Professional Documents
Culture Documents
ANXIETY
ANXIETY
Uploaded by
memeland0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views4 pagesanxiety
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentanxiety
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views4 pagesANXIETY
ANXIETY
Uploaded by
memelandanxiety
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
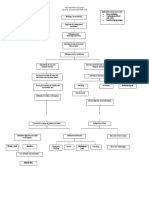
ANXIETY
• a nervous disorder characterized by a state of excessive
uneasiness and apprehension, typically with compulsive
behavior or panic attacks.
• Normal anxiety is adaptive. It is an inborn response to threat
or to the absence of people or objects that signify safety can
result in cognitive (worry) and somatic (sweating, shaking,
freezing, shaking, etc)
• Pathologic anxiety is anxiety that is excessive, impairs
function.
Causes of Anxiety
There is no specific cause for anxiety disorders, Several factors can play
a role.
• -Genetic
• -Overactive flight or flight response
• Caused by too much stress
• -life circumstances
• -Personality
• People with low esteem and poor coping skills may be more prone.
• -certain drugs
• It can lead symptoms of anxiety due to either side effects or
withdrawal from the drug.
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY
In the central nervous system (CNS), the major mediators of
the symptoms of anxiety disorders appear to be
norepinephrine, serotonin, dopamine, and gamma-
aminobutyric acid (GABA). Other neurotransmitters and
peptides, such as corticotropin-releasing factor, may be
involved. Peripherally, the autonomic nervous system,
especially the sympathetic nervous system, mediates many of
the symptoms.
CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS
• (+) Dizziness
• (+) headache
• (+) Dehydration
• (+) weakness
• (+) Blurred vision
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5820)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1093)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (845)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (348)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- Essential Element RESEARCHDocument4 pagesEssential Element RESEARCHKita kita83% (6)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- PathophysiologyDocument3 pagesPathophysiologyKita kita100% (1)
- B. Risk Classifications of ENT Patients: Tier-Based Classification SchemeDocument2 pagesB. Risk Classifications of ENT Patients: Tier-Based Classification SchemeKita kitaNo ratings yet
- CPG On OmeDocument6 pagesCPG On OmeKita kitaNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Ent MalignanciesDocument69 pagesPediatric Ent MalignanciesKita kitaNo ratings yet
- General Data:: S O C R A TDocument9 pagesGeneral Data:: S O C R A TKita kitaNo ratings yet
- Precursor B and T CellDocument8 pagesPrecursor B and T CellKita kitaNo ratings yet
- Based On Your Possible Final Diagnosis, What Are The Treatment Plans For Our Patient?Document63 pagesBased On Your Possible Final Diagnosis, What Are The Treatment Plans For Our Patient?Kita kitaNo ratings yet
- Arterial Blood Gas (Abg)Document10 pagesArterial Blood Gas (Abg)Kita kitaNo ratings yet
- BIOETH - Applied EthicsDocument3 pagesBIOETH - Applied EthicsKita kitaNo ratings yet
- Drugs Affecting The Respiratory SystemDocument32 pagesDrugs Affecting The Respiratory SystemKita kitaNo ratings yet
- Arthropods of Medical ImportanceDocument82 pagesArthropods of Medical ImportanceKita kita0% (1)
- Medicine 2021: Specific Health Problems: Genetic DisordersDocument7 pagesMedicine 2021: Specific Health Problems: Genetic DisordersKita kitaNo ratings yet
- Mycology TransDocument11 pagesMycology TransKita kitaNo ratings yet
- History of Barangay TalebDocument13 pagesHistory of Barangay TalebKita kitaNo ratings yet