Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Light Propagation in Optical Fiber
Uploaded by
Bhagyalaxmi Behera0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views22 pagesOriginal Title
Lecture 4.pptx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views22 pagesLight Propagation in Optical Fiber
Uploaded by
Bhagyalaxmi BeheraCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 22
Lecture 4
Light Propagation in Optical Fiber
• Light Propagation Mechanism
• Types of Optical Fibers
• Attenuation and Dispersion
• Light Propagation Mechanism
Fiber Optic Communications Technology by D. K. Mynbaev &
Lowell L. Scheiner - Pearson Education.
• At the end of this lecture students should be able to:
– Understand and apply the knowledge of light propagation
mechanisms in an optical fiber.
– Explain basic characteristics of fiber optics.
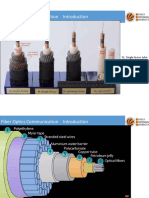
Transmission Medium (Optical Fiber)
• Optical fiber is replacing copper (low loss <= 0.2dB/km)
• Light is used as the fastest and transparent carrier of information
• Much higher data rate (less affected by electromagnetic
interference)
• What is Optical Fiber?
– Thin strands of pure glass
– Carry data over long distances
– At very high speeds (by managing the
dispersion)
– Fiber can be bent or twisted (With bend insensitive
Fiber design)
What is Optical Waveguide?
• “An optical waveguide is a physical structure that guides electromagnetic
waves in optical spectrum” i.e., in micrometre wavelength zone of the
frequency spectrum (frequency between 1014Hz to 1015Hz).
• Optical waveguides are used as components in integrated optical circuits
or as the transmission medium in local and long haul optical
communication systems.
• An optical fiber is a thin, transparent, flexible strand that consists of a core
surrounded by a cladding.
– What is the need of core and cladding?
Light Propagation
Quantum Nature of Light
Basic Optical Laws and Definitions
Fig. Basic structure and light propagation in side a step-index fiber
Total Internal Reflection: Critical Propagation
angle and Critical Incident angle
Acceptance angle (θa)
Fig. Lunching light into the fiber
Numerical Aperture (NA)
?
bhagyalaxmibehera@soa.ac.in
You might also like
- Light Propagation Mechanisms in Optical FiberDocument22 pagesLight Propagation Mechanisms in Optical FiberBhagyalaxmi BeheraNo ratings yet
- Optic FiberDocument31 pagesOptic Fiberkeregi100% (1)
- Fiber Optic Communication FundamentalsDocument201 pagesFiber Optic Communication FundamentalsMax DurendNo ratings yet
- Optics Fundamentals and Applications of Optical FibersDocument12 pagesOptics Fundamentals and Applications of Optical FibersFadil N.Muhammad58% (12)
- Fibre Optic Communication PDFDocument199 pagesFibre Optic Communication PDFBiswarup MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- Pertemuan Pertama - PPTX (Autosaved)Document66 pagesPertemuan Pertama - PPTX (Autosaved)VickyodianaNo ratings yet
- Fiber Optics: By: Engr. Syed Asad AliDocument20 pagesFiber Optics: By: Engr. Syed Asad Alisyedasad114No ratings yet
- Fiber Optics Part IDocument46 pagesFiber Optics Part ImariahvahNo ratings yet
- Topic 14Document41 pagesTopic 14Torres JeromeNo ratings yet
- Topic: Optical Fiber: Design By: Rahul Ohlan IndiaDocument33 pagesTopic: Optical Fiber: Design By: Rahul Ohlan IndiaArnela CamovicNo ratings yet
- Optical Fiber: By: Warqa'a Hashim Alkhaled Asst - Prof. DR Jinan.F.Mahdi April - 2020Document25 pagesOptical Fiber: By: Warqa'a Hashim Alkhaled Asst - Prof. DR Jinan.F.Mahdi April - 2020noor deenNo ratings yet
- Fiber Optics-Understanding The BasicsDocument7 pagesFiber Optics-Understanding The BasicsAmir SalahNo ratings yet
- Optical Fibers: High-Speed, Long-Distance Data TransmissionDocument9 pagesOptical Fibers: High-Speed, Long-Distance Data Transmissionmuhammad atiqNo ratings yet
- Optical Fiber SeminarDocument20 pagesOptical Fiber Seminaryash patil100% (1)
- Module 4A: Understanding Optical FibresDocument39 pagesModule 4A: Understanding Optical FibresAnshuman NandanNo ratings yet
- Fiber Cable-Network OverviewDocument15 pagesFiber Cable-Network Overviewsaifullahmalik100% (1)
- Optical FiberDocument33 pagesOptical FiberUmesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Fiber OpticsDocument5 pagesFiber OpticsMaissa HmdNo ratings yet
- Fiber Optics and Laser Instrumentation - Module 1Document35 pagesFiber Optics and Laser Instrumentation - Module 1maheshnaikm143No ratings yet
- Unit II Fiber OpticsDocument11 pagesUnit II Fiber OpticsSonu GoudNo ratings yet
- ContentDocument12 pagesContentExtramailNo ratings yet
- Optical Fibre CommunicationDocument17 pagesOptical Fibre CommunicationSoumya ShyamasundarNo ratings yet
- Physics 5Document13 pagesPhysics 5ExtramailNo ratings yet
- OPTICAL FIBER COMMUNICATION: HOW DATA IS TRANSMITTED USING LIGHTDocument18 pagesOPTICAL FIBER COMMUNICATION: HOW DATA IS TRANSMITTED USING LIGHTAkhil RajuNo ratings yet
- Op Com SeminarDocument16 pagesOp Com Seminarmuskan sNo ratings yet
- Optical Fiber Communications: Dr. Ali Waqar AzimDocument359 pagesOptical Fiber Communications: Dr. Ali Waqar AzimIfra MalikNo ratings yet
- Optical Fibre (Physics For Engeering Btech)Document38 pagesOptical Fibre (Physics For Engeering Btech)priyanshu gautamNo ratings yet
- Submitted To:-Er. Somesh Malhotra Er. Atul Agnihotri (Summer Training In-Charge)Document22 pagesSubmitted To:-Er. Somesh Malhotra Er. Atul Agnihotri (Summer Training In-Charge)SagarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document126 pagesChapter 1Johny SinghNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 Optical Fibres: Fig: An Optical Fiber Junction BoxDocument11 pagesAssignment 1 Optical Fibres: Fig: An Optical Fiber Junction BoxSagar Kale100% (1)
- Optical Fibers in CommunicationDocument10 pagesOptical Fibers in CommunicationGeorge Francis100% (1)
- Physcis Project On Optical Fibre Cable TDDocument14 pagesPhyscis Project On Optical Fibre Cable TDsoumityachaudharyNo ratings yet
- Optical FibreDocument16 pagesOptical FibrehellogamingprosNo ratings yet
- AttachmentDocument285 pagesAttachmentAman jaiNo ratings yet
- Mid OBEDocument4 pagesMid OBEShuvo Dip RoyNo ratings yet
- Fiber OpfDocument18 pagesFiber Opfvipinchauhan247No ratings yet
- Fiber Optics Understanding The Basics Photonic PDFDocument1 pageFiber Optics Understanding The Basics Photonic PDFRonefer Misa CuyosNo ratings yet
- Opto & Optical ComDocument222 pagesOpto & Optical ComRansford SackeyNo ratings yet
- Fibre Optic PresentationDocument71 pagesFibre Optic Presentationkxngcertn9No ratings yet
- DDIT, Electrical and Computer Engineering Department: Optics and Optical Communication SystemsDocument31 pagesDDIT, Electrical and Computer Engineering Department: Optics and Optical Communication SystemsMihret DeribeNo ratings yet
- Mod 6Document107 pagesMod 6SAHIL NDWRNo ratings yet
- Optical Fiber Communication System ComponentsDocument96 pagesOptical Fiber Communication System ComponentsBerhane KifleNo ratings yet
- Optical Fibre: Kendriya Viyalaya No.2, Colaba, Mumbai - 05Document16 pagesOptical Fibre: Kendriya Viyalaya No.2, Colaba, Mumbai - 05Prerna AmzareNo ratings yet
- Lec5 ES475 2023 UploadDocument25 pagesLec5 ES475 2023 UploadEmad RazaNo ratings yet
- Fiber Optics Module 1Document63 pagesFiber Optics Module 1Ravi Teja AJNo ratings yet
- ETEG 422 Lecture 2Document35 pagesETEG 422 Lecture 2Prishma DahalNo ratings yet
- Fiber Optics CommunicationsDocument23 pagesFiber Optics CommunicationsRyan Paul RiwarinNo ratings yet
- Optical FiberDocument47 pagesOptical FiberAbhijith S.SNo ratings yet
- Fiber Optics CommunicationsDocument21 pagesFiber Optics CommunicationsJack HammerNo ratings yet
- Optical Fibres and It's ApplicationsDocument24 pagesOptical Fibres and It's ApplicationsSumit AnandNo ratings yet
- Optical Fibres: Total Internal Reflection and ComponentsDocument15 pagesOptical Fibres: Total Internal Reflection and ComponentsSai Printers67% (3)
- Mech Optical Fiber Communication ReportDocument16 pagesMech Optical Fiber Communication ReportAdmirable VishalNo ratings yet
- Optical FibersDocument44 pagesOptical FibersVimala ElumalaiNo ratings yet
- OFC TechnologyDocument52 pagesOFC TechnologyBattinapati ShivaNo ratings yet
- Optical Fiber CommunicationsDocument49 pagesOptical Fiber CommunicationsShebNo ratings yet
- Dr.K. Anitha - Optical CommunicationDocument117 pagesDr.K. Anitha - Optical Communicationjohnsai003No ratings yet
- Chapter One Introduction To Fiber OpticDocument28 pagesChapter One Introduction To Fiber OpticHogr RgohNo ratings yet
- Download Free College Physics Project on Optical Fiber and its ApplicationsDocument30 pagesDownload Free College Physics Project on Optical Fiber and its ApplicationsGautam KumarNo ratings yet
- Design and Analysis of Resonant Cavity Enhanced-Waveguide Photodetectors For Microwave Photonics ApplicationsDocument3 pagesDesign and Analysis of Resonant Cavity Enhanced-Waveguide Photodetectors For Microwave Photonics ApplicationsBhagyalaxmi BeheraNo ratings yet
- Guest Editorial Special Issue On Microwave PhotonicsDocument2 pagesGuest Editorial Special Issue On Microwave PhotonicsBhagyalaxmi BeheraNo ratings yet
- Guest Editorial Microwave Photonics: Microwave Photonics Can Be Defined As The Study of PhoDocument3 pagesGuest Editorial Microwave Photonics: Microwave Photonics Can Be Defined As The Study of PhoBhagyalaxmi BeheraNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3Document9 pagesLecture 3Bhagyalaxmi BeheraNo ratings yet
- Microwave PhotonicsDocument11 pagesMicrowave Photonicsveneethanair88No ratings yet
- Light Propagation in Optical FiberDocument22 pagesLight Propagation in Optical FiberBhagyalaxmi BeheraNo ratings yet
- Double-Locked Laser Diode for Microwave PhotonicsDocument3 pagesDouble-Locked Laser Diode for Microwave PhotonicsBhagyalaxmi BeheraNo ratings yet
- Direct Optical Injection Locking of Inp/Ingaas HPT Oscillator Ics For Microwave Photonics and 40-Gbit/S-Class Optoelectronic Clock RecoveryDocument7 pagesDirect Optical Injection Locking of Inp/Ingaas HPT Oscillator Ics For Microwave Photonics and 40-Gbit/S-Class Optoelectronic Clock RecoveryBhagyalaxmi BeheraNo ratings yet
- WDM Concept and Major Elements of Optical Fiber CommunicationDocument9 pagesWDM Concept and Major Elements of Optical Fiber CommunicationBhagyalaxmi BeheraNo ratings yet
- Light Propagation in Optical FiberDocument22 pagesLight Propagation in Optical FiberBhagyalaxmi BeheraNo ratings yet
- A Uniplanar Compact Photonic-Bandgap (UC-PBG)Document6 pagesA Uniplanar Compact Photonic-Bandgap (UC-PBG)Bhagyalaxmi BeheraNo ratings yet
- Light Propagation in Optical FiberDocument22 pagesLight Propagation in Optical FiberBhagyalaxmi BeheraNo ratings yet
- OFC - Syllabus+Lesson PlanDocument2 pagesOFC - Syllabus+Lesson PlanBhagyalaxmi BeheraNo ratings yet
- OFC - Syllabus+Lesson PlanDocument2 pagesOFC - Syllabus+Lesson PlanBhagyalaxmi BeheraNo ratings yet
- Light Propagation in Optical FiberDocument22 pagesLight Propagation in Optical FiberBhagyalaxmi BeheraNo ratings yet
- Silicon-Based Integrated Microwave Photonics - 1st - AugustDocument12 pagesSilicon-Based Integrated Microwave Photonics - 1st - AugustBhagyalaxmi BeheraNo ratings yet
- A Tutorial On Microwave Photonic FiltersDocument30 pagesA Tutorial On Microwave Photonic FiltersBhagyalaxmi BeheraNo ratings yet
- A Tutorial On Microwave Photonic FiltersDocument30 pagesA Tutorial On Microwave Photonic FiltersBhagyalaxmi BeheraNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Microwave Photonic Filter Using Separate CarrierDocument3 pagesDynamic Microwave Photonic Filter Using Separate CarrierBhagyalaxmi BeheraNo ratings yet
- A Tutorial On Microwave Photonic FiltersDocument30 pagesA Tutorial On Microwave Photonic FiltersBhagyalaxmi BeheraNo ratings yet