurve424No ratings yet
- Introduction To Computing Lesson 1 Notes BautistaDocument5 pagesIntroduction To Computing Lesson 1 Notes BautistaJulianna SudlaNo ratings yet
- Unit IDocument86 pagesUnit Imvmohitkumar17No ratings yet
- Ict8 - PresentationDocument95 pagesIct8 - PresentationCashmir Mabaquiao JoquinoNo ratings yet
- Unit-3 Computer SystemDocument12 pagesUnit-3 Computer SystemKunal SahNo ratings yet
- User Manual For - Review: (Online Case Management For Court of Appeal and Federal Court)Document11 pagesUser Manual For - Review: (Online Case Management For Court of Appeal and Federal Court)Tsai Shiang YeapNo ratings yet
- Cognizant Trizetto Keyword Loader For FacetsDocument2 pagesCognizant Trizetto Keyword Loader For FacetsKavitha RamalingamNo ratings yet
- The Future of The Internet: English Written TestDocument4 pagesThe Future of The Internet: English Written TestCarlosNo ratings yet
- 1.4 HDFS Lab 1HDocument23 pages1.4 HDFS Lab 1HSabir MoussaouiNo ratings yet
- PSSE PlottingDocument3 pagesPSSE PlottingAmberMeerabNo ratings yet
- Workstation Adobe 4k GuideDocument8 pagesWorkstation Adobe 4k Guidetwo wheelsNo ratings yet
- Brief Review On SQL and NoSQLDocument4 pagesBrief Review On SQL and NoSQLEditor IJTSRDNo ratings yet
- BIS4225.3 - Components of Information Systems ArchitectureDocument36 pagesBIS4225.3 - Components of Information Systems Architecturevicrattlehead2013No ratings yet
- Installation-SAPGUI For Windows For V750Document16 pagesInstallation-SAPGUI For Windows For V75027296621No ratings yet
- Review your answers, feedback, and question scoresDocument17 pagesReview your answers, feedback, and question scoresSrdjanVuksan100% (1)
- Hologic Digital Mammo Selenia 3dimensions User Manual PDFDocument100 pagesHologic Digital Mammo Selenia 3dimensions User Manual PDFanderson soares bezerraNo ratings yet
- Java 1Document34 pagesJava 1Hami KittaNo ratings yet
- NEO-6 - Hardware Integration Manual - U-BloxDocument83 pagesNEO-6 - Hardware Integration Manual - U-BloxAdriano RamosNo ratings yet
- CCNA2 Chapter 6 ExamDocument9 pagesCCNA2 Chapter 6 ExamjkzhNo ratings yet
- Exfo Max 720C - ManualDocument175 pagesExfo Max 720C - ManualElmo MarihuanoNo ratings yet
- Uttarakhand Technical University, Dehradun: Evaluation Schemes For B. Tech 2 To4 YearDocument57 pagesUttarakhand Technical University, Dehradun: Evaluation Schemes For B. Tech 2 To4 YearDev MehtaNo ratings yet
- Wi-Fi Jamming Using Raspberry Pi: ISSN: 1314-3395 (On-Line Version) Url: Http://acadpubl - Eu/hub Special IssueDocument8 pagesWi-Fi Jamming Using Raspberry Pi: ISSN: 1314-3395 (On-Line Version) Url: Http://acadpubl - Eu/hub Special IssueSarangNo ratings yet
- VL3 USB Stick Update PDFDocument5 pagesVL3 USB Stick Update PDFAZNo ratings yet
- Proposal Simulation and Execution of Embedded Scheme Centred Dual Horn by Wireless TechnologyDocument5 pagesProposal Simulation and Execution of Embedded Scheme Centred Dual Horn by Wireless TechnologyKARTHIKNo ratings yet
- Obiee - LdapDocument8 pagesObiee - Ldapvenkatesh.gollaNo ratings yet
- Jawaharlal Nehru Technological University: Technical Seminor On SkinplexDocument18 pagesJawaharlal Nehru Technological University: Technical Seminor On SkinplexVinay ReddyNo ratings yet
- Prn256m8v69ag8gkf 15eDocument12 pagesPrn256m8v69ag8gkf 15eArif YuliantoNo ratings yet
- Data Representation Homework 2 Binary Arithmetic HexadecimalDocument3 pagesData Representation Homework 2 Binary Arithmetic HexadecimalWinfred GotahNo ratings yet
- Everything You Need to Know About IP Address LookupDocument2 pagesEverything You Need to Know About IP Address LookuprozinaNo ratings yet
- Comprehensive Guide On Crunch ToolDocument1 pageComprehensive Guide On Crunch Toolm7md 3bd ellahNo ratings yet
- Zone Min Der CCTV StreamingDocument9 pagesZone Min Der CCTV StreamingrusnandiNo ratings yet
- Web UI NavigationDocument37 pagesWeb UI NavigationMamta Saboo ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- The Great AwkDocument3 pagesThe Great AwkharijiNo ratings yet
- Mae-Ann E. Bardaje Computer Systems Servicing NCIIDocument6 pagesMae-Ann E. Bardaje Computer Systems Servicing NCIIMae Ann BardajeNo ratings yet
- Computer Network Assignment HelpDocument5 pagesComputer Network Assignment HelpComputer Network Assignment HelpNo ratings yet