0% found this document useful (0 votes)
84 views23 pagesPresented By: An Advanced Technology in Computer World
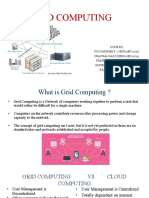
Grid computing allows for the sharing of computer resources from multiple administrative domains for common goals. It enables sharing, selection, and aggregation of resources like processors, disks, and displays. The grid unites servers and storage into a single system that acts like a single computer. It provides benefits like increased capacity, improved efficiency and reduced costs, and faster results. Key components of a grid include portals, security, brokers, schedulers, data management, and job flows. While still evolving, grid computing supports distributed supercomputing and multimedia applications across heterogeneous systems.
Uploaded by
coharishCopyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
84 views23 pagesPresented By: An Advanced Technology in Computer World
Grid computing allows for the sharing of computer resources from multiple administrative domains for common goals. It enables sharing, selection, and aggregation of resources like processors, disks, and displays. The grid unites servers and storage into a single system that acts like a single computer. It provides benefits like increased capacity, improved efficiency and reduced costs, and faster results. Key components of a grid include portals, security, brokers, schedulers, data management, and job flows. While still evolving, grid computing supports distributed supercomputing and multimedia applications across heterogeneous systems.
Uploaded by
coharishCopyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 23