Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Steam Condenser and It's Types-2: Footer Text
Uploaded by
doomraOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Steam Condenser and It's Types-2: Footer Text
Uploaded by
doomraCopyright:
Available Formats
Steam Condenser
and it’s types-2
1
Footer Text 05/16/2020
Surface Condensers
2
In surface condenser, the exhaust steam and cooling water do
not come in physical contact, rather they are separated by heat
transfer wall. Hence condensate remains pure & can be reused.
Footer Text 05/16/2020
Down Flow Surface Condenser:
3
Exhaust steam enters the
top of condenser shell &
flows downward over
water tubes.
Water tubes are double
passed. The cold water
flows in lower side first &
then in upper side in the
reverse direction, which
enables the maximum heat
transfer.
Footer Text 05/16/2020
Central Flow Surface Condenser
4
The steam flows radially inward
The condensate is collected
at the bottom of the shell from
where it is taken out by the
condensate extraction pump.
The steam gets access to the
entire periphery of tubes, and
thus a large surface area for the
hear transfer is available as
compared to the down flow.
Footer Text 05/16/2020
Inverted Flow Condenser:
5
The steam enters the bottom of the shell and
air extraction pump connected at the top.
Steam flows upward first and subsequently,
returns to the bottom of the condenser.
The condensate extraction pump is connected
at the bottom of the shell to extract the
condensate.
Footer Text 05/16/2020
Evaporative Condenser:
6
The evaporation of some
cooling water provides the
cooling effect, thereby
steam condenses.
Steam to be condensed is
passed through grilled tubes
& cooling water is sprayed
over outer surface of tubes.
The evaporative condensers
are most suitable for small
plants, where supply of cold
water is limited.
Footer Text 05/16/2020
Advantages & Disadvantages of Surface
Condensers:
7
Advantages:
High vacuum efficiency.
Pure condensate.
Low quality cooling water can be used.
It allows the expansion of steam through a higher pressure ratio.
Disadvantages:
Large amount of water is required.
Construction is complicated.
Costly maintenance and skilled workers.
Large floor area.
Footer Text 05/16/2020
Comparison of Jet & Surface Condensers:
Jet Condensers Surface Condensers
1) Cooling water and steam are mixed up 1) Cooling water & steam aren’t mixed up
2) Requires small floor space 2) Requires large floor space
3) The condensate cannot be used as feed water to 3) The condensate can be used as feed water to
boiler unless it is free from impurities boiler as it is not mixed with cooling water
4) More power is required for air pump 4) Less power is required for air pump
5) Less power is required for water pump 5) More power is required for water pump
6) Requires less quantity of cooling water 6) Requires large quantity of cooling water
7) The condensing plant is simple 7) The condensing plant is complicated
8) Less suitable for high capacity plants due to low 8) More suitable for high capacity plants as
vacuum efficiency vacuum efficiency is high
Footer Text 05/16/2020
Sources of Air in the Condenser:
9
The ambient air leaks to the condenser chamber at the joints & glands
which are internally under pressure lower than that of ambient.
Another source of air is the dissolved air with feed water. The dissolved
air in feed water enters into boiler and it travels with steam into
condenser.
Effects of Air Leakage:
The presence of air lowers vacuum in the condenser. Thus back pressure
of the plant increases, and consequently, the work output decreases.
Air has very poor thermal conductivity. Hence, the rate of heat transfer
from vapour to cooling medium is reduced.
The presence of air in the condenser corrodes to the metal surfaces.
Therefore, the life of condenser is reduced.
Footer Text 05/16/2020
Footer Text 10 05/16/2020
Vacuum Creation in Condenser:
11
• When the steam condenses in a closed vessel, the vapour phase of
working substance changes to liquid phase, and thus its specific
volume reduces to more than one thousand times.
• Due to change in specific volume, the absolute pressure in the
condenser falls below atmospheric pressure and a high vacuum is
created.
• This minimum pressure that can be attained depends on the
temperature of condensate and air present in the condenser.
The absolute pressure = Atmospheric pressure – Vacuum Gauge
in the condenser Pressure
Footer Text 05/16/2020
Effect of Condenser Pressure on Rankine
Efficiency:
12
Lowering the condenser pressure will
increase the area enclosed by the cycle
on a T-s diagram which indicates that
the net work will increase. Thus, the
thermal efficiency of the cycle will be
increased
Lowering the back pressure causes an
increase in moisture content of steam
leaving the turbine.
Increase in moisture content of steam in
low pressure stages, there is decrease in
efficiency & erosion of blade may be a
very serious problem and also the pump
work required will be high.
Footer Text 05/16/2020
You might also like
- Air-Cooled Condenser Fundamentals: Design, Operations, Troubleshooting, Maintenance, and Q&AFrom EverandAir-Cooled Condenser Fundamentals: Design, Operations, Troubleshooting, Maintenance, and Q&ARating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Condenser PDFDocument14 pagesCondenser PDFnirmalk1222No ratings yet
- Dynamic Balancing of RotorsDocument60 pagesDynamic Balancing of RotorsAmir Mahmoud Mahdavi Abhari100% (3)
- Steam Turbine Auxiliaries Question & AnswersDocument10 pagesSteam Turbine Auxiliaries Question & AnswersLaxman Veerepalli100% (1)
- Understanding Process Equipment for Operators and EngineersFrom EverandUnderstanding Process Equipment for Operators and EngineersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Difference Between Heat Recovery Steam Generators (HRSG) & Combustion BoilerDocument3 pagesDifference Between Heat Recovery Steam Generators (HRSG) & Combustion Boilerazeemmet9924No ratings yet
- 17 Condensers 5-1Document28 pages17 Condensers 5-1Omar AhmedNo ratings yet
- Oregen Wasted Heat Recovery CycleDocument6 pagesOregen Wasted Heat Recovery CyclesbiliristhodNo ratings yet
- No Category Brend Machine Number Cross Part Name Unit Weight RemarkDocument15 pagesNo Category Brend Machine Number Cross Part Name Unit Weight RemarkИгорь Терещенко100% (7)
- Refrigeration System Components: - Vishakh GaneshDocument34 pagesRefrigeration System Components: - Vishakh GaneshS R Akhil KrishnanNo ratings yet
- Necessity of condensers in thermal power plantsDocument14 pagesNecessity of condensers in thermal power plantsShankar Jha67% (3)
- Training On Steam CondensersDocument33 pagesTraining On Steam CondensersMayank GuptaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Steam CondenserDocument52 pagesChapter 6 Steam CondenserMisge ChekoleNo ratings yet
- ABMA Water GuideDocument1 pageABMA Water GuidesizmaruNo ratings yet
- Condenser in Power PlantDocument20 pagesCondenser in Power PlantPrabir Kumar PatiNo ratings yet
- Steam Condensers and Evaporators ExplainedDocument32 pagesSteam Condensers and Evaporators Explainedvipul sharma100% (1)
- 02 - Condensers & Cooling Towers PDFDocument61 pages02 - Condensers & Cooling Towers PDFVimleshKumarSharmaNo ratings yet
- Troubleshooting Vacuum Systems: Steam Turbine Surface Condensers and Refinery Vacuum TowersFrom EverandTroubleshooting Vacuum Systems: Steam Turbine Surface Condensers and Refinery Vacuum TowersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Steam Condensers: 3/28/2015 1 Footer TextDocument23 pagesSteam Condensers: 3/28/2015 1 Footer TextKumari YehwaNo ratings yet
- By: Ankit Saxena Asst. Professor Mangalmay Institute of Engineering and TechnologyDocument24 pagesBy: Ankit Saxena Asst. Professor Mangalmay Institute of Engineering and TechnologyHana HermawanNo ratings yet
- Steam CondensersDocument59 pagesSteam CondensersBLACK GAMINGNo ratings yet
- Types and Functions of Steam CondensersDocument14 pagesTypes and Functions of Steam CondensersdoomraNo ratings yet
- Thermal Engineering-CondenserDocument17 pagesThermal Engineering-CondenserJayNo ratings yet
- Gaurav - Surface Condenser1Document10 pagesGaurav - Surface Condenser1gauravkotkar7No ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Steam CondenserDocument40 pagesChapter 5 Steam CondenserHabtamu Tkubet EbuyNo ratings yet
- Steam Condenser: Me 420 - Me Laboratory 2Document74 pagesSteam Condenser: Me 420 - Me Laboratory 2daanNo ratings yet
- Condenser Efficiency EngineeringDocument9 pagesCondenser Efficiency Engineeringโอม ปามาติกะ100% (2)
- Steam Condesers Note 2Document7 pagesSteam Condesers Note 2diksahu wfeeNo ratings yet
- Condenser8 5 2020Document3 pagesCondenser8 5 2020anupnaskar naskarNo ratings yet
- CondensersDocument34 pagesCondensersShreyash VihirghareNo ratings yet
- Experiment # 8 "Demonstration of Steam Condenser" ObjectiveDocument6 pagesExperiment # 8 "Demonstration of Steam Condenser" ObjectiveAiman SherdilNo ratings yet
- Presentation By: 3 Year Mech-D 17985A077 17985A078 17985A079 17985A083 17985A084 17985A088 17985A092 17985A095 17985A098Document15 pagesPresentation By: 3 Year Mech-D 17985A077 17985A078 17985A079 17985A083 17985A084 17985A088 17985A092 17985A095 17985A098pranavNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 - Thermal Engineering and Gas Dynamics - WWW - Rgpvnotes.inDocument13 pagesUnit 5 - Thermal Engineering and Gas Dynamics - WWW - Rgpvnotes.inFno FnoNo ratings yet
- Chapter SixDocument25 pagesChapter SixADEFRIS BELACHEWNo ratings yet
- Condensers PDF - 1586610713Document8 pagesCondensers PDF - 1586610713Mint PepperNo ratings yet
- Steam CondenserDocument16 pagesSteam CondenserAtharv MarneNo ratings yet
- Applied Thermodynamics CondensorDocument14 pagesApplied Thermodynamics CondensorKUSHAL MITTALNo ratings yet
- CondenserDocument18 pagesCondenserHusnain AliNo ratings yet
- Te - Ii 2 MarksDocument12 pagesTe - Ii 2 MarksVenkata lohithNo ratings yet
- I A L R: Ntroduction ND Iterature EviewDocument42 pagesI A L R: Ntroduction ND Iterature Eviewyfyfkfuf100% (1)
- CONDENSERDocument24 pagesCONDENSERAmlan ShomeNo ratings yet
- CondenserDocument8 pagesCondenserManish MauryaNo ratings yet
- Power plant condensers: types, working principle and advantagesDocument7 pagesPower plant condensers: types, working principle and advantagesMustafam98No ratings yet
- Air Conditioning EfficiencyDocument3 pagesAir Conditioning EfficiencyVed PrakashNo ratings yet
- 2_Steam CondenserDocument15 pages2_Steam CondenserHarshil ChaddhaNo ratings yet
- Steam Surface Condenser OperationDocument10 pagesSteam Surface Condenser OperationJohn Noel TalandronNo ratings yet
- Condenser and It's TypesDocument6 pagesCondenser and It's Typeskaacho piece pieceNo ratings yet
- 9 Condenser-1Document50 pages9 Condenser-1as2899142No ratings yet
- Chapter One: CondenserDocument10 pagesChapter One: Condenserشاكر العاقل100% (1)
- Unit Notes PDFDocument29 pagesUnit Notes PDFPrashant UbarhandeNo ratings yet
- Advantages of Jet and Surface Condensers in Power PlantsDocument9 pagesAdvantages of Jet and Surface Condensers in Power PlantsshihabNo ratings yet
- KIET Group of Institutions, GhaziabadDocument8 pagesKIET Group of Institutions, GhaziabadSandeep ChhabraNo ratings yet
- Turbine AccessoriesDocument22 pagesTurbine Accessoriessrikanth9555No ratings yet
- Turbine Auxilaries Q A PDFDocument22 pagesTurbine Auxilaries Q A PDFGanesh DasaraNo ratings yet
- Condenser & ReboilersDocument6 pagesCondenser & Reboilersapi-3774373No ratings yet
- Steam Condenser and Cooling TowerDocument25 pagesSteam Condenser and Cooling TowerDeep KhandhediaNo ratings yet
- Ppe Activity 6Document3 pagesPpe Activity 6Marycris Bautista RosarioNo ratings yet
- Study of Condenser Performance Evaluation and Measures To Improve ItDocument26 pagesStudy of Condenser Performance Evaluation and Measures To Improve ItPrudhvi RajNo ratings yet
- Design Based Comparative Study of Several Condensers Ijariie2142 PDFDocument7 pagesDesign Based Comparative Study of Several Condensers Ijariie2142 PDFFranceNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of the Household: A Course of Study Devoted to Domestic Machinery and Household Mechanical AppliancesFrom EverandMechanics of the Household: A Course of Study Devoted to Domestic Machinery and Household Mechanical AppliancesNo ratings yet
- A Review Study On Cooling Towers Types, Performance and ApplicationDocument10 pagesA Review Study On Cooling Towers Types, Performance and ApplicationdoomraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6.1 Transmission System ClutchDocument33 pagesChapter 6.1 Transmission System ClutchdoomraNo ratings yet
- LUBRIDocument21 pagesLUBRIdoomraNo ratings yet
- Steam Turbine 2 Types, Losses and CompundingDocument9 pagesSteam Turbine 2 Types, Losses and Compundingdoomra50% (2)
- 13-Steam Turbines (Compatibility Mode) - 43-50Document8 pages13-Steam Turbines (Compatibility Mode) - 43-50doomraNo ratings yet
- 13-Steam Turbines (Compatibility Mode) - 35-42Document8 pages13-Steam Turbines (Compatibility Mode) - 35-42doomraNo ratings yet
- Losses in Steam TurbinesDocument3 pagesLosses in Steam TurbinesdoomraNo ratings yet
- Calculating Dryness Fraction and Vacuum Efficiency of Steam CondensersDocument4 pagesCalculating Dryness Fraction and Vacuum Efficiency of Steam CondensersdoomraNo ratings yet
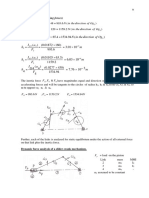
- Chapter - 2: Dynamic Force AnalysisDocument9 pagesChapter - 2: Dynamic Force AnalysisdoomraNo ratings yet
- 13-Steam Turbines (Compatibility Mode) - 35-42Document8 pages13-Steam Turbines (Compatibility Mode) - 35-42doomraNo ratings yet
- Inertia Force of Slider Crank-9-13Document5 pagesInertia Force of Slider Crank-9-13doomraNo ratings yet
- Balancing OF Reciprocating Masses: Vtu Edusat Programme-17Document43 pagesBalancing OF Reciprocating Masses: Vtu Edusat Programme-17doomraNo ratings yet
- b7 Force Analysis PDFDocument25 pagesb7 Force Analysis PDFGamini SureshNo ratings yet
- Steam Turbines Intro and Rankine CycleDocument15 pagesSteam Turbines Intro and Rankine CycledoomraNo ratings yet
- b7 Force Analysis PDFDocument25 pagesb7 Force Analysis PDFGamini SureshNo ratings yet
- 152lecture 1 1 Static Force Analysis of Planar Mechanism PDFDocument29 pages152lecture 1 1 Static Force Analysis of Planar Mechanism PDFSai SushmaNo ratings yet
- Concept of Direct and Reverse CranksDocument7 pagesConcept of Direct and Reverse CranksVinay H. B.No ratings yet
- 3 - Dynamics Force and Motion Analysis of Plane MechanismDocument21 pages3 - Dynamics Force and Motion Analysis of Plane MechanismdoomraNo ratings yet
- Balancing Rotating MassesDocument225 pagesBalancing Rotating MassesBaran Shafqat100% (1)
- 152lecture 1 1 Static Force Analysis of Planar Mechanism PDFDocument29 pages152lecture 1 1 Static Force Analysis of Planar Mechanism PDFSai SushmaNo ratings yet
- Unit - V BalancingDocument9 pagesUnit - V BalancingdoomraNo ratings yet
- Calculating Dryness Fraction and Vacuum Efficiency of Steam CondensersDocument4 pagesCalculating Dryness Fraction and Vacuum Efficiency of Steam CondensersdoomraNo ratings yet
- Steam Turbine 2 Types, Losses and CompundingDocument9 pagesSteam Turbine 2 Types, Losses and Compundingdoomra50% (2)
- Lakshminarayanan2011 PDFDocument7 pagesLakshminarayanan2011 PDFdoomraNo ratings yet
- Classifying and Explaining Common Boiler TypesDocument8 pagesClassifying and Explaining Common Boiler TypesKarthiKeyanNo ratings yet
- Solar PowerDocument32 pagesSolar PowerJoyjoy C LbanezNo ratings yet
- Cummins QSK19-C700 Engine Spare PartsDocument2 pagesCummins QSK19-C700 Engine Spare PartsIbrahim YunusNo ratings yet
- ENERGY+HARVESTING+FROM+EXHAUST+WASTE+HEAT+USING+THERMOELECTRIC+GENERATOR+ (TEG) +MODULES CheckedDocument10 pagesENERGY+HARVESTING+FROM+EXHAUST+WASTE+HEAT+USING+THERMOELECTRIC+GENERATOR+ (TEG) +MODULES CheckednugrohoNo ratings yet
- Partial Loading Optimal Control - Steam Turbine EffDocument6 pagesPartial Loading Optimal Control - Steam Turbine EffLTE002No ratings yet
- Lab Manual (TME-426) Non-Conventional Energy Sources and SystemsDocument30 pagesLab Manual (TME-426) Non-Conventional Energy Sources and SystemsJITENDRA SINGH100% (1)
- 6KW Fire Station SLDDocument1 page6KW Fire Station SLDB . G STUDIONo ratings yet
- TG-24 Battery Charger System TG-24 Battery Charger System TG-24 Battery Charger System TG-25 Battery Charger SystemDocument11 pagesTG-24 Battery Charger System TG-24 Battery Charger System TG-24 Battery Charger System TG-25 Battery Charger SystemBHUVANESH MNo ratings yet
- Electric Characteristics of Photovoltaic Cells and ModulesDocument15 pagesElectric Characteristics of Photovoltaic Cells and ModulesredwaneNo ratings yet
- Steam TableDocument7 pagesSteam TableAsraf AliNo ratings yet
- Solar RefrigeratorDocument12 pagesSolar RefrigeratorSheeraz AliNo ratings yet
- Drum in BoilerDocument18 pagesDrum in BoilerRuban Kumar100% (1)
- Parker Steam Boiler Quarterly Inspection Report: QTR 101-5Document2 pagesParker Steam Boiler Quarterly Inspection Report: QTR 101-5Danu KautsarNo ratings yet
- Thermal Power Plants-FinalDocument61 pagesThermal Power Plants-FinalBhavya ShrivastwaNo ratings yet
- Comparison of Different Power PlantsDocument38 pagesComparison of Different Power Plantsراشد سردارNo ratings yet
- Utilizing Process Engineering for Efficient Utilitas & Effluent ManagementDocument13 pagesUtilizing Process Engineering for Efficient Utilitas & Effluent ManagementditaNo ratings yet
- Pison Cooling Jets Remove and installSMCS - 1331 - 010Document3 pagesPison Cooling Jets Remove and installSMCS - 1331 - 010DjNo ratings yet
- 15MW电缆表 1031Document4 pages15MW电缆表 1031sontnieNo ratings yet
- Alarm Clock: Operating Instructions Care and MaintenanceDocument5 pagesAlarm Clock: Operating Instructions Care and MaintenanceAre BratttNo ratings yet
- Steam Engine - WikipediaDocument129 pagesSteam Engine - WikipediaEndhy Wisnu NovindraNo ratings yet
- Genebraldo Solved ProblemsDocument5 pagesGenebraldo Solved ProblemsDarwin Lim50% (2)
- CODURI HyundaiDocument101 pagesCODURI Hyundaiulianburca5277No ratings yet
- Steam Turbine Working and TypesDocument1 pageSteam Turbine Working and Typesbekaen bekaenNo ratings yet
- Generator Set Data Sheet: Fuel ConsumptionDocument3 pagesGenerator Set Data Sheet: Fuel Consumptionmohsen_cumminsNo ratings yet
- Enc-025l DatasheetDocument2 pagesEnc-025l Datasheetcriman45No ratings yet
- Unit Shut Down ProcedureDocument35 pagesUnit Shut Down ProcedureAjayKurekarNo ratings yet