Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Synapse-To-Nuclear +trafficking+of+crtc1
Synapse-To-Nuclear +trafficking+of+crtc1
Uploaded by
Shamia Chowdhury0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views6 pagesThis document discusses the synapse-to-nuclear trafficking of CRTC1 in hippocampal neurons. It finds that local glutamate stimulation leads to loss of CRTC1 only in the stimulated dendrite, not adjacent dendrites. Pretreatment with CsA blocks CRTC1 nuclear translocation induced by bicuculline or forskolin, showing nuclear import requires calcineurin activation. Elevated cAMP alone does not trigger CRTC1 nuclear translocation, but allows CRTC1 to persist in the nucleus. This spatial trafficking of CRTC1 may preserve spatial memory of the initial stimulation site.
Original Description:
cell biology assignment
Original Title
SYNAPSE-TO-NUCLEAR +TRAFFICKING+OF+CRTC1
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses the synapse-to-nuclear trafficking of CRTC1 in hippocampal neurons. It finds that local glutamate stimulation leads to loss of CRTC1 only in the stimulated dendrite, not adjacent dendrites. Pretreatment with CsA blocks CRTC1 nuclear translocation induced by bicuculline or forskolin, showing nuclear import requires calcineurin activation. Elevated cAMP alone does not trigger CRTC1 nuclear translocation, but allows CRTC1 to persist in the nucleus. This spatial trafficking of CRTC1 may preserve spatial memory of the initial stimulation site.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views6 pagesSynapse-To-Nuclear +trafficking+of+crtc1
Synapse-To-Nuclear +trafficking+of+crtc1
Uploaded by
Shamia ChowdhuryThis document discusses the synapse-to-nuclear trafficking of CRTC1 in hippocampal neurons. It finds that local glutamate stimulation leads to loss of CRTC1 only in the stimulated dendrite, not adjacent dendrites. Pretreatment with CsA blocks CRTC1 nuclear translocation induced by bicuculline or forskolin, showing nuclear import requires calcineurin activation. Elevated cAMP alone does not trigger CRTC1 nuclear translocation, but allows CRTC1 to persist in the nucleus. This spatial trafficking of CRTC1 may preserve spatial memory of the initial stimulation site.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 6
Synapse-to-nuclear trafficking of
CRTC1 in neurons
The task of hippocampus calls for retrieval,
processing short-term memory and transferring
memory from short term to longer delay periods.
CRTC1 nuclear translocation; LTP
Synapse-to-Nucleus Translocation
of CRTC1 in Organotypic Slice Cultures
and Acute Hippocampal Slice Preparations
Synapse-to-Nucleus Translocation of
CRTC1 in Hippocampal Neurons
Experiment using local glutamate uncaging followed by CRTC1
immunocytochemistry indicate that the loss of CRTC1 is confined to the
stimulated dendrite
CRTC1 in the glutamate uncaged = CRTC1 in adjacent control dendrite
Nuclear Translocation of CRTC1 Requires
Activation of Calcineurin; cAMP Regulates the
Persistence of CRTC1 in the Nucleus
• Hippocampal cultures were pretreated with CsA (5 mM) for 4 hr
prior to a 1 hr stimulation with bicuculline (BIC; 40 mM) or with
forskolin (FSK; 25 mM).
• Neurons were fixed and immunostained with antibodies against
MAP2 (red), CRTC1 (green), and Hoechst nuclear dye (blue,
merged),
ANALYSIS: ELEVATED intracellular cAMP in ABSENCE of neuronal activity
does not trigger CRTC1 nuclear translocation.
NO NUCLEAR IMPORT
BUT cAMP ALLOWS CRTC1 to stay within nucleus
Synapse to neuron translocation
bZIP
• May contribute to specificity of CREB-dependent
transcriptional responses domain
• CRTC1 translocation could preserve spatial information
about initial site of stimulation
• TRANSCRIPTION at nucleus:
• CREB required at LATE STAGE LTP
• CREB –phosphorylation by PKA and Ca++/calmodulin protien
kinases
Secondary messenger cascades causes this spatial information
to be lost
• Stimuli triggering loss of CRTC1 from stimulating synapses
provides that spatial Information
NATURE OF STIMULATION REQUIRED FOR LONG TERM
SYNAPTIC EFFICACY
CREB PROTEIN DNA BINDING
STIMULUS acting through neuromodulators like
norepinephrine, dopamine at hippocampus following
strong tetanic stimulation enhances long-term memory
formation.
Different CRTC1-dependent gene expression trigger
distinct types of CREB-dependent memory
You might also like
- Pharmacology of Central Nervous SystemDocument20 pagesPharmacology of Central Nervous SystemAngelic khan100% (1)
- NeuromodulationDocument14 pagesNeuromodulationapi-3710904No ratings yet
- Proyecto de Tesis - Nicole SanguinettiDocument26 pagesProyecto de Tesis - Nicole SanguinettiPau Fer Mujica CNo ratings yet
- Devraj Parasar CGRPDocument15 pagesDevraj Parasar CGRPMukesh PatelNo ratings yet
- 4 RNA TransportDocument35 pages4 RNA TransportUmar KhitabNo ratings yet
- Phosphorylation of P-Glycoprotein by PKA and PKC Modulates Swelling-Activated CL CurrentsDocument9 pagesPhosphorylation of P-Glycoprotein by PKA and PKC Modulates Swelling-Activated CL CurrentsDr-Dalya ShakirNo ratings yet
- CREB Regulation of BK Channel Gene Expression Underlies Rapid Drug ToleranceDocument28 pagesCREB Regulation of BK Channel Gene Expression Underlies Rapid Drug TolerancestefanocasalottiNo ratings yet
- Zhong 1999Document4 pagesZhong 1999Araceli Enríquez OvandoNo ratings yet
- Ni Hms 21239Document9 pagesNi Hms 21239Ionut NeagaNo ratings yet
- TMP 9 DA2Document11 pagesTMP 9 DA2FrontiersNo ratings yet
- GSL Marc MalenkaDocument10 pagesGSL Marc MalenkaDebanjan GoswamiNo ratings yet
- Ni Hms 262290Document8 pagesNi Hms 262290Ignacio MazzitelliNo ratings yet
- Central Synapse and Neuromuscular Junction: Same Players, Different RolesDocument8 pagesCentral Synapse and Neuromuscular Junction: Same Players, Different RolesMarcelo Pires de OliveiraNo ratings yet
- Cotransmission: Geoffrey BurnstockDocument6 pagesCotransmission: Geoffrey BurnstockSuryasumanthNo ratings yet
- Patofisiologi MigrainDocument48 pagesPatofisiologi Migrainnesya_fanniaNo ratings yet
- Optical Activation of TRKB SignalingDocument10 pagesOptical Activation of TRKB Signalingwang蕊如No ratings yet
- Mechanism of mRNA Transport in The NucleusDocument6 pagesMechanism of mRNA Transport in The NucleusNarayla LailaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5, Ch. 11Document8 pagesLecture 5, Ch. 11S. SpencerNo ratings yet
- CDC14 TreatiseDocument12 pagesCDC14 TreatiseasdfweafsplashNo ratings yet
- NeurotrofinasDocument12 pagesNeurotrofinasAlfredo Lagos FusterNo ratings yet
- Loreto, M (2002) - Functional Cooperation Between C-CBL and Src-Like Adaptor Protein 2 in The Negative Regulation of T-Cell Receptor SignalingDocument15 pagesLoreto, M (2002) - Functional Cooperation Between C-CBL and Src-Like Adaptor Protein 2 in The Negative Regulation of T-Cell Receptor SignalingAnadahiNo ratings yet
- BY2201 Colm Basic NeurochemOct11Document96 pagesBY2201 Colm Basic NeurochemOct11Rhys DunneNo ratings yet
- Bembenek 2005Document11 pagesBembenek 2005good devilNo ratings yet
- BMC NeuroscienceDocument7 pagesBMC NeuroscienceDmitry DiykovNo ratings yet
- tPA and NMDA Receptor PDFDocument9 pagestPA and NMDA Receptor PDFsaurabh mahajanNo ratings yet
- Nicotinic α7 receptors enhance NMDA cognitive circuits in dorsolateral prefrontal cortexDocument6 pagesNicotinic α7 receptors enhance NMDA cognitive circuits in dorsolateral prefrontal cortexDouglas DiasNo ratings yet
- Ginger 2007 Slca Encodes A Trans Golgi NetworkDocument11 pagesGinger 2007 Slca Encodes A Trans Golgi NetworkDr. Ọbádélé KambonNo ratings yet
- Polymerase Chain Reaction ProtocolDocument14 pagesPolymerase Chain Reaction ProtocolDespoina ChatziNo ratings yet
- Vanderwaal Et Al. 69 (16) 6454. (2009)Document9 pagesVanderwaal Et Al. 69 (16) 6454. (2009)Nancy CharóNo ratings yet
- Nakayama, 2006Document22 pagesNakayama, 2006Giulia AndreeaNo ratings yet
- Methods For Studying Epigenetic ModificationsDocument23 pagesMethods For Studying Epigenetic ModificationslordniklausNo ratings yet
- Acin Biochem Biophys Res Commun 1998Document6 pagesAcin Biochem Biophys Res Commun 1998vnq6gd6qbxNo ratings yet
- Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification of DNADocument7 pagesLoop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification of DNAChristian Moises CasasNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle & Axonal RegenerationDocument20 pagesCell Cycle & Axonal Regenerationapi-3821304No ratings yet
- PCR in Infectious DiseasesDocument3 pagesPCR in Infectious Diseasesthị sô phiaNo ratings yet
- GABA-Activated CL - Channels in Astrocytes of Hippocampal SlicesDocument7 pagesGABA-Activated CL - Channels in Astrocytes of Hippocampal Sliceshector3nu3ezNo ratings yet
- Regulation of Eukaryotic DNA Replication at The Initiation StepDocument4 pagesRegulation of Eukaryotic DNA Replication at The Initiation Steprickylion25051983No ratings yet
- A Light-Inducible Crispr-Cas9 System For Control of Endogenous Gene ActivationDocument4 pagesA Light-Inducible Crispr-Cas9 System For Control of Endogenous Gene ActivationCarlos ManginoNo ratings yet
- Headache CurrentsDocument12 pagesHeadache CurrentslucymayNo ratings yet
- 2.5.) Central Dogma of Molecular Biology (BIO40)Document21 pages2.5.) Central Dogma of Molecular Biology (BIO40)Mary Ferl Jasmin LupagueNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle Dna Poster 2016Document1 pageCell Cycle Dna Poster 2016fosudavid.jfNo ratings yet
- Gaba Actions and Ionic Plasticity in Epilepsy: SciencedirectDocument8 pagesGaba Actions and Ionic Plasticity in Epilepsy: SciencedirectMuhammad Bayu Zohari HutagalungNo ratings yet
- RT-PCR Used IN Covid-19 TestingDocument34 pagesRT-PCR Used IN Covid-19 Testinganjali SINGHNo ratings yet
- Bava 2013Document7 pagesBava 2013Julián David RoldánNo ratings yet
- Jurnal 5 KalsitoninDocument5 pagesJurnal 5 KalsitoninPrawido AndriadiNo ratings yet
- ABG: Nguyen Bao Ngoc Diep, Pham Yen Giang, Pham Thi Ngoc Phuong, Van Phuong TrangDocument1 pageABG: Nguyen Bao Ngoc Diep, Pham Yen Giang, Pham Thi Ngoc Phuong, Van Phuong TrangAmilian ParkerNo ratings yet
- GENEDocument5 pagesGENEhanthuyNo ratings yet
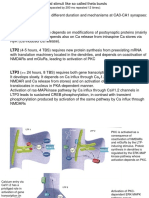
- LTP1 ( 2 Hours, 1 TBS) Depends On Modifications of Postsynaptic Proteins (MainlyDocument12 pagesLTP1 ( 2 Hours, 1 TBS) Depends On Modifications of Postsynaptic Proteins (MainlyThe Panda EntertainerNo ratings yet
- Reciprocal Regulation Between: TOC1 and LHY/CCA1 Within The Arabidopsis Circadian ClockDocument5 pagesReciprocal Regulation Between: TOC1 and LHY/CCA1 Within The Arabidopsis Circadian ClockShreetama BhattacharyaNo ratings yet
- Molecular Mechanisms of Neurotransmitter ReleaseDocument21 pagesMolecular Mechanisms of Neurotransmitter ReleaseNusrat JahanNo ratings yet
- Reversing A Model of Parkinson's Disease With in Situ Converted Nigral NeuronsDocument28 pagesReversing A Model of Parkinson's Disease With in Situ Converted Nigral NeuronsRhotmy Raúl Escobar GuzmánNo ratings yet
- T Cell Activation and Signaling: TCR TalinDocument8 pagesT Cell Activation and Signaling: TCR TalinMst Monira KhatonNo ratings yet
- 2002-Signaling Pathways For PC12 Cell Differentiation - Making The Right ConnectionsDocument3 pages2002-Signaling Pathways For PC12 Cell Differentiation - Making The Right ConnectionsWim ZhuNo ratings yet
- Solanum Lycopersicum Cryptochrome 1 Expression in Response To Short and Long PhotoperiodsDocument22 pagesSolanum Lycopersicum Cryptochrome 1 Expression in Response To Short and Long PhotoperiodsPatrick StumpsNo ratings yet
- PNAS 2001 West 11024 31Document8 pagesPNAS 2001 West 11024 31Vehpi YILDIRIMNo ratings yet
- Activation of PKA and Epac Proteins by Cyclic AMP Depletes Intracellular Calcium Stores and Reduces Calcium Availability For VasoconstrictionDocument30 pagesActivation of PKA and Epac Proteins by Cyclic AMP Depletes Intracellular Calcium Stores and Reduces Calcium Availability For VasoconstrictionLeonel LedezmaNo ratings yet
- The Impact On Synaptic Transmission by Removal of Endocannabinoid Signaling in Specific NeuronsDocument6 pagesThe Impact On Synaptic Transmission by Removal of Endocannabinoid Signaling in Specific NeuronsPau Fer Mujica CNo ratings yet
- Toh Review Genetics CRSDsDocument7 pagesToh Review Genetics CRSDsPatti MurphyNo ratings yet