0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1K views21 pagesScapular Region
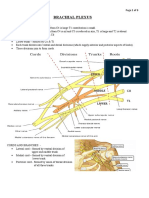
The document describes the muscles that connect the upper limb to the vertebral column. It discusses the deltoid, supraspinatus, infraspinatus, teres minor, teres major, and subscapularis muscles. For each muscle it provides the origin, insertion, nerve supply, and action. It also briefly discusses the rotator cuff and important arterial anastomosis around the shoulder joint to ensure adequate blood flow.
Uploaded by
Nick KlyshkoCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1K views21 pagesScapular Region
The document describes the muscles that connect the upper limb to the vertebral column. It discusses the deltoid, supraspinatus, infraspinatus, teres minor, teres major, and subscapularis muscles. For each muscle it provides the origin, insertion, nerve supply, and action. It also briefly discusses the rotator cuff and important arterial anastomosis around the shoulder joint to ensure adequate blood flow.
Uploaded by
Nick KlyshkoCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd