Professional Documents
Culture Documents
2 Data Warehousing Components L3 L4 L5
Uploaded by
MANOJ KUMAWAT0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views26 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views26 pages2 Data Warehousing Components L3 L4 L5
Uploaded by
MANOJ KUMAWATCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 26
Data warehousing Components
Lecture-3,4,5
Dr. Sumit Dhariwal
School of Computing Information Technology
Manipal University Jaipur
India
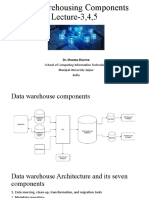
Data warehouse components
Data warehouse Architecture and its seven
components
1. Data sourcing, clean-up, transformation, and migration tools
2. Metadata repository
3. Warehouse/database technology
4. Data marts
5. Application & tools
6. Data warehouse administration and management
7. Information delivery system
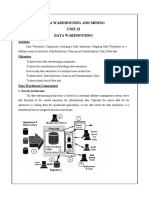
Data warehouse is an environment, not a product which is based on
relational database management system that functions as the central
repository for informational data. The central repository information is
surrounded by number of key components designed to make the
environment is functional, manageable and accessible.
1. Operational and external data (Data sourcing,
clean-up, transformation, and migration tools)
The data source for the data
warehouse is coming from
operational applications. The
data entered into the data
warehouse transformed into an
integrated structure and format.
The transformation process
involves conversion,
summarization, filtering, and
condensation. The data
warehouse must be capable of
holding and managing large
volumes of data as well as
different structures of data
structures over time.
2. Metadata repository
Conti…
• Metadata repository is an integral part of a data warehouse system. It has the
following metadata −
• Definition of data warehouse − It includes the description of structure of data
warehouse. The description is defined by schema, view, hierarchies, derived data
definitions, and data mart locations and contents.
• Business metadata − It contains has the data ownership information, business
definition, and changing policies.
• Operational Metadata − It includes currency of data and data lineage. Currency
of data means whether the data is active, archived, or purged. Lineage of data
means the history of data migrated and transformation applied on it.
• Data for mapping from operational environment to data warehouse − It
includes the source databases and their contents, data extraction, data partition
cleaning, transformation rules, data refresh and purging rules.
• Algorithms for summarization − It includes dimension algorithms, data on
granularity, aggregation, summarizing, etc.
3. Data warehouse DBMS
It is used for maintaining, managing, and using the data
warehouse. It is classified into two:
1. Technical Metadata: It contains information about
data warehouse data used by warehouse designers,
administrators to carry out development and
management tasks. It includes,
• Info about data stores
• Transformation descriptions.
• That is mapping methods from operational DB to
warehouse DB
• Warehouse Object and data structure definitions for
target data.
• The rules used to perform clean up, and data
enhancement.
• Data mapping operations.
• Access authorization, backup history, archive history,
info delivery history, data acquisition history, data
access etc.
Conti…
2. Business Metadata: It contains info that gives info
stored in the data warehouse to users. It includes.
• Subject areas, and info object type including
queries, reports, images, video, audio clips etc.
• Internet home pages.
• Info related to info delivery system.
• Data warehouse operational info such as
ownerships, audit trails etc.,
• Meta data helps the users to understand the
content and find the data.
• Meta data are stored in separate data stores
which is known as informational directory or Meta
data repository which helps to integrate, maintain
and view the contents of the data warehouse.
Conti…
The following lists the characteristics of info directory/ Metadata:
• It is the gateway to the data warehouse environment.
• It supports easy distribution and replication of content for high performance and
availability.
• It should be searchable by business-oriented keywords.
• It should act as a launch platform for end users to access data and analysis tools
It should support the sharing of info.
• It should support scheduling options for requests.
• IT should support and provide an interface to other applications.
• It should support end-user monitoring of the status of the data warehouse
environment.
• g lists the characteristics of info directory/ Metadata
4. Data marts
A Data Mart is focused on a single functional
area of an organization and contains a subset of
data stored in a Data Warehouse. A Data Mart is
a condensed version of a Data Warehouse and is
designed for use by a specific department, unit,
or set of users in an organization. E.g.,
Marketing, Sales, HR, or finance. It is often
controlled by a single department in an
organization. Extremely urgent user
requirement.
• The absence of a budget for a full-scale data
warehouse strategy.
• The decentralization of business needs.
• The attraction of easy to use tools and mind sized
project
Why do we need Data Mart?
• Data Mart helps to enhance user’s response time due to reduction in volume of
data
• It provides easy access to frequently requested data.
• Data mart are simpler to implement when compared to corporate
Datawarehouse. At the same time, the cost of implementing Data Mart is
certainly lower compared with implementing a full data warehouse.
• Compared to Data Warehouse, a datamart is agile. In case of change in model,
datamart can be built quicker due to a smaller size.
• A Datamart is defined by a single Subject Matter Expert. On the contrary data
warehouse is defined by interdisciplinary SME from a variety of domains.
Hence, Data mart is more open to change compared to Datawarehouse.
• Data is partitioned and allows very granular access control privileges.
• Data can be segmented and stored on different hardware/software platforms.
Types of Data Mart
• There are three main types of data mart:
1.Dependent: Dependent data marts are created by drawing data
directly from operational, external or both sources.
2.Independent: Independent data mart is created without the use of
a central data warehouse.
3.Hybrid: This type of data marts can take data from data
warehouses or operational systems.
1. Dependent Data Mart
• A dependent data mart allows
sourcing organization’s data from a
single Data Warehouse. It is one of
the data mart example which offers
the benefit of centralization. If you
need to develop one or more
physical data marts, then you need
to configure them as dependent
data marts.
2. Independent Data Mart
• An independent data mart is created
without the use of a central Data
warehouse. This kind of Data Mart is an
ideal option for smaller groups within
an organization.
• An independent data mart has neither a
relationship with the enterprise data
warehouse nor with any other data
mart. In an Independent data mart, the
data is input separately, and its
analyses are also performed
autonomously.
3.Hybrid Data Mart
• A hybrid data mart combines input
from sources apart from the Data
warehouse. This could be helpful
when you want ad-hoc integration,
like after a new group or product is
added to the organization.
• It is the best data mart example
suited for multiple database
environments and a fast
implementation turnaround for any
organization. It also requires the least
data cleansing effort. Hybrid Data
mart also supports large storage
Steps in Implementing a Datamart
5. Application & Tools
• Data mining queries are useful for many purposes. You can:
• Apply the model to new data, to make single or multiple predictions.
You can provide input values as parameters, or in a batch.
• Get a statistical summary of the data used for training.
• Extract patterns and rules, or generate a profile of the typical case
representing a pattern in the model.
• Extract regression formulas and other calculations that explain
patterns.
• Get the cases that fit a particular pattern.
• Retrieve details about individual cases used in the model, including
data not used in the analysis.
• Retrain a model by adding new data, or performing cross-prediction.
Conti…
Its purpose is to provide info to business users for decision making. There are
five categories:
• Data query and reporting tools.
• Application development tools.
• Executive info system tools (EIS).
• OLAP tools.
• Data mining tools Query and reporting tools are used to generate query
and report.
• There are two types of reporting tools. They are:
• Production reporting tool used to generate regular operational reports Desktop
report writer are inexpensive desktop tools designed for end users.
Conti…
• Managed Query tools: used to generate SQL query. It uses Meta layer software in
between users and databases which offers a point-and-click creation of SQL
statement. This tool is a preferred choice of users to perform segment
identification, demographic analysis, territory management and preparation of
customer mailing lists etc.
• Application development tools: This is a graphical data access environment
which integrates OLAP tools with data warehouse and can be used to access all
db systems.
• OLAP Tools: are used to analyze the data in multi dimensional and complex views.
To enable multidimensional properties it uses MDDB and MRDB where MDDB
refers multi dimensional data base and MRDB refers multi relational data bases.
• Data mining tools: are used to discover knowledge from the data warehouse data
also can be used for data visualization and data correction purposes.
6. Data warehouse administration and
management
The management of data warehouse include…
• Security and priority management.
• Monitoring updates from multiple sources.
• Data quality checks Managing and updating meta data Auditing
and reporting data warehouse usage and status Purging data
Replicating, sub setting and distributing data Backup and
recovery Data warehouse storage management which includes
capacity planning, hierarchical storage management and purging of
aged data etc.
7. Information delivery system
• It is used to enable the process of subscribing for data warehouse
info.
• Delivery to one or more destinations according to the specified
scheduling algorithm
Data extraction, clean up, transformation and
migration
• A proper attention must be paid to data extraction which represents a
success factor for a data warehouse architecture. When
implementing data warehouse several the following selection criteria
that affect the ability to transform, consolidate, integrate and repair
the data should be considered:
Timeliness of data delivery to the warehouse.
• The tool must have the ability to identify the particular data and that can be read by
conversion tool.
• The tool must support flat files, indexed files since corporate data is still in this type.
• The tool must have the capability to merge data from multiple data stores.
• The tool should have specification interface to indicate the data to be extracted
• The tool should have the ability to read data from data dictionary.
• The code generated by the tool should be completely maintainable.
• The tool should permit the user to extract the required data.
• The tool must have the facility to perform data type and character set translation.
• The tool must have the capability to create summarization, aggregation and derivation of
records.
• The data warehouse database system must be able to perform loading data directly from
these tools
Benefits of data warehousing
• Data warehouse usage includes,
– Locating the right info
– Presentation of info
– Testing of hypothesis
– Discovery of info
– Sharing the analysis
The benefits can be classified into two:
Tangible benefits (quantified / measureable):It includes, – Improvement in
product inventory
• – Decrement in production cost
• – Improvement in selection of target markets
• – Enhancement in asset and liability management.
Intangible benefits (not easy to quantified): It includes,
• – Improvement in productivity by keeping all data in single location and
eliminating rekeying of data
• – Reduced redundant processing
• – Enhanced customer relation
You might also like
- Data Warehousing Components - L3 - L4 - L5Document26 pagesData Warehousing Components - L3 - L4 - L5Deepika GargNo ratings yet
- Data Warehouse and Data Mining NotesDocument31 pagesData Warehouse and Data Mining NotesSamrat SaxenaNo ratings yet
- CS2032 Data Warehousing and Data Mining PPT Unit IDocument88 pagesCS2032 Data Warehousing and Data Mining PPT Unit IvdsrihariNo ratings yet
- Knowledge Discovery in Databases: Data Warehousing and Business AnalysisDocument55 pagesKnowledge Discovery in Databases: Data Warehousing and Business AnalysisSANGAVI NNo ratings yet
- DWH Week 03Document17 pagesDWH Week 03Sibtain TahirNo ratings yet
- Data Warehouse ArchituctureDocument5 pagesData Warehouse ArchituctureJanmejay PantNo ratings yet
- Data Mining and Warehousing - L1 & L2Document30 pagesData Mining and Warehousing - L1 & L2Deepika GargNo ratings yet
- Unit II Lecture NotesDocument26 pagesUnit II Lecture NotesRussian CarxgameNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document44 pagesChapter 2Bikila SeketaNo ratings yet
- DW ArchDocument9 pagesDW Archsharon sylvia .sNo ratings yet
- Data Mining & HousingDocument13 pagesData Mining & Housingpankaj2908No ratings yet
- 1a RaviDocument37 pages1a RaviKrishna ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Data Warehouse NotesDocument21 pagesData Warehouse NotesMILINDNo ratings yet
- History of DatawarehouseDocument17 pagesHistory of DatawarehouseMr Sathesh Abraham Leo CSENo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Data Warehousing and MiningDocument19 pagesUnit 1 Data Warehousing and MiningLindaNo ratings yet
- Unit No: 02 Architecture/Infrastructure & Data Representation of DWHDocument166 pagesUnit No: 02 Architecture/Infrastructure & Data Representation of DWHRavi SistaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Data Warehouse: Unit I: Data WarehousingDocument110 pagesIntroduction To Data Warehouse: Unit I: Data WarehousingRONYROY222No ratings yet
- Module1 DMDocument37 pagesModule1 DM1DT19CS032 Chethana T SNo ratings yet
- DWDM Notes 5 UnitsDocument110 pagesDWDM Notes 5 UnitsDrPrabu MNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document22 pagesUnit 1MananNo ratings yet
- SQL Cheat Sheet - 1557131235Document12 pagesSQL Cheat Sheet - 1557131235RahulNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Data Warehouse NewDocument45 pagesUnit 2 Data Warehouse NewSUMAN SHEKHARNo ratings yet
- Data WarehousingDocument111 pagesData WarehousingSaikumar PoliNo ratings yet
- Data Warehouse ComponentsDocument18 pagesData Warehouse ComponentsMaja Kostic Ex SimicNo ratings yet
- DWH Fundamentals (Training Material)Document21 pagesDWH Fundamentals (Training Material)svdonthaNo ratings yet
- 12 01 09 10 32 12 1287 Sindhujam PDFDocument23 pages12 01 09 10 32 12 1287 Sindhujam PDFPrasad DhanikondaNo ratings yet
- UNIT-1 (RIT-062) : Data WarehousingDocument34 pagesUNIT-1 (RIT-062) : Data WarehousingNikhil GuptaNo ratings yet
- Unit - 1 Introduction To Data WarehousingDocument57 pagesUnit - 1 Introduction To Data WarehousingRuchiraNo ratings yet
- Data Warehousing AssignmentDocument9 pagesData Warehousing AssignmentRushil Nagwan100% (2)
- Data WarehouseDocument109 pagesData WarehouseAbhishek UpadhyayNo ratings yet
- Olap and OltapDocument14 pagesOlap and OltapVivek SinghNo ratings yet
- Data Warehouse Week 1Document78 pagesData Warehouse Week 1bsit fall20No ratings yet
- Need of Two Types of Data: InformationDocument7 pagesNeed of Two Types of Data: InformationPranav SharmaNo ratings yet
- DATA Ware House & Mining NOTESDocument31 pagesDATA Ware House & Mining NOTESABHISHEK KUMAR SAH100% (1)
- CS2032 Unit I NotesDocument23 pagesCS2032 Unit I NotesRaj KumarNo ratings yet
- Data Warehouse - FinalDocument28 pagesData Warehouse - Finallatikaverma93No ratings yet
- Paper Presentation: Data Ware Housing AND Data MiningDocument10 pagesPaper Presentation: Data Ware Housing AND Data Miningapi-19799369No ratings yet
- DM - MOD - 2 Part - IDocument19 pagesDM - MOD - 2 Part - IsandrarajuofficialNo ratings yet
- What Is A Data Warehouse?Document48 pagesWhat Is A Data Warehouse?Kishori PatilNo ratings yet
- BAunit-2 NotesDocument31 pagesBAunit-2 NotesDimpy JindalNo ratings yet
- Data WarehouseDocument5 pagesData WarehouseVinetha J MNo ratings yet
- Data Warehousing and Data MiningDocument48 pagesData Warehousing and Data MiningVijay Anand100% (1)
- Data Warehouse Definition: - Users and System OrientationDocument6 pagesData Warehouse Definition: - Users and System OrientationAminaNo ratings yet
- Data Ware Housing1Document18 pagesData Ware Housing1Toaster97No ratings yet
- Data Warehousing FundamentalsDocument108 pagesData Warehousing FundamentalsTea CoffeeNo ratings yet
- Unit IDocument33 pagesUnit IAkash RavichandranNo ratings yet
- BDA Unit 2 B.techDocument9 pagesBDA Unit 2 B.techSakshi SinghNo ratings yet
- DMDW RefDocument26 pagesDMDW RefShrimohan TripathiNo ratings yet
- What Is Data Warehouse?: DefinationDocument17 pagesWhat Is Data Warehouse?: Definationapi-26830587No ratings yet
- Introduction To Data MiningDocument29 pagesIntroduction To Data MiningBulmi HilmeNo ratings yet
- CDM Class4Document4 pagesCDM Class4AIEMP EXAMCELLNo ratings yet
- 5-7-2010 Components of A Data Warehouse: Overall ArchitectureDocument4 pages5-7-2010 Components of A Data Warehouse: Overall ArchitectureRamakrishnan Harihara VenkatasubramaniaNo ratings yet
- Data MiningDocument65 pagesData MiningAshutosh SinghNo ratings yet
- Unit - I Data Extraction, Cleanup, and Transformation ToolsDocument10 pagesUnit - I Data Extraction, Cleanup, and Transformation ToolsKalaivani DNo ratings yet
- Data WarehousingDocument16 pagesData WarehousingRaman SinghNo ratings yet
- BMIS Chapter 4 SCMSBDocument35 pagesBMIS Chapter 4 SCMSBNainika ReddyNo ratings yet
- Data Extraction Cleanup and Transformation ToolsDocument10 pagesData Extraction Cleanup and Transformation Toolssethu sacoe100% (2)
- Data Mesh: Building Scalable, Resilient, and Decentralized Data Infrastructure for the Enterprise. Part 2From EverandData Mesh: Building Scalable, Resilient, and Decentralized Data Infrastructure for the Enterprise. Part 2No ratings yet
- 3 Business Analysis in Data Mining L6 7 8-9-10Document39 pages3 Business Analysis in Data Mining L6 7 8-9-10MANOJ KUMAWATNo ratings yet
- MTE 1 SyllabusDocument3 pagesMTE 1 SyllabusMANOJ KUMAWATNo ratings yet
- CsaDocument8 pagesCsaMANOJ KUMAWATNo ratings yet
- Course Handout Engineering Mathematics-III - MA2101 (Aug-Dec 2021) Online ClassesDocument8 pagesCourse Handout Engineering Mathematics-III - MA2101 (Aug-Dec 2021) Online ClassesMANOJ KUMAWATNo ratings yet
- Rishab ModiDocument4 pagesRishab ModiMANOJ KUMAWATNo ratings yet
- Print PC - PC Builder - Star TechDocument1 pagePrint PC - PC Builder - Star TechTania HuqNo ratings yet
- LVM RecoveryDocument11 pagesLVM RecoverySiddu ReddyNo ratings yet
- Compiler Design - Theory Tools and Examples PDFDocument320 pagesCompiler Design - Theory Tools and Examples PDFrubaNo ratings yet
- All Cloud InternshipsDocument6 pagesAll Cloud InternshipsManish KumarNo ratings yet
- Exam Away: Latest Exam Guide & Learning MaterialsDocument6 pagesExam Away: Latest Exam Guide & Learning MaterialsHieu TranNo ratings yet
- Important ARM LTD Application Notes For TI Hercules ARM Safety MCUsDocument4 pagesImportant ARM LTD Application Notes For TI Hercules ARM Safety MCUsanu_guoptaNo ratings yet
- CSE 220 - Intro To JavaDocument36 pagesCSE 220 - Intro To Javasayedul abrarNo ratings yet
- Responsibilities:: Responsibilities Manual With MS-OfficeDocument3 pagesResponsibilities:: Responsibilities Manual With MS-OfficeKrishna GottipatiNo ratings yet
- LAS EZ User ManualDocument76 pagesLAS EZ User ManualBruno MeloNo ratings yet
- Scada/Ems Systems - Hierarchy &: by AGMDocument38 pagesScada/Ems Systems - Hierarchy &: by AGMLD&C ULDCNo ratings yet
- IIT SyllabusDocument20 pagesIIT Syllabusritesh_necNo ratings yet
- 2 Online Complaint Registration and Management System in Mobile ApplicationDocument4 pages2 Online Complaint Registration and Management System in Mobile ApplicationKeerthi Vasan LNo ratings yet
- Tkinter Tutorial For BeginnersDocument23 pagesTkinter Tutorial For BeginnersA Walí DexentNo ratings yet
- Deploy and Update Windows 10Document739 pagesDeploy and Update Windows 10fama beyeNo ratings yet
- 17BCE10018 Digital PortfolioDocument14 pages17BCE10018 Digital PortfolioYAYADY S 18BCY10118No ratings yet
- Simple Synchronization With DropboxDocument13 pagesSimple Synchronization With DropboxEvelyn AquizeNo ratings yet
- Computer Networking: A Top-Down Approach, 8 Edition: Table of Contents Chapter 1 Computer Networks and The InternetDocument6 pagesComputer Networking: A Top-Down Approach, 8 Edition: Table of Contents Chapter 1 Computer Networks and The Internetvignesh sivaNo ratings yet
- AVB-Manager User-Manual v1 2Document60 pagesAVB-Manager User-Manual v1 2daniel.mentelNo ratings yet
- Multimedia Systems Lab: PracticalDocument3 pagesMultimedia Systems Lab: PracticalDivya RajeshwarNo ratings yet
- ES - 2 Marks Questions-1Document17 pagesES - 2 Marks Questions-1DurgadeviNo ratings yet
- .Archivetempen US - LangDocument109 pages.Archivetempen US - LangLady LaraNo ratings yet
- Application Development Using FlutterDocument5 pagesApplication Development Using FlutterDee Pan KarNo ratings yet
- Blockchain Stackfor First Party DMPV 1Document88 pagesBlockchain Stackfor First Party DMPV 1suhasNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3Document23 pagesLecture 3myself.azeem04No ratings yet
- A Technical Report On StudentDocument13 pagesA Technical Report On StudentEzekiel JeremiahNo ratings yet
- Certified Information Systems Auditor (CISA) - Mock Exam 3Document8 pagesCertified Information Systems Auditor (CISA) - Mock Exam 3Nishant KulshresthaNo ratings yet
- Courseworksheet (MD)Document3 pagesCourseworksheet (MD)cheikhNo ratings yet
- SONOS PC Configuration Section (Printable Version)Document80 pagesSONOS PC Configuration Section (Printable Version)HectoRxNo ratings yet
- Wifi-Hacking Cheat Sheet: by ViaDocument1 pageWifi-Hacking Cheat Sheet: by ViaCarlos MirandaNo ratings yet
- BDA Module-2 Notes PDFDocument14 pagesBDA Module-2 Notes PDFVTU ML WorkshopNo ratings yet