Professional Documents
Culture Documents
WWW - Fo8.Dswd - Gov.Ph DSWD Field Office 08 @dswdfo8: #Dswdkalingaatpagmamahal #Dswdmaymalasakit
Uploaded by
maria carmela pullantes0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
186 views28 pagesThe document discusses the Magna Carta of Women, which is the comprehensive women's human rights law in the Philippines. It seeks to eliminate discrimination against women and promote gender equality. Some key rights guaranteed under the law include protection from violence, participation in decision making, equal treatment before the law, non-discrimination in education and employment, and non-derogatory portrayal of women in media.
Original Description:
Original Title
PPT.pptx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses the Magna Carta of Women, which is the comprehensive women's human rights law in the Philippines. It seeks to eliminate discrimination against women and promote gender equality. Some key rights guaranteed under the law include protection from violence, participation in decision making, equal treatment before the law, non-discrimination in education and employment, and non-derogatory portrayal of women in media.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
186 views28 pagesWWW - Fo8.Dswd - Gov.Ph DSWD Field Office 08 @dswdfo8: #Dswdkalingaatpagmamahal #Dswdmaymalasakit
Uploaded by
maria carmela pullantesThe document discusses the Magna Carta of Women, which is the comprehensive women's human rights law in the Philippines. It seeks to eliminate discrimination against women and promote gender equality. Some key rights guaranteed under the law include protection from violence, participation in decision making, equal treatment before the law, non-discrimination in education and employment, and non-derogatory portrayal of women in media.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 28
www.fo8.dswd.gov.
ph DSWD Field Office 08 @dswdfo8 #DSWDMayMalasakit
#DSWDKalingaAtPagmamahal
Topic 1: R.A. 9710, otherwise
known as “Magna Carta of
Women”
What is Magna Carta for Women?
• The Magna Carta of Women is comprehensive
women’s human rights law that seeks to eliminate
discrimination against women by recognizing,
protecting, fulfilling and promoting the rights of
Filipino women, especially those in marginalized
sector.
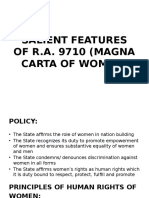
Declaration of Policy
• Recognizing that the economic, political, and sociocultural realities
affect women’s current condition, the State affirms the role of women
in nation building and ensures the substantive equality of women and
men. It shall promote empowerment of women and pursue equal
opportunities for women and men and ensure equal access to
resources and to development results and outcome.
Declaration of Policy
• The State realizes that equality of men and women entails the abolition
of the unequal structures Republic of the Philippines Congress of the
Philippines Metro Manila 2 and practices that perpetuate discrimination
and inequality. To realize this, the State shall endeavor to develop plans,
policies, programs, measures, and mechanisms to address discrimination
and inequality in the economic, political, social, and cultural life of
women and men.
Declaration of Policy
• The State condemns discrimination against women in all its forms and
pursues by all appropriate means and without delay the policy of
eliminating discrimination against women in keeping with the
Convention on the Elimination of All Forms of Discrimination Against
Women (CEDAW) and other international instruments consistent with
Philippine law. The State shall accord women the rights, protection,
and opportunities available to every member of society.
Declaration of Policy
• The State affirms women’s rights as human rights and shall intensify
its efforts to fulfill its duties under international and domestic law to
recognize, respect, protect, fulfill, and promote all human rights and
fundamental freedoms of women, especially marginalized women, in
the economic, social, political, cultural, and other fields without
distinction or discrimination on account of class, age, sex, gender,
language, ethnicity, religion, ideology, disability, education, and
status.
Declaration of Policy
• The State shall provide the necessary mechanisms to enforce
women’s rights and adopt and undertake all legal measures necessary
to foster and promote the equal opportunity for women to
participate in and contribute to the development of the political,
economic, social, and cultural realms. The State, in ensuring the full
integration of women’s concerns in the mainstream of development,
shall provide ample opportunities to enhance and develop their skills,
acquire productive employment and contribute to their families and
communities to the fullest of their capabilities.
Declaration of Policy
• In pursuance of this policy, the State reaffirms the right of women in
all sectors to participate in policy formulation, planning, organization,
implementation, management, monitoring, and evaluation of all
programs, projects, and services. It shall support policies, researches,
technology, and training programs and other support services such as
financing, production, and marketing to encourage active
participation of women in national development.
Principles of Human Rights of Women
• Human rights are universal and inalienable. All people in the world
are entitled to them.
• The universality of human rights is encompassed in the words of
Article 1 of the Universal Declaration of Human Rights, which states
that all human beings are free and equal in dignity and rights.
• Human rights are indivisible. Human rights are inherent to the
dignity of every human being whether they relate to civil, cultural,
economic, political, or social issues.
Principles of Human Rights of Women
• Human rights are interdependent and interrelated. The fulfillment of
one right often depends, wholly or in part, upon the fulfillment of
others.
• All individuals are equal as human beings by virtue of the inherent
dignity of each human person. No one, therefore, should suffer
discrimination on the basis of ethnicity, gender, age, language, sexual
orientation, race, color, religion, political, or other opinion, national,
social, or geographical origin, disability, property, birth, or other
status as established by human rights standards.
Principles of Human Rights of Women
• All people have the rights to participate in and access information
relating to the decision-making processes that affect their lives and
well-being. Rights-based approached require a high degree of
participation by communities, civil society, minorities, women, young
people, indigenous peoples, and other identified groups.
• States and other duty-bearers are answerable for the observance of
human rights. They have to comply with the legal norms and standards
enshrined in international human rights instruments in accordance with
the Philippine Constitution. Where they fail to do so, aggrieved rights-
holders are entitled to institute proceedings for appropriate redress
before a competent court or other adjudicator in accordance with the
rules and procedures provided by law.
What is discrimination against women?
any gender-based distinction, exclusion, or restriction which
has the effect or purpose of impairing or nullifying the
recognition, enjoyment, or exercise by women, irrespective
of their marital status, on a basis of equality of men and
women, of human rights and fundamental freedoms in the
political, economic, social, cultural, civil or any other field;
any act or omission, including by law, policy, administrative
measure, or practice, that directly or indirectly excludes or
restricts women in the recognition and promotion of their
rights and their access to and enjoyment of opportunities,
benefits, or privileges;
What is discrimination against women?
a measure or practice of general application that fails to provide
for mechanisms to offset or address sex or gender-based
disadvantages or limitations of women, as a result of which
women are denied or restricted in the recognition and protection
of their rights and in their access to and enjoyment of
opportunities, benefits, or privileges; or women, more than men
are shown to have suffered the greater adverse effects of those
measures or practices; and
discrimination compounded by or intersecting with other
grounds, status, or condition, such as ethnicity, age, poverty, or
religion.
What are the rights of women guaranteed under the
Magna Carta of Women?
Protection from all forms of violence, including those committed by
the State. This includes the incremental increase in the recruitment
and training of women in government services that cater to women
victims of gender-related offenses. It also ensures mandatory
training on human rights and gender sensitivity to all government
personnel involved in the protection and defense of women against
gender-based violence, and mandates local government units to
establish a Violence Against Women Desk in every barangay to
address violence against women cases;
Protection and security in times of disaster, calamities and other
crisis situations, especially in all phases of relief, recovery,
rehabilitation and construction efforts, including protection from
sexual exploitation and other sexual and gender-based violence.
What are the rights of women guaranteed under the
Magna Carta of Women?
Participation and representation, including undertaking temporary
special measures and affirmative actions to accelerate and ensure
women's equitable participation and representation in the third level
civil service, development councils and planning bodies, as well as
political parties and international bodies, including the private sector.
Equal treatment before the law, including the State's review and
when necessary amendment or repeal of existing laws that are
discriminatory to women;
Equal access and elimination of discrimination against women in
education, scholarships and training. This includes revising
educational materials and curricula to remove gender stereotypes
and images, and outlawing the expulsion, non-readmission,
prohibiting enrollment and other related discrimination against
women students and faculty due to pregnancy outside of marriage;
What are the rights of women guaranteed under the
Magna Carta of Women?
Equal participation in sports. This includes measures to ensure that
gender-based discrimination in competitive and non-competitive
sports is removed so that women and girls can benefit from sports
development;
Non-discrimination in employment in the field of military, police and
other similar services. This includes according the same promotional
privileges and opportunities as their men counterpart, including pay
increases, additional benefits, and awards, based on competency
and quality of performance. The dignity of women in the military,
police and other similar services shall always be respected, they shall
be accorded with the same capacity as men to act in and enter into
contracts, including marriage, as well as be entitled to leave benefits
for women such as maternity leave, as provided for in existing laws;
What are the rights of women guaranteed under the
Magna Carta of Women?
Non-discriminatory and non-derogatory portrayal
of women in media and film to raise the
consciousness of the general public in recognizing
the dignity of women and the role and contribution
of women in family, community, and the society
through the strategic use of mass media;
What are the rights of women
guaranteed under the Magna Carta of
Women?
Comprehensive health services and health information and
education covering all stages of a woman's life cycle, and which
addresses the major causes of women's mortality and morbidity,
including access to among others, maternal care, responsible, ethical,
legal, safe and effective methods of family planning, and encouraging
healthy lifestyle activities to prevent diseases;
Leave benefits of two (2) months with full pay based on gross
monthly compensation, for women employees who undergo surgery
caused by gynecological disorders, provided that they have rendered
continuous aggregate employment service of at least six (6) months
for the last twelve (12) months;
What are the rights of women
guaranteed under the Magna Carta of
Women?
Equal rights in all matters relating to marriage and family relations. The State
shall ensure the same rights of women and men to: enter into and leave
marriages, freely choose a spouse, decide on the number and spacing of their
children, enjoy personal rights including the choice of a profession, own,
acquire, and administer their property, and acquire, change, or retain their
nationality. It also states that the betrothal and marriage of a child shall have
no legal effect.
The Magna Carta of Women also guarantees the civil,
political and economic rights of women in the
marginalized sectors, particularly their right to:
Food security and resources for food production, including equal rights
in the titling of the land and issuance of stewardship contracts and
patents;
Localized, accessible, secure and affordable housing;
Employment, livelihood, credit, capital and technology;
Skills training, scholarships, especially in research and development
aimed towards women friendly farm technology;
Representation and participation in policy-making or decision-making
bodies in the regional, national, and international levels;
Access to information regarding policies on women, including
programs, projects and funding outlays that affect them;
Social protection;
The Magna Carta of Women defines the
marginalized sectors as:
Those who belong to the basic, disadvantaged, or vulnerable groups who are
mostly living in poverty and have little or no access to land and other
resources, basic social and economic services such as health care, education,
water and sanitation, employment and livelihood opportunities, housing
security, physical infrastructure and the justice system.
These include, but are not limited to women in the following sectors or groups:
o Small farmers and rural workers
o Fisherfolk
o Urban poor
o Workers in the formal economy
o Workers in the informal economy
o Migrant workers
o Indigenous Peoples
o Moro
o Children
o Senior citizens
o Persons with disabilities
o Solo parents
Roles and Responsibilities of Duty-bearersa
Carta of Women?
The State, the private sector, society in general, and all individuals shall contribute to
the recognition, respect and promotion of the rights of women defined and
guaranteed in the Magna Carta of Women.
The Philippine Government shall be the primary duty-bearer in implementing the
said law. This means that all government offices, including local government units
and government-owned and controlled corporations shall be responsible to
implement the provisions of Magna Carta of Women that falls within their mandate,
particularly those that guarantee rights of women that require specific action from
the State.
As the primary duty-bearer, the Government is tasked to:
o refrain from discriminating against women and violating their rights;
o protect women against discrimination and from violation of their rights by private
corporations, entities, and individuals;
o promote and fulfill the rights of women in all spheres, including their rights to
substantive equality and non-discrimination.
Roles and Responsibilities of Duty-bearersa ific
responsibilities of government under the Magna Carta of
Women?
The Magna Carta of Women mandates all government offices,
including government-owned and controlled corporations and
local government units to adopt gender mainstreaming as a
strategy for implementing the law and attaining its objectives.
It also mandates (a) planning, budgeting, monitoring and
evaluation for gender and development, (b) the creation
and/or strengthening of gender and development focal points,
and (c) the generation and maintenance of gender statistics
and sex-disaggregated databases to aid in planning,
programming and policy formulation.
Under this law, the National Commission on the Role of Filipino Women which will be renamed as the
What are the specific responsibilities of government
Philippine Commission on Women (PCW) shall be the overall monitoring and oversight body to ensure
the implementation of the law. As an agency under the Office of the President of the Philippines, it will
under the Magna Carta of Women?
be the primary policy-making and coordinating body for women and gender equality concerns and
shall lead in ensuring that government agencies are capacitated on the effective implementation of the
Magna Carta of Women.
Consistent with its mandate, the Commission on Human Rights shall act as the Gender and
Development Ombudsman to ensure the promotion and protection of women's human rights.
The Commission on Audit shall conduct an annual audit on the government offices' use of their gender
and development budgets for the purpose of determining its judicious use and the efficiency, and
effectiveness of interventions in addressing gender issues.
Local government units are also encouraged to develop and pass a gender and development code to
address the issues and concerns of women in their respective localities based on consultation with
their women constituents.
All local government units shall establish a Violence Against Women’s Desk in every barangay to ensure
that violence against women cases are fully addressed in a gender-responsive manner.
If the violation is committed by a government agency or any government
What are the penalties of violators?
office, including government-owned and controlled corporations and local
government units, the person directly responsible for the violation, as well as
the head of the agency or local chief executive shall be held liable under the
Magna Carta of Women.
The sanctions under administrative law, civil service or other appropriate laws
shall be re commended by the Commission on Human Rights to the Civil
Service Commission and the Department of the Interior and Local
Government.
Further, in cases where violence has been proven to be perpetrated by agents
of the State, such shall be considered aggravating offenses with
corresponding penalties depending on the severity of the offenses.
If the violation is committed by a private entity or individual, the person
directly responsible for the violation shall be liable to pay damages. Further,
the offended party can also pursue other remedies available under the law
and can invoke any of the other provisions of existing laws, especially those
that protect the rights of women.
How will the implementation of the Magna Carta of
Women be funded?
• The Magna Carta of Women provides that the State agencies
should utilize their gender and development budgets for
programs and activities to implement its provisions. Funds
necessary for the implementation of the Magna Carta of
Women shall be charged against the current
appropriations of the concerned agencies, and shall be
included in their annual budgets for the succeeding years.
• The Magna Carta of Women also mandates the State to
prioritize allocation of all available resources to effectively
fulfill its obligations under the said law.
WE MAKE CHANGE WORK FOR WOMEN!
You might also like
- Protecting Women and Children from Violence ActDocument58 pagesProtecting Women and Children from Violence ActMoon Beams100% (7)
- PWDsDocument34 pagesPWDsmaria carmela pullantes100% (1)
- PWDsDocument34 pagesPWDsmaria carmela pullantes100% (1)
- RA 9710 PresentationDocument27 pagesRA 9710 PresentationPam UrsolinoNo ratings yet
- Infographics About VAWCDocument2 pagesInfographics About VAWCJezzel Keyt Ordo Quimoyog100% (1)
- Thomas Aquinas Philosophy in EducationDocument3 pagesThomas Aquinas Philosophy in EducationJanet Paggao100% (1)
- Anti-VAWC PowerpointDocument26 pagesAnti-VAWC Powerpointroy ruba100% (2)
- The Gad Evolution & Legal MandatesDocument35 pagesThe Gad Evolution & Legal MandatesAserethNo ratings yet
- PH Anti-Hazing Act bans all initiation ritesDocument53 pagesPH Anti-Hazing Act bans all initiation ritesRosalie B. Candido100% (2)
- Violence Against WomenDocument14 pagesViolence Against Womenlachel joy tahinayNo ratings yet
- Identification and Disclosure FormDocument1 pageIdentification and Disclosure Formmaria carmela pullantesNo ratings yet
- R.A. 6975Document24 pagesR.A. 6975Edgar Joshua Timbang100% (1)
- Magna Carta of WomenDocument8 pagesMagna Carta of WomenBrylle BeronillaNo ratings yet
- Magna Carta of WomenDocument71 pagesMagna Carta of WomenJongNo ratings yet
- Magna Carta of Women Rights LawDocument24 pagesMagna Carta of Women Rights LawSj Eclipse100% (2)
- R.A. 9710 Magna Carta of WomenDocument17 pagesR.A. 9710 Magna Carta of Womenbaleno100% (1)
- MCW's Herstory: A Summary of the Salient Features and Significance of the Magna Carta of WomenDocument36 pagesMCW's Herstory: A Summary of the Salient Features and Significance of the Magna Carta of WomenErnie B LabradorNo ratings yet
- Gender Awareness Development Advocacy FINALDocument63 pagesGender Awareness Development Advocacy FINALRocel Esoj100% (1)
- Magna Carta of WomenDocument34 pagesMagna Carta of WomenKevinNo ratings yet
- Implementing Rules and Regulations of the Magna Carta of WomenDocument27 pagesImplementing Rules and Regulations of the Magna Carta of WomenIrwin Ariel D. MielNo ratings yet
- RA 9262 Law SummaryDocument17 pagesRA 9262 Law Summarydave bermilNo ratings yet
- GAD Campaign Raises Awareness on Concepts and MandatesDocument41 pagesGAD Campaign Raises Awareness on Concepts and MandatesFrancis Gutierrez BalazonNo ratings yet
- Ra 9262 For I-DingDocument51 pagesRa 9262 For I-DingRabhak Khal-HadjjNo ratings yet
- Gender Sensitivity ModulesDocument91 pagesGender Sensitivity ModulesGeraldNo ratings yet
- United Nations PROPOSALDocument5 pagesUnited Nations PROPOSALDens Campillo Olasiman100% (1)
- Ra 7877Document37 pagesRa 7877Jordan CabaguingNo ratings yet
- Republic Act 9262Document55 pagesRepublic Act 9262ZannyRyanQuiroz100% (1)
- VAWCDocument31 pagesVAWCjayzzah100% (3)
- Magna Carta of WomenDocument44 pagesMagna Carta of WomenLeslie BajetNo ratings yet
- Ra 9262Document18 pagesRa 9262Weddanever Cornel100% (1)
- Anti-Violence Against Women and Their Children Act of 2004Document33 pagesAnti-Violence Against Women and Their Children Act of 2004Lucian LucianNo ratings yet
- Women and Children With Law ScaleDocument30 pagesWomen and Children With Law ScaleDeanette MichaelaNo ratings yet
- Basic GAD ConceptsDocument42 pagesBasic GAD Conceptsbm100% (1)
- VawcDocument40 pagesVawcAbi Ni Thiya100% (2)
- Rights of Filipino Women: A Summary of the Magna Carta of Women LawDocument17 pagesRights of Filipino Women: A Summary of the Magna Carta of Women LawEbony Landry0% (1)
- Various Laws Involving ChildrenDocument99 pagesVarious Laws Involving ChildrenPring SumNo ratings yet
- Safe Spaces Act PresentationDocument38 pagesSafe Spaces Act PresentationFerlyn Solima100% (1)
- Gender Sensitivity: Understanding Sex, Gender, and ViolenceDocument15 pagesGender Sensitivity: Understanding Sex, Gender, and ViolenceErah Syl ArcallanaNo ratings yet
- IPRADocument7 pagesIPRAJhane100% (1)
- VAWC LectureDocument23 pagesVAWC LectureFaith Roslyndale Fidés100% (2)
- GAD LEGAL MANDATESDocument87 pagesGAD LEGAL MANDATEScrixzam100% (1)
- The Anti-Violence Against Women and Their Children Act (Ra 9262)Document39 pagesThe Anti-Violence Against Women and Their Children Act (Ra 9262)Mimhy VallegaNo ratings yet
- Republic Act 9262Document30 pagesRepublic Act 9262Romy Wacas100% (1)
- Ra 9262 - Vawc LawDocument10 pagesRa 9262 - Vawc Lawchie du100% (1)
- Group 7 Lesson 17 18Document55 pagesGroup 7 Lesson 17 18Absalon, J. A. (2201986)No ratings yet
- Anti-VAWC Seminar Discussion PaperDocument9 pagesAnti-VAWC Seminar Discussion PaperDaryl Dumayas100% (2)
- Beed 3. Rose Sanico RoqueroDocument22 pagesBeed 3. Rose Sanico RoqueroRosalinda Rubio SanicoNo ratings yet
- 2020 GAD Webinar 1 - Intro To SOGIESCDocument47 pages2020 GAD Webinar 1 - Intro To SOGIESCCherry May Logdat-Ng100% (1)
- RA 11313-Refined - July 7 2022Document25 pagesRA 11313-Refined - July 7 2022Katrina Budlong100% (3)
- Orientation On Basic GAD ConceptsDocument34 pagesOrientation On Basic GAD ConceptsMelymay Palaroan Remorin100% (3)
- Anti Rape LawDocument27 pagesAnti Rape LawAnonymous KvztB3No ratings yet
- The Laws On Violence Against Women and Children in The PhilippinesDocument32 pagesThe Laws On Violence Against Women and Children in The PhilippinesCHARLOTTE GALLEGONo ratings yet
- Intimate Partner Violence: Tension ReductionDocument23 pagesIntimate Partner Violence: Tension ReductionjhoyNo ratings yet
- RA 9710 Magna Carta For WomenDocument6 pagesRA 9710 Magna Carta For WomenLim Xu Win100% (2)
- R.A. 9262Document69 pagesR.A. 9262PSMS Rosemarie L IbarraNo ratings yet
- Anti-Violence Against Women and Children (Vawc)Document80 pagesAnti-Violence Against Women and Children (Vawc)Chin Martinz100% (3)
- RA11930 (Anti OSAEC) Law IRRDocument73 pagesRA11930 (Anti OSAEC) Law IRRSig G. MiNo ratings yet
- Group 5 - THE SAFE SPACES ACTDocument42 pagesGroup 5 - THE SAFE SPACES ACTMaria Domenic DomporNo ratings yet
- Explaining Contextualizing The MAGNA CARTA OF WOMENDocument44 pagesExplaining Contextualizing The MAGNA CARTA OF WOMENiana_fajardoNo ratings yet
- Program Plan For Bahay Pagbabago Reformation CenterDocument2 pagesProgram Plan For Bahay Pagbabago Reformation CenterElla Lim PanenNo ratings yet
- Ra 9344Document49 pagesRa 9344Thea Thei Ya100% (1)
- Magna Carta For WomenDocument5 pagesMagna Carta For WomenJeanetteNardoNo ratings yet
- What Is Magna Carta of Women (Republic Act No. 9710) ?Document5 pagesWhat Is Magna Carta of Women (Republic Act No. 9710) ?dwight yuNo ratings yet
- Magna Carta Q.ADocument8 pagesMagna Carta Q.AVerlin Amarante EntenaNo ratings yet
- $unit 5 Eating Disorders PDFDocument29 pages$unit 5 Eating Disorders PDFkrishmasethiNo ratings yet
- Duties and Responsibilities: Terms of Reference DSWD-led Inter-Agency Council SecretariatDocument1 pageDuties and Responsibilities: Terms of Reference DSWD-led Inter-Agency Council Secretariatmaria carmela pullantesNo ratings yet
- Sample NoticeDocument48 pagesSample Noticemaria carmela pullantesNo ratings yet
- Work Experience Sheet for Supervising PositionsDocument2 pagesWork Experience Sheet for Supervising PositionsCes Camello100% (1)
- 1582286188unit 1 Life Coaching Basics EDITDocument6 pages1582286188unit 1 Life Coaching Basics EDITmaria carmela pullantesNo ratings yet
- Public RelationsDocument29 pagesPublic RelationsSaleh MuhammadNo ratings yet
- Stages Writing Reports ProposalsDocument19 pagesStages Writing Reports Proposalsmaria carmela pullantesNo ratings yet
- World Day Against Trafficking Activities ProposalDocument5 pagesWorld Day Against Trafficking Activities Proposalmaria carmela pullantesNo ratings yet
- Proposal Strengthening Couples Relationship 2020Document4 pagesProposal Strengthening Couples Relationship 2020maria carmela pullantesNo ratings yet
- Auxiliary GuidelinesDocument8 pagesAuxiliary Guidelinesmaria carmela pullantesNo ratings yet
- Job and Role Description Template FinalDocument6 pagesJob and Role Description Template Finalmaria carmela pullantesNo ratings yet
- Online Sexual ExploitationDocument60 pagesOnline Sexual Exploitationmaria carmela pullantesNo ratings yet
- Online Sexual Exploitation of ChildrenDocument21 pagesOnline Sexual Exploitation of Childrenmaria carmela pullantesNo ratings yet
- Bianchi 2005 - 99 - AJIL - 242Document9 pagesBianchi 2005 - 99 - AJIL - 242Andrea NegriNo ratings yet
- Sample WaiverDocument1 pageSample WaiverEthel Dreda100% (1)
- Sca Hygiene Products Corporation Employees AssociaDocument2 pagesSca Hygiene Products Corporation Employees AssociaLeslie LernerNo ratings yet
- Identify The Choice That Best Completes The Statement or Answers The QuestionDocument13 pagesIdentify The Choice That Best Completes The Statement or Answers The QuestionAnne EstrellaNo ratings yet
- Facts:: Calacala v. Republic of The Philippines G.R. No. 154415. July 28, 2005. (MAG)Document2 pagesFacts:: Calacala v. Republic of The Philippines G.R. No. 154415. July 28, 2005. (MAG)Ann Marie100% (2)
- BL - ContractDocument15 pagesBL - ContractPrincessAngelaDeLeon0% (1)
- LAMP VS. SEC OF BUDGET ON PORK BARREL FUNDSDocument4 pagesLAMP VS. SEC OF BUDGET ON PORK BARREL FUNDSAnthony Rey BayhonNo ratings yet
- 09 Chapter3 PDFDocument28 pages09 Chapter3 PDFShakshi MehtaNo ratings yet
- Felipe vs. Atty. MacapagalDocument8 pagesFelipe vs. Atty. MacapagalMarga CastilloNo ratings yet
- SilverLake Intern-Job Application FormDocument6 pagesSilverLake Intern-Job Application FormBigBoiNo ratings yet
- Whitepaper - Quantfury Help CenterDocument3 pagesWhitepaper - Quantfury Help CenterProbertoecnNo ratings yet
- Independent Assignment Request and Maintenance AgreementDocument8 pagesIndependent Assignment Request and Maintenance Agreementhockeystack669No ratings yet
- Jurisdiction of MTC and RTC courtsDocument2 pagesJurisdiction of MTC and RTC courtsMark Anthony Ruiz DelmoNo ratings yet
- 2022 Global Legislative Predictions - IAPPDocument31 pages2022 Global Legislative Predictions - IAPPBiovisao OftaNo ratings yet
- Company and PartnershipDocument1 pageCompany and PartnershiprahulNo ratings yet
- Separation of PowersDocument23 pagesSeparation of PowersLubna Iftikhar 4506-FSL/LLB/F15No ratings yet
- Yanza, Case Digest Set Number 1Document20 pagesYanza, Case Digest Set Number 1ynnahNo ratings yet
- Vienna Conventionon Diplomatic RelationsDocument8 pagesVienna Conventionon Diplomatic Relationsswarnimpaudelv2.0No ratings yet
- National Visa Application3Document2 pagesNational Visa Application3david ifeNo ratings yet
- Local Media3850153745883480017Document6 pagesLocal Media3850153745883480017Romulo EguillosNo ratings yet
- Not No 3029 To 3032 Dated 30 11 2023Document2 pagesNot No 3029 To 3032 Dated 30 11 2023smedical8052No ratings yet
- Device Payment T C 122016Document4 pagesDevice Payment T C 122016Amy Steele100% (1)
- Police PhotoDocument205 pagesPolice PhotoCrissNo ratings yet
- All Contracts Are Agreement But All Agreement Are Not ContractsDocument5 pagesAll Contracts Are Agreement But All Agreement Are Not Contractsamritraz55% (11)
- 2018 Bar Exams QuestionsDocument62 pages2018 Bar Exams QuestionsDale ContarNo ratings yet
- Stocking George W Ed Romantic Motives Essays On Anthropologi PDFDocument296 pagesStocking George W Ed Romantic Motives Essays On Anthropologi PDFОльга ЖолудьNo ratings yet
- Mabo V Queensland (No 2) ("Mabo Case") (1992) HCA 23 (1992) 175 CLR 1 (3 June 1992)Document137 pagesMabo V Queensland (No 2) ("Mabo Case") (1992) HCA 23 (1992) 175 CLR 1 (3 June 1992)MikeJacksonNo ratings yet
- Promoting Public Order and SafetyDocument4 pagesPromoting Public Order and Safetymjpjore0% (1)
- Mijares DigestDocument3 pagesMijares DigestYerdXXNo ratings yet