Professional Documents
Culture Documents
CHP 3
Uploaded by
Daniyal Gaikwad0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views6 pagesOriginal Title
Chp3
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views6 pagesCHP 3
Uploaded by
Daniyal GaikwadCopyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 6
The Management spectrum
Effective software project management
focuses on the four P’s:
1) The People
2) The Product
3) The Process
4) The Project
The People
• The “people factor” is so important that the
Software Engineering institute has
developed a people management
capability maturity model (PM-CMM).
• If people factor is strong software
organization can easily undertake
increasingly comprehensive complex
applications.
The People
• The people involved in a S/W Project includes
1. Senior managers who defines the business issues
that often have significant influence on the project.
2. Project (technical) managers who must plan,
motivate, organize and control the practitioners who do
software work.
3. Practitioners who deliver the technical skills that are
necessary to engineer a product or application
4. Customers who specify the requirements for the S/W
to be engineered
5. End-users who interact with the S/W once it is
released for production use
The Product
• Before a project can be planned, product objectives should be
established, alternative solutions should be considered, and technical
and management constraints should be identified.
• Without this information, it is impossible to identify cost, risk, project
schedule.
• The s/W Developer and customer must meet to define product
objectives and scope.
• Objectives identifies the overall goals for the product (from the
customers’ s point of view) without considering how these goals are
achieved.
• Scope identifies the primary data, functions and behaviors and
bounding these characteristics in a quantitative manner.
• Once the product objectives and scope are understood, alternative
solutions are considered.
• The alternatives enable managers and practitioners to select a best
approach which suits to the delivery deadlines, budgetary restrictions,
personnel availability, technical interfaces and other factors
•
The Process
• A particular method of doing something is
generally involving number of steps or
operations.
• The process that deals with the technical and
management issues of S/W development is
called as S/W Process
• A S/W Process provides a framework from
which a comprehensive plan for S/W
development can be estalished
• Framework activities are populated with tasks,
milestones, work products, and quality
assurance points.
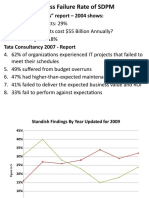
The Project
• Software projects are planned to manage
complexity.
• In 1998, industry data indicated that 26%
of S/w projects failed & 46% experienced
cost and schedule overruns.
• In order to avoid project failure, a S/w
project manager and the S/w engineers
who build the product must plan, monitor
and control the project well.
You might also like
- Week-11 Lecture 21-22Document40 pagesWeek-11 Lecture 21-22Rafia ShoukatNo ratings yet
- Software Project Success Rates Over TimeDocument18 pagesSoftware Project Success Rates Over TimeAKHIL JOSEPHNo ratings yet
- Unit3 MU Newpdf 2024 01 23 08 44 49Document51 pagesUnit3 MU Newpdf 2024 01 23 08 44 49nagabe8303No ratings yet
- SPM Unit1 Part-1Document25 pagesSPM Unit1 Part-1agrawaldeepti917No ratings yet
- SPPMDocument134 pagesSPPMdevils devilNo ratings yet
- Finisar's New Product Design and Development ProcessDocument39 pagesFinisar's New Product Design and Development Processpriyaa03No ratings yet
- Chap 2 Software Project ManagementDocument49 pagesChap 2 Software Project Managementmigad100% (1)
- Software - Engg Chap 05Document57 pagesSoftware - Engg Chap 052008 AvadhutNo ratings yet
- CP 5Document26 pagesCP 5Abhijit BhongNo ratings yet
- PM Triangle Balancing Performance, Time and CostDocument25 pagesPM Triangle Balancing Performance, Time and CostThiyaga RajanNo ratings yet
- Pme Unit-3Document47 pagesPme Unit-3Akriti SonkerNo ratings yet
- Software Engineering Project PlanningDocument53 pagesSoftware Engineering Project PlanningZacheous KasondaNo ratings yet
- PMLCDocument5 pagesPMLCiyappanaNo ratings yet
- Software Engg Chap 05Document22 pagesSoftware Engg Chap 05R JadhavNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document71 pagesUnit 1sudo apt install RanaNo ratings yet
- Adp 06Document55 pagesAdp 06alifaldindaNo ratings yet
- 1 - Project Management FrameworkDocument60 pages1 - Project Management Frameworklaxave8817No ratings yet
- Master of Business Administration Semester 2 Project Management Assignment Set-1Document32 pagesMaster of Business Administration Semester 2 Project Management Assignment Set-1vbolly12No ratings yet
- Multimedia Project Management - IntroDocument44 pagesMultimedia Project Management - IntroAllyia Syahida100% (1)
- Project Management Concepts ExplainedDocument21 pagesProject Management Concepts ExplainedDevika SanjayNo ratings yet
- CS042 Unit I Introduction and Software PlanningDocument25 pagesCS042 Unit I Introduction and Software Planningpawanipec2010No ratings yet
- SW Project ManagementDocument64 pagesSW Project ManagementVignesh DksNo ratings yet
- Project ManagementDocument74 pagesProject ManagementChrizel Breytenbach100% (2)
- Project Management Factors that Influence ResultsDocument8 pagesProject Management Factors that Influence ResultsJames DinoyNo ratings yet
- SDLCDocument18 pagesSDLCCHRISTINE KARENDINo ratings yet
- Software Project Management in 40 CharactersDocument9 pagesSoftware Project Management in 40 CharactersAnas AzeemNo ratings yet
- Mb0028 Set 02 VKGDocument12 pagesMb0028 Set 02 VKGAmbrishNo ratings yet
- CH 3Document19 pagesCH 3Rishabhraj SharmaNo ratings yet
- Type The Document SubtitleDocument10 pagesType The Document SubtitlecoolestpuneetNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Project ManagementDocument26 pagesIntroduction To Project ManagementMohammad ParioNo ratings yet
- Dwnload Full Project Management Process Technology and Practice 1st Edition Vaidyanathan Solutions Manual PDFDocument36 pagesDwnload Full Project Management Process Technology and Practice 1st Edition Vaidyanathan Solutions Manual PDFinsuliteskinch4wjca100% (11)
- Project Management Concepts ChapterDocument24 pagesProject Management Concepts ChapterJeri Agus RahadianNo ratings yet
- Project Management EssentialsDocument103 pagesProject Management EssentialsMagarsa BedasaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document57 pagesChapter 3Desala HabteNo ratings yet
- W5HH PrincipleDocument28 pagesW5HH PrincipleSumit Garg0% (1)
- Software Project ManagementDocument32 pagesSoftware Project ManagementdivyaNo ratings yet
- Principles of Construction Management: Lecture No. 2 - Overview of The Construction Industry ContDocument54 pagesPrinciples of Construction Management: Lecture No. 2 - Overview of The Construction Industry ContJesser SollerNo ratings yet
- SEN_Unit_4Document31 pagesSEN_Unit_4A KNo ratings yet
- SPM Lecture Notes UNIT IDocument22 pagesSPM Lecture Notes UNIT Ifarooq60% (5)
- Project Scope Management: MS-20 Lec6 DR Muhammad AbbasDocument71 pagesProject Scope Management: MS-20 Lec6 DR Muhammad AbbasSharjeel KhanNo ratings yet
- Mendoza, Mecaela Janine R. M4T1 - Essay QuestionsDocument3 pagesMendoza, Mecaela Janine R. M4T1 - Essay QuestionsMecaela Janine MENDOZANo ratings yet
- List and Explain The Ten Project Management Knowledge AreasDocument30 pagesList and Explain The Ten Project Management Knowledge AreasThuli MashininiNo ratings yet
- PM 333 Lecture 8 Project Integration ManagementDocument35 pagesPM 333 Lecture 8 Project Integration ManagementJesse TungarazaNo ratings yet
- PM Chapter 01 IntroductionDocument51 pagesPM Chapter 01 Introductionfahadneo100% (1)
- Chapter 04Document30 pagesChapter 04Fikreab LopisoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3Document32 pagesLecture 3NINGA gamingNo ratings yet
- Software Requirement Engineering Lecture - 2Document11 pagesSoftware Requirement Engineering Lecture - 2Anzala DarNo ratings yet
- CourseDocument18 pagesCourseCHRISTINE KARENDINo ratings yet
- Project Management Process Technology and Practice 1st Edition Vaidyanathan Solutions ManualDocument40 pagesProject Management Process Technology and Practice 1st Edition Vaidyanathan Solutions Manualrowenathuyzdwqr100% (24)
- Project Management Process Technology and Practice 1St Edition Vaidyanathan Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocument61 pagesProject Management Process Technology and Practice 1St Edition Vaidyanathan Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFpaulphelanjan100% (10)
- 569-The Project Life CycleDocument15 pages569-The Project Life CycleHusnain KhalidNo ratings yet
- 4 Stakeholder ManagementDocument45 pages4 Stakeholder Managementsetsuna99930% (1)
- Chapter Three part IDocument33 pagesChapter Three part IBizuneh getuNo ratings yet
- Unit 01 Software Management Practice & Software EconomicsDocument85 pagesUnit 01 Software Management Practice & Software EconomicsSajjan PaudelNo ratings yet
- Introduction Part CaeyDocument5 pagesIntroduction Part CaeyCaey ShahirNo ratings yet
- PROJECT PLANNING SOFTWARE GUIDEDocument79 pagesPROJECT PLANNING SOFTWARE GUIDEThuận AnhNo ratings yet
- Project Synopsis TanujDocument8 pagesProject Synopsis TanujAnshul SinghNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document5 pagesChapter 3Sharmila ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Engr. Ch. Jamil Ahmad: B.Sc. Civil Engg. Postgradip. Cpm. (Uk), Mba (Uet), PMPDocument60 pagesEngr. Ch. Jamil Ahmad: B.Sc. Civil Engg. Postgradip. Cpm. (Uk), Mba (Uet), PMPUmairNo ratings yet
- CN8001 PacketCraftingUsingScapy WilliamZerenehDocument0 pagesCN8001 PacketCraftingUsingScapy WilliamZerenehJosh Meier MartinNo ratings yet
- CATIA Piping TutorialDocument37 pagesCATIA Piping TutorialDSM CikarangNo ratings yet
- UML Sequence Diagram ExplainedDocument24 pagesUML Sequence Diagram ExplainedMuhammad Nauman AkramNo ratings yet
- 8086 MicroprocessorDocument24 pages8086 Microprocessorsamrat kumar100% (1)
- DACTS705 English PDFDocument21 pagesDACTS705 English PDFgiapy0000No ratings yet
- Social Security System Manila registrationDocument1 pageSocial Security System Manila registrationBJ SERRANONo ratings yet
- Entes CatalogueDocument154 pagesEntes CatalogueShvan NajeebNo ratings yet
- Qlik ViewDocument34 pagesQlik ViewAbhishekNo ratings yet
- Building 8 CO PDFDocument5 pagesBuilding 8 CO PDFDelmar GicaNo ratings yet
- IEEE Xplore - Enterprise Information Security Architecture A Review of Frameworks, Methodology, and Case StudiesDocument2 pagesIEEE Xplore - Enterprise Information Security Architecture A Review of Frameworks, Methodology, and Case StudiesHugo PagolaNo ratings yet
- BIOS update instructions for Satellite P50/P55/P55t modelsDocument5 pagesBIOS update instructions for Satellite P50/P55/P55t modelsJeNo ratings yet
- Explanation About Photo CollageDocument2 pagesExplanation About Photo CollagePham Duc HienNo ratings yet
- IT Grade-7-Teacher Guide-Last Edition-Confirmed Writers 2Document94 pagesIT Grade-7-Teacher Guide-Last Edition-Confirmed Writers 2biruk damtew100% (6)
- b0700bp CDocument90 pagesb0700bp Cyoucef hamzaNo ratings yet
- Restore Failed SQL Express 2005Document1 pageRestore Failed SQL Express 2005Andri van der DoelenNo ratings yet
- How To Submit To D2LDocument1 pageHow To Submit To D2LArtem GovorovNo ratings yet
- Harry Potter InsDocument8 pagesHarry Potter InsAlex ManchabajoyNo ratings yet
- Data Privacy GovernanceDocument22 pagesData Privacy GovernanceSimarNo ratings yet
- Lampiran SpesifikasiDocument7 pagesLampiran SpesifikasiLede HidrofarmNo ratings yet
- M61250EFPDocument50 pagesM61250EFPJesus SilvaNo ratings yet
- C-Arrays & Strings and FunctionsDocument33 pagesC-Arrays & Strings and FunctionsSambhaviNo ratings yet
- Ascendance VillivakkamDocument3 pagesAscendance Villivakkamsonaiya software solutionsNo ratings yet
- Five-Phase Induction Motor Drive-A Comprehensive RDocument17 pagesFive-Phase Induction Motor Drive-A Comprehensive RAnshuman MohantyNo ratings yet
- Firstnaukri End To End Campus Hiring Assistance - LT Technology ServicesDocument30 pagesFirstnaukri End To End Campus Hiring Assistance - LT Technology ServicestestmailjobNo ratings yet
- "Flexible Bench": S.P.M Polytechnic Kumathe, Solapur 2018-2019Document3 pages"Flexible Bench": S.P.M Polytechnic Kumathe, Solapur 2018-2019Abhijeet DhavaleNo ratings yet
- L32W981 32" LCD-TV: DTV DVB-TDocument1 pageL32W981 32" LCD-TV: DTV DVB-TirfanNo ratings yet
- CISSP Review QuestionsDocument87 pagesCISSP Review QuestionsGsk SkNo ratings yet
- 722k UserGuideDocument165 pages722k UserGuideSrikanth MarepalliNo ratings yet
- Step by Step Guide: How To Update Institute'S Profile in Navttc-PmsDocument15 pagesStep by Step Guide: How To Update Institute'S Profile in Navttc-PmsMohammad AtherNo ratings yet
- Brochure Cold Water PressureDocument4 pagesBrochure Cold Water PressuresitaNo ratings yet