Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Data Ware House and Its Purposes
Uploaded by
Nimi KhanOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Data Ware House and Its Purposes
Uploaded by
Nimi KhanCopyright:
Available Formats
DATA WARE
HOUSE AND ITS
PURPOSES
BSCS7TH
Definition
■ a database created by combining data that is gathered through
various sources that can be of different types and formats (e.g. text,
sql, xml etc).
■ a nutshell Data warehouse is a process of collecting data ,
transforming it, loading into single database and then using a BI
(Business Intelligence) tool to answer your analytical queries and
prediction of any further questions that may arise are helpful to your
domain or business.
History of Datawarehouse
■ The Datawarehouse benefits users to understand and enhance their organization's
performance. The need to warehouse data evolved as computer systems became more
complex and needed to handle increasing amounts of Information
■ 1960- Dartmouth and General Mills in a joint research project, develop the terms
dimensions and facts.
■ 1970- A Nielsen and IRI introduces dimensional data marts for retail sales.
■ 1983- Tera Data Corporation introduces a database management system which is
specifically designed for decision support
■ Data warehousing started in the late 1980s when IBM worker Paul Murphy and Barry Devlin
developed the Business Data Warehouse.
■ However, the real concept was given by Inmon Bill. He was considered as a father of data
warehouse. He had written about a variety of topics for building, usage, and maintenance
of the warehouse & the Corporate Information Factory
How Datawarehouse works?
■ A Data Warehouse works as a central repository where information
arrives from one or more data sources. Data flows into a data
warehouse from the transactional system and other relational
databases.
■ Data may be:
■ Structured
■ Semi-structured
■ Unstructured data
Types of Data Warehouse
■ Three main types of Data Warehouses are:
1. Enterprise Data Warehouse:
Enterprise Data Warehouse is a centralized warehouse. It provides decision support service across the
enterprise. It offers a unified approach for organizing and representing data. It also provide the ability to
classify data according to the subject and give access according to those divisions.
operational data store
Operational Data Store, which is also called ODS, are nothing but data store required when neither Data
warehouse nor OLTP systems support organizations reporting needs. In ODS, Data warehouse is
refreshed in real time. Hence, it is widely preferred for routine activities like storing records of the
Employees.
Data Mart
A data mart is a subset of the data warehouse. It specially designed for a particular line of business,
such as sales, finance, sales or finance. In an independent data mart, data can collect directly from
sources.
General stages of Data
Warehouse
■ Offline operational database
In this stage, data is just copied from an operational system to another server. In this way, loading,
processing, and reporting of the copied data do not impact the operational system's performance.
■ Offline data ware house
Data in the Datawarehouse is regularly updated from the Operational Database. The data in
Datawarehouse is mapped and transformed to meet the Datawarehouse objectives.
■ Real time data ware house
Data warehouses are updated whenever any transaction takes place in operational database. For
example, Airline or railway booking system.
■ Integrated data ware house
Data Warehouses are updated continuously when the operational system performs a transaction.
The Datawarehouse then generates transactions which are passed back to the operational system.
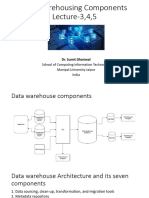
Components of Data
warehouse
■ Four components of Data Warehouses are:
■ Load manager: Load manager is also called the front component. It performs with all the operations
associated with the extraction and load of data into the warehouse. These operations include
transformations to prepare the data for entering into the Data warehouse.
■ Warehouse Manager: Warehouse manager performs operations associated with the management
of the data in the warehouse. It performs operations like analysis of data to ensure consistency,
creation of indexes and views, generation of denormalization and aggregations, transformation and
merging of source data and archiving and baking-up data.
■ Query Manager: Query manager is also known as backend component. It performs all the operation
operations related to the management of user queries. The operations of this Data warehouse
components are direct queries to the appropriate tables for scheduling the execution of queries.
■ End-user access tools:
■ This is categorized into five different groups like 1. Data Reporting 2. Query Tools 3. Application
development tools 4. EIS tools, 5. OLAP tools and data mining tools.
Who needs Data warehouse?
■ Data warehouse is needed for all types of users like:
■ Decision makers who rely on mass amount of data
■ Users who use customized, complex processes to obtain information from multiple
data sources.
■ It is also used by the people who want simple technology to access the data
■ It also essential for those people who want a systematic approach for making
decisions.
■ If the user wants fast performance on a huge amount of data which is a necessity
for reports, grids or charts, then Data warehouse proves useful.
■ Data warehouse is a first step If you want to discover 'hidden patterns' of data-
flows and groupings.
What Is a Data Warehouse Used For?
■ Here, are most common sectors where Data warehouse is used:
■ Airline
■ Banking
■ Healthcare
■ Public sector
■ Investment and insurance sector
■ Retain chain
■ Telecommunication
■ Hospitality industry
Steps to Implement Data
Warehouse
■ The best way to address the business risk associated with a Datawarehouse
implementation is to employ a three-prong strategy as below
■ Enterprise strategy: Here we identify technical including current
architecture and tools. We also identify facts, dimensions, and attributes.
Data mapping and transformation is also passed.
■ Phased delivery: Datawarehouse implementation should be phased based
on subject areas. Related business entities like booking and billing should
be first implemented and then integrated with each other.
■ Iterative Prototyping: Rather than a big bang approach to
implementation, the Datawarehouse should be developed and tested
iteratively.
The Future of Data
Warehousing
■ Change in Regulatory constrains may limit the ability to combine
source of disparate data. These disparate sources may include
unstructured data which is difficult to store.
■ As the size of the databases grows, the estimates of what constitutes
a very large database continue to grow. It is complex to build and run
data warehouse systems which are always increasing in size. The
hardware and software resources are available today do not allow to
keep a large amount of data online.
■ Multimedia data cannot be easily manipulated as text data,
whereas textual information can be retrieved by the relational
software available today. This could be a research subject
Data ware house Tools
■ MarkLogic:
MarkLogic is useful data warehousing solution that makes data integration easier and faster
using an array of enterprise features. This tool helps to perform very complex search
operations. It can query different types of data like documents, relationships, and metadata
■ Oracle:
Oracle is the industry-leading database. It offers a wide range of choice of data warehouse
solutions for both on-premises and in the cloud. It helps to optimize customer experiences
by increasing operational efficiency.
■ 3. Amazon RedShift:
Amazon Redshift is Data warehouse tool. It is a simple and cost-effective tool to analyze all
types of data using standard SQL and existing BI tools. It also allows running complex
queries against petabytes of structured data, using the technique of query optimization.
You might also like
- Data Warehousing & Data Mining: Unit-1Document24 pagesData Warehousing & Data Mining: Unit-1Harkeet BajajNo ratings yet
- Data WarehousingDocument111 pagesData WarehousingSaikumar PoliNo ratings yet
- Etl Testing Documentation PDFDocument22 pagesEtl Testing Documentation PDFPradeep SatwarkarNo ratings yet
- DWDM Notes 5 UnitsDocument110 pagesDWDM Notes 5 UnitsDrPrabu MNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Data Warehouse: Unit I: Data WarehousingDocument110 pagesIntroduction To Data Warehouse: Unit I: Data WarehousingRONYROY222No ratings yet
- Data Warehousing & Data Mining-A ViewDocument11 pagesData Warehousing & Data Mining-A Viewapi-19799369No ratings yet
- Data Mining Warehousing I & IIDocument7 pagesData Mining Warehousing I & IItanvi kamaniNo ratings yet
- Data Warehousing and Data MiningDocument48 pagesData Warehousing and Data MiningVijay Anand100% (1)
- INFORMATION MANAGEMENT Unit 3 NEWDocument61 pagesINFORMATION MANAGEMENT Unit 3 NEWThirumal Azhagan100% (1)
- Data Warehouse and Data Mining NotesDocument31 pagesData Warehouse and Data Mining NotesSamrat SaxenaNo ratings yet
- Data Warehouse Material ConceptsDocument28 pagesData Warehouse Material Conceptsapi-26304852100% (2)
- THE STEP BY STEP GUIDE FOR SUCCESSFUL IMPLEMENTATION OF DATA LAKE-LAKEHOUSE-DATA WAREHOUSE: "THE STEP BY STEP GUIDE FOR SUCCESSFUL IMPLEMENTATION OF DATA LAKE-LAKEHOUSE-DATA WAREHOUSE"From EverandTHE STEP BY STEP GUIDE FOR SUCCESSFUL IMPLEMENTATION OF DATA LAKE-LAKEHOUSE-DATA WAREHOUSE: "THE STEP BY STEP GUIDE FOR SUCCESSFUL IMPLEMENTATION OF DATA LAKE-LAKEHOUSE-DATA WAREHOUSE"Rating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- CS2032 Data Warehousing and Data Mining PPT Unit IDocument88 pagesCS2032 Data Warehousing and Data Mining PPT Unit IvdsrihariNo ratings yet
- History of DatawarehouseDocument17 pagesHistory of DatawarehouseMr Sathesh Abraham Leo CSENo ratings yet
- SQL Cheat Sheet - 1557131235Document12 pagesSQL Cheat Sheet - 1557131235RahulNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document12 pagesLecture 1mohammed.riad.bi.2020No ratings yet
- MT Coverage BUMA 30043Document23 pagesMT Coverage BUMA 30043nesty policyNo ratings yet
- Unit II Lecture NotesDocument26 pagesUnit II Lecture NotesRussian CarxgameNo ratings yet
- Data WarehousingDocument35 pagesData WarehousingRoronoa ZoldyckNo ratings yet
- Unit IDocument33 pagesUnit IAkash RavichandranNo ratings yet
- Data Warehousing Chapter 1Document8 pagesData Warehousing Chapter 1Luntian Amour JustoNo ratings yet
- Data Warehouse-Ccs341 MaterialDocument58 pagesData Warehouse-Ccs341 Materialragavaharish463No ratings yet
- Data WarehouseDocument5 pagesData WarehouseVinetha J MNo ratings yet
- R16 4-2 DataMining Notes UNIT-IDocument31 pagesR16 4-2 DataMining Notes UNIT-IMark KiraNo ratings yet
- AD - Data Warehousing PRESENTATIONDocument19 pagesAD - Data Warehousing PRESENTATIONKingsleyphilanimafayo JereNo ratings yet
- Data Warehouse ConceptsDocument18 pagesData Warehouse ConceptsShaina Marie RefranNo ratings yet
- Data Ware Housing1Document18 pagesData Ware Housing1Toaster97No ratings yet
- Unit 1 - Data Mining - WWW - Rgpvnotes.in PDFDocument13 pagesUnit 1 - Data Mining - WWW - Rgpvnotes.in PDFprince keshriNo ratings yet
- Data WarehouseDocument74 pagesData WarehouseDev kartik AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Data Warehousing SlidesDocument76 pagesData Warehousing SlidesFaridNo ratings yet
- What Is Data Warehouse?: DefinationDocument17 pagesWhat Is Data Warehouse?: Definationapi-26830587No ratings yet
- BI Unit-II DWHDocument131 pagesBI Unit-II DWHSharon SusmithaNo ratings yet
- Pharma Batch: Data WarehousingDocument32 pagesPharma Batch: Data WarehousingrmeralaNo ratings yet
- Data Warehouse ConceptsDocument53 pagesData Warehouse ConceptsVikram Singh TomarNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document22 pagesUnit 1MananNo ratings yet
- Data Warehouse NotesDocument21 pagesData Warehouse NotesMILINDNo ratings yet
- UNITyssu 1 LTDocument12 pagesUNITyssu 1 LTSahil KumarNo ratings yet
- Introduction To DWDocument28 pagesIntroduction To DWsomoraycNo ratings yet
- Business AnalyticsDocument27 pagesBusiness Analyticssnehavenkatt27No ratings yet
- WarehousingDocument15 pagesWarehousingmanoramanNo ratings yet
- DW Unit1Document26 pagesDW Unit1SECOND YEAR ITNo ratings yet
- Data MiningDocument65 pagesData MiningAshutosh SinghNo ratings yet
- Untitled DocumentDocument2 pagesUntitled DocumentRovelyn MoralesNo ratings yet
- Data MiningDocument142 pagesData Miningmr2b9jfhy4No ratings yet
- DATA Ware House & Mining NOTESDocument31 pagesDATA Ware House & Mining NOTESABHISHEK KUMAR SAH100% (1)
- Unit - 1 Introduction To Data WarehousingDocument57 pagesUnit - 1 Introduction To Data WarehousingRuchiraNo ratings yet
- Paper Presentation: Data Ware Housing AND Data MiningDocument10 pagesPaper Presentation: Data Ware Housing AND Data Miningapi-19799369No ratings yet
- Advanced Database PresentationDocument11 pagesAdvanced Database PresentationKingsleyphilanimafayo JereNo ratings yet
- 2 Data Warehousing Components L3 L4 L5Document26 pages2 Data Warehousing Components L3 L4 L5MANOJ KUMAWATNo ratings yet
- Business Intelligence Introduced by HowardDocument59 pagesBusiness Intelligence Introduced by HowardkuldiipsNo ratings yet
- Difference Between Data Warehousing and Data Mining: Data Warehouse Architecture Three-Tier Data Warehouse ArchitectureDocument10 pagesDifference Between Data Warehousing and Data Mining: Data Warehouse Architecture Three-Tier Data Warehouse ArchitecturepriyaNo ratings yet
- DMW p1 MergedDocument316 pagesDMW p1 MergedGaurav bansodeNo ratings yet
- Data Mining & HousingDocument13 pagesData Mining & Housingpankaj2908No ratings yet
- Data Lake: Strategies and Best Practices for Storing, Managing, and Analyzing Big DataFrom EverandData Lake: Strategies and Best Practices for Storing, Managing, and Analyzing Big DataNo ratings yet
- Data Mesh: Building Scalable, Resilient, and Decentralized Data Infrastructure for the Enterprise. Part 2From EverandData Mesh: Building Scalable, Resilient, and Decentralized Data Infrastructure for the Enterprise. Part 2No ratings yet