Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ike Dayi Febriana, S.Si., M.T
Uploaded by
Ike Dayi Febriana0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views7 pagesOriginal Title
TERMOKIMIA.pptx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views7 pagesIke Dayi Febriana, S.Si., M.T
Uploaded by
Ike Dayi FebrianaCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 7
IKE DAYI FEBRIANA, S.Si., M.T.
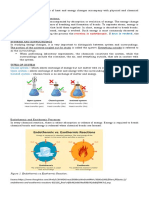
To quantify the heat flow into or out of a system in a constant
pressure process, chemists use a property called enthalpy (H).
The enthalpy of reaction, H, is the difference between the
enthalpies of the products and the enthalpies of the
reactants:
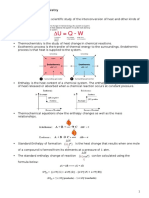
1. Bila persamaan dikalikan suatu konstanta k
maka nilai ∆H = k∆Ho.
2. Bila suatu reaksi dibalik maka ∆H berubah tanda
Calculate ∆H for the complete combustion of 1.00 mole of propane, a
major component of lighter fluid!
∆Hreaksi = ∑∆Hproduk - ∑∆Hreaktan
∆Hreaksi = [(3∆H CO2 + 4 ∆H H2O)] – [(∆H C3H8 + ∆H O2)
∆Hreaksi = {[3mol (-393.5 kJ/mol) + 4 mol(-285.9 kJ/mol)] –
[1 mol(-105 kJ/mol)+ 0]}
∆Hreaksi = - 2324.1 – (- 105)
∆Hreaksi = - 2429.1 kJ
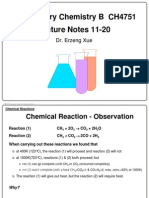
Senyawa kimia yang merupakan unsur tunggal atau
diatomik memiliki ∆H = 0
1. By using data of ∆Ho, Calculation ∆H reaction for
combustion of ammonia with excess oxygen!
4NH3(g) + 7O2(g) 4NO2(g) + 6H2O(g)
2. Calculate the enthalpy change for the combustion
of 1.00 mol of butane (C4H10), to give CO2 and H2O!
3. Calculate the value of 1.00 mol of ethyl alcohol
(C2H5OH), if we know that entalphy of combustion is –
1371 kJ/mole !
4. Tentukan ΔHreaksi :
C(s) + H2O(g) H2(g) + CO(g)
You might also like
- Grade 12 Lesson 10Document60 pagesGrade 12 Lesson 10Van CometaNo ratings yet
- Ike Dayi Febriana, S.Si., M.TDocument7 pagesIke Dayi Febriana, S.Si., M.TIke Dayi FebrianaNo ratings yet
- Delta H Mix Sample 45Document8 pagesDelta H Mix Sample 45Neeraj JadhavarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 ThermochemistryDocument6 pagesChapter 6 ThermochemistrysamNo ratings yet
- THERMOCHEMISTRY Hand Outs 2023Document6 pagesTHERMOCHEMISTRY Hand Outs 2023Paul Willard GumapacNo ratings yet
- Enthalpy 2Document11 pagesEnthalpy 2SB KPNo ratings yet
- 14 ThermochemistryDocument161 pages14 Thermochemistrysiewkiat0% (1)
- Chapter 1 CHM476 (Part 2)Document13 pagesChapter 1 CHM476 (Part 2)PUTRI DAYANA BATRIESYA ABDUL HANIFNo ratings yet
- Heat Energy Is Absorbed And: Energy Cannot Be Created or Destroyed But Can Be Converted From One Form To AnotherDocument12 pagesHeat Energy Is Absorbed And: Energy Cannot Be Created or Destroyed But Can Be Converted From One Form To AnotherAeyyjayyNo ratings yet
- Expt.4 - Heats of Reaction - Hess's LawDocument7 pagesExpt.4 - Heats of Reaction - Hess's LawNajah IzzatiNo ratings yet
- Introductory Chemistry B CH4751 Lecture Notes 11-20: Dr. Erzeng XueDocument81 pagesIntroductory Chemistry B CH4751 Lecture Notes 11-20: Dr. Erzeng XuethanhndbNo ratings yet
- EnthalpyDocument8 pagesEnthalpyKissiedu YirenkyiNo ratings yet
- AS Chem CH 1.2 Hess LawDocument21 pagesAS Chem CH 1.2 Hess LawRaymond Chan100% (1)
- Final ExamDocument8 pagesFinal ExamermiasNo ratings yet
- Lesson 04: Thermochemistry Unit 02: Thermochemical Equations Learning ObjectivesDocument7 pagesLesson 04: Thermochemistry Unit 02: Thermochemical Equations Learning ObjectivesLelouchNo ratings yet
- 1.4 EnergeticsDocument12 pages1.4 EnergeticschwalidNo ratings yet
- 5.thermochemical EquationsDocument21 pages5.thermochemical EquationsKristine Joy BaldozaNo ratings yet
- Thermochemistry 2 - Entropy and EnthalpyDocument18 pagesThermochemistry 2 - Entropy and Enthalpyx seyiNo ratings yet
- EnthalpyDocument27 pagesEnthalpyMichael BJ BragatNo ratings yet
- WorksheetDocument3 pagesWorksheetJomari GaliasNo ratings yet
- GC2 3 ThermochemistryDocument34 pagesGC2 3 ThermochemistryBea MoradaNo ratings yet
- ThermochemistryDocument44 pagesThermochemistryAmi NatNo ratings yet
- Thermo - Chem 1132022T2Document33 pagesThermo - Chem 1132022T2Kent DosejoNo ratings yet
- Chemical EnergeticsDocument34 pagesChemical EnergeticsNisidini JasingheNo ratings yet
- Aldrin Ramirez - Energy Changes in Chemical Reaction-GenChem2Document3 pagesAldrin Ramirez - Energy Changes in Chemical Reaction-GenChem2aldrinramirez20No ratings yet
- Plan 8 Hess's Law ChemDocument9 pagesPlan 8 Hess's Law ChemBernardo AblenNo ratings yet
- Thermochemistry 3 (Enthalpy of Reaction 2 and Hess's Law) - 2022Document14 pagesThermochemistry 3 (Enthalpy of Reaction 2 and Hess's Law) - 2022GloryNo ratings yet
- 2 ThermochemistryDocument9 pages2 ThermochemistryRachelHechanovaNo ratings yet
- 9th Class Chapter 8 Chemistry Notes Sindh BoardDocument5 pages9th Class Chapter 8 Chemistry Notes Sindh BoardmotivonovaNo ratings yet
- Lecture-Unit 7 Chemical EnergeticsDocument5 pagesLecture-Unit 7 Chemical EnergeticsKemoy FrancisNo ratings yet
- Ib PPT 5 SL PDFDocument39 pagesIb PPT 5 SL PDFzarna nirmal rawalNo ratings yet
- Hukum HessDocument4 pagesHukum HessLys HopeNo ratings yet
- Senior Chem - Controlling ReactionsDocument58 pagesSenior Chem - Controlling ReactionschiggsNo ratings yet
- Thermochemistry BookletDocument29 pagesThermochemistry Bookletdurmic_suadaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11: Thermochemistry - Heat and Chemical Changes Part 1 - Notes: Enthalpy and Bond EnergiesDocument11 pagesChapter 11: Thermochemistry - Heat and Chemical Changes Part 1 - Notes: Enthalpy and Bond EnergiesSarthakNo ratings yet
- ChemDocument29 pagesChemPearl LingbawanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5a (AS-Level) : Chemical EnergeticsDocument12 pagesChapter 5a (AS-Level) : Chemical EnergeticsMohamed AkkashNo ratings yet
- Isek. Men. Keb. Sultan Ismail, Johor Bahru. Physical Chemistry/ Upper Six/ 2013 Topic: Chemical EnergeticsDocument22 pagesIsek. Men. Keb. Sultan Ismail, Johor Bahru. Physical Chemistry/ Upper Six/ 2013 Topic: Chemical EnergeticsPh'ng Jiun YanNo ratings yet
- W8 Energy Balance On Reactive ProcessesDocument52 pagesW8 Energy Balance On Reactive ProcessesZafirahAhmadFauzi0% (1)
- Endothermic and Exothermic ReactionsDocument5 pagesEndothermic and Exothermic ReactionsIrvi Firqotul Aini100% (1)
- Enthalpy of Neutralisation of Water Temperature ProbeDocument7 pagesEnthalpy of Neutralisation of Water Temperature ProbeSharanya SrinivasanNo ratings yet
- 5.1. Hess's LawDocument16 pages5.1. Hess's LawKaihlaNo ratings yet
- Thermochemistry PowerPointDocument43 pagesThermochemistry PowerPointMagno CostaNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics: MR Edd VillamorDocument25 pagesThermodynamics: MR Edd VillamorEdd VillamorNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics 2Document28 pagesThermodynamics 2Edd VillamorNo ratings yet
- Q3 Pointers To ReviewDocument10 pagesQ3 Pointers To ReviewRonel CahayagNo ratings yet
- L13 Energy EnthalpyDocument9 pagesL13 Energy EnthalpyMariel Luciano CordovaNo ratings yet
- Energy Relationships in Chemical ReactionsDocument11 pagesEnergy Relationships in Chemical ReactionsDanise NicoleNo ratings yet
- 04combustion TechnologyDocument70 pages04combustion TechnologySheensky V. SalasaNo ratings yet
- Thermochemistry Is The Study of The Heat Released or Absorbed As A Result of Chemical ProcessesDocument3 pagesThermochemistry Is The Study of The Heat Released or Absorbed As A Result of Chemical Processesonesnia88No ratings yet
- MEB Concepts For DP1Document17 pagesMEB Concepts For DP1Shanthana LoshiniNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes Compiled by Dr. Soundarajan KrishnanDocument17 pagesLecture Notes Compiled by Dr. Soundarajan KrishnanShanthana LoshiniNo ratings yet
- Energetics and ThermochemistryDocument60 pagesEnergetics and ThermochemistryIsadora ThibauNo ratings yet
- Module 5 Chemistry For EngineersDocument7 pagesModule 5 Chemistry For EngineersElleazar JonesNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 - Termochemistry 55Document55 pagesChapter 9 - Termochemistry 55ABC_Ais Batu CampurNo ratings yet
- Enthalpy Changes ChemDocument4 pagesEnthalpy Changes Chemp01084240882No ratings yet
- CO3 ThermodynamicsDocument72 pagesCO3 ThermodynamicsRonna IturaldeNo ratings yet
- Yildiz Technical University Department of Chemical EngineeringDocument30 pagesYildiz Technical University Department of Chemical EngineeringBelis MercanNo ratings yet
- Critical Evaluation of Some Equilibrium Constants Involving Organophosphorus ExtractantsFrom EverandCritical Evaluation of Some Equilibrium Constants Involving Organophosphorus ExtractantsNo ratings yet
- ch05 StereochemistryDocument10 pagesch05 StereochemistrySankar SasmalNo ratings yet
- Kuliah Ir Part IiiDocument19 pagesKuliah Ir Part IiiIke Dayi FebrianaNo ratings yet
- Kuliah Ir Part IiDocument62 pagesKuliah Ir Part IiIke Dayi FebrianaNo ratings yet
- ASME V Art 6 PTDocument10 pagesASME V Art 6 PTmarutoagilNo ratings yet
- Kesetimbangan ReaksiDocument14 pagesKesetimbangan ReaksiIke Dayi FebrianaNo ratings yet
- Kesetimbangan ReaksiDocument14 pagesKesetimbangan ReaksiIke Dayi FebrianaNo ratings yet