Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Order Birds Southern Hemisphere Galápagos Penguin Krill Fish Temperate Little Blue Penguin Prehistoric Subantarctic Equato
Uploaded by
Angelo Astudillo0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views12 pagesOriginal Title
Penguins.pptx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views12 pagesOrder Birds Southern Hemisphere Galápagos Penguin Krill Fish Temperate Little Blue Penguin Prehistoric Subantarctic Equato
Uploaded by
Angelo AstudilloCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 12
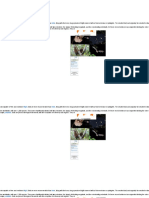
Penguins (order Sphenisciformes, family Spheniscidae) are a group of aquatic flightless birds.
They live almost exclusively in the Southern Hemisphere
, with only one species, the Galápagos penguin, found north of the equator. Highly adapted for life in the water, penguins have countershaded dark and
white plumage and flippers for swimming. Most penguins feed on krill, fish, squid and other forms of sea life which they catch while swimming
underwater. They spend roughly half of their lives on land and the other half in the sea.
Although almost all penguin species are native to the Southern Hemisphere, they are not found only in cold climates, such as Antarctica. In fact, only a
few species of penguin live so far south. Several species are found in the temperate zone, but one species, the Galápagos penguin, lives near the equator.
The largest living species is the emperor penguin (Aptenodytes forsteri):[1] on average, adults are about 1.1 m (3 ft 7 in) tall and weigh 35 kg (77 lb). The
smallest penguin species is the little blue penguin (Eudyptula minor), also known as the fairy penguin, which stands around 33 cm (13 in) tall and weighs
1 kg (2.2 lb).[2] Among extant penguins, larger penguins inhabit colder regions, while smaller penguins are generally found in temperate or even tropical
climates. Some prehistoric species attained enormous sizes, becoming as tall or as heavy as an adult human. These were not restricted to Antarctic
regions; on the contrary, subantarctic regions harboured high diversity, and at least one giant penguin occurred in a region around 2,000 km south of the
equato
Penguins (order Sphenisciformes, family Spheniscidae) are a group of aquatic flightless birds. They live almost exclusively in the Southern Hemisphere
, with only one species, the Galápagos penguin, found north of the equator. Highly adapted for life in the water, penguins have countershaded dark and
white plumage and flippers for swimming. Most penguins feed on krill, fish, squid and other forms of sea life which they catch while swimming
underwater. They spend roughly half of their lives on land and the other half in the sea.
Although almost all penguin species are native to the Southern Hemisphere, they are not found only in cold climates, such as Antarctica. In fact, only a
few species of penguin live so far south. Several species are found in the temperate zone, but one species, the Galápagos penguin, lives near the equator.
The largest living species is the emperor penguin (Aptenodytes forsteri):[1] on average, adults are about 1.1 m (3 ft 7 in) tall and weigh 35 kg (77 lb). The
smallest penguin species is the little blue penguin (Eudyptula minor), also known as the fairy penguin, which stands around 33 cm (13 in) tall and weighs
1 kg (2.2 lb).[2] Among extant penguins, larger penguins inhabit colder regions, while smaller penguins are generally found in temperate or even tropical
climates. Some prehistoric species attained enormous sizes, becoming as tall or as heavy as an adult human. These were not restricted to Antarctic
regions; on the contrary, subantarctic regions harboured high diversity, and at least one giant penguin occurred in a region around 2,000 km south of the
equato
Penguins (order Sphenisciformes, family Spheniscidae) are a group of aquatic flightless birds. They live almost exclusively in the Southern Hemisphere
, with only one species, the Galápagos penguin, found north of the equator. Highly adapted for life in the water, penguins have countershaded dark and
white plumage and flippers for swimming. Most penguins feed on krill, fish, squid and other forms of sea life which they catch while swimming
underwater. They spend roughly half of their lives on land and the other half in the sea.
Although almost all penguin species are native to the Southern Hemisphere, they are not found only in cold climates, such as Antarctica. In fact, only a
few species of penguin live so far south. Several species are found in the temperate zone, but one species, the Galápagos penguin, lives near the equator.
The largest living species is the emperor penguin (Aptenodytes forsteri):[1] on average, adults are about 1.1 m (3 ft 7 in) tall and weigh 35 kg (77 lb). The
smallest penguin species is the little blue penguin (Eudyptula minor), also known as the fairy penguin, which stands around 33 cm (13 in) tall and weighs
1 kg (2.2 lb).[2] Among extant penguins, larger penguins inhabit colder regions, while smaller penguins are generally found in temperate or even tropical
climates. Some prehistoric species attained enormous sizes, becoming as tall or as heavy as an adult human. These were not restricted to Antarctic
regions; on the contrary, subantarctic regions harboured high diversity, and at least one giant penguin occurred in a region around 2,000 km south of the
equato
Penguins (order Sphenisciformes, family Spheniscidae) are a group of aquatic flightless birds. They live almost exclusively in the Southern Hemisphere
, with only one species, the Galápagos penguin, found north of the equator. Highly adapted for life in the water, penguins have countershaded dark and
white plumage and flippers for swimming. Most penguins feed on krill, fish, squid and other forms of sea life which they catch while swimming
underwater. They spend roughly half of their lives on land and the other half in the sea.
Although almost all penguin species are native to the Southern Hemisphere, they are not found only in cold climates, such as Antarctica. In fact, only a
few species of penguin live so far south. Several species are found in the temperate zone, but one species, the Galápagos penguin, lives near the equator.
The largest living species is the emperor penguin (Aptenodytes forsteri):[1] on average, adults are about 1.1 m (3 ft 7 in) tall and weigh 35 kg (77 lb). The
smallest penguin species is the little blue penguin (Eudyptula minor), also known as the fairy penguin, which stands around 33 cm (13 in) tall and weighs
1 kg (2.2 lb).[2] Among extant penguins, larger penguins inhabit colder regions, while smaller penguins are generally found in temperate or even tropical
climates. Some prehistoric species attained enormous sizes, becoming as tall or as heavy as an adult human. These were not restricted to Antarctic
regions; on the contrary, subantarctic regions harboured high diversity, and at least one giant penguin occurred in a region around 2,000 km south of the
equato
Penguins (order Sphenisciformes, family Spheniscidae) are a group of aquatic flightless birds. They live almost exclusively in the Southern Hemisphere
, with only one species, the Galápagos penguin, found north of the equator. Highly adapted for life in the water, penguins have countershaded dark and
white plumage and flippers for swimming. Most penguins feed on krill, fish, squid and other forms of sea life which they catch while swimming
underwater. They spend roughly half of their lives on land and the other half in the sea.
Although almost all penguin species are native to the Southern Hemisphere, they are not found only in cold climates, such as Antarctica. In fact, only a
few species of penguin live so far south. Several species are found in the temperate zone, but one species, the Galápagos penguin, lives near the equator.
The largest living species is the emperor penguin (Aptenodytes forsteri):[1] on average, adults are about 1.1 m (3 ft 7 in) tall and weigh 35 kg (77 lb). The
smallest penguin species is the little blue penguin (Eudyptula minor), also known as the fairy penguin, which stands around 33 cm (13 in) tall and weighs
1 kg (2.2 lb).[2] Among extant penguins, larger penguins inhabit colder regions, while smaller penguins are generally found in temperate or even tropical
climates. Some prehistoric species attained enormous sizes, becoming as tall or as heavy as an adult human. These were not restricted to Antarctic
regions; on the contrary, subantarctic regions harboured high diversity, and at least one giant penguin occurred in a region around 2,000 km south of the
equato
Penguins (order Sphenisciformes, family Spheniscidae) are a group of aquatic flightless birds. They live almost exclusively in the Southern Hemisphere
, with only one species, the Galápagos penguin, found north of the equator. Highly adapted for life in the water, penguins have countershaded dark and
white plumage and flippers for swimming. Most penguins feed on krill, fish, squid and other forms of sea life which they catch while swimming
underwater. They spend roughly half of their lives on land and the other half in the sea.
Although almost all penguin species are native to the Southern Hemisphere, they are not found only in cold climates, such as Antarctica. In fact, only a
few species of penguin live so far south. Several species are found in the temperate zone, but one species, the Galápagos penguin, lives near the equator.
The largest living species is the emperor penguin (Aptenodytes forsteri):[1] on average, adults are about 1.1 m (3 ft 7 in) tall and weigh 35 kg (77 lb). The
smallest penguin species is the little blue penguin (Eudyptula minor), also known as the fairy penguin, which stands around 33 cm (13 in) tall and weighs
1 kg (2.2 lb).[2] Among extant penguins, larger penguins inhabit colder regions, while smaller penguins are generally found in temperate or even tropical
climates. Some prehistoric species attained enormous sizes, becoming as tall or as heavy as an adult human. These were not restricted to Antarctic
regions; on the contrary, subantarctic regions harboured high diversity, and at least one giant penguin occurred in a region around 2,000 km south of the
equato
Penguins (order Sphenisciformes, family Spheniscidae) are a group of aquatic flightless birds. They live almost exclusively in the Southern Hemisphere
, with only one species, the Galápagos penguin, found north of the equator. Highly adapted for life in the water, penguins have countershaded dark and
white plumage and flippers for swimming. Most penguins feed on krill, fish, squid and other forms of sea life which they catch while swimming
underwater. They spend roughly half of their lives on land and the other half in the sea.
Although almost all penguin species are native to the Southern Hemisphere, they are not found only in cold climates, such as Antarctica. In fact, only a
few species of penguin live so far south. Several species are found in the temperate zone, but one species, the Galápagos penguin, lives near the equator.
The largest living species is the emperor penguin (Aptenodytes forsteri):[1] on average, adults are about 1.1 m (3 ft 7 in) tall and weigh 35 kg (77 lb). The
smallest penguin species is the little blue penguin (Eudyptula minor), also known as the fairy penguin, which stands around 33 cm (13 in) tall and weighs
1 kg (2.2 lb).[2] Among extant penguins, larger penguins inhabit colder regions, while smaller penguins are generally found in temperate or even tropical
climates. Some prehistoric species attained enormous sizes, becoming as tall or as heavy as an adult human. These were not restricted to Antarctic
regions; on the contrary, subantarctic regions harboured high diversity, and at least one giant penguin occurred in a region around 2,000 km south of the
equato
Penguins (order Sphenisciformes, family Spheniscidae) are a group of aquatic flightless birds. They live almost exclusively in the Southern Hemisphere
, with only one species, the Galápagos penguin, found north of the equator. Highly adapted for life in the water, penguins have countershaded dark and
white plumage and flippers for swimming. Most penguins feed on krill, fish, squid and other forms of sea life which they catch while swimming
underwater. They spend roughly half of their lives on land and the other half in the sea.
Although almost all penguin species are native to the Southern Hemisphere, they are not found only in cold climates, such as Antarctica. In fact, only a
few species of penguin live so far south. Several species are found in the temperate zone, but one species, the Galápagos penguin, lives near the equator.
The largest living species is the emperor penguin (Aptenodytes forsteri):[1] on average, adults are about 1.1 m (3 ft 7 in) tall and weigh 35 kg (77 lb). The
smallest penguin species is the little blue penguin (Eudyptula minor), also known as the fairy penguin, which stands around 33 cm (13 in) tall and weighs
1 kg (2.2 lb).[2] Among extant penguins, larger penguins inhabit colder regions, while smaller penguins are generally found in temperate or even tropical
climates. Some prehistoric species attained enormous sizes, becoming as tall or as heavy as an adult human. These were not restricted to Antarctic
regions; on the contrary, subantarctic regions harboured high diversity, and at least one giant penguin occurred in a region around 2,000 km south of the
equato
Penguins (order Sphenisciformes, family Spheniscidae) are a group of aquatic flightless birds. They live almost exclusively in the Southern Hemisphere
, with only one species, the Galápagos penguin, found north of the equator. Highly adapted for life in the water, penguins have countershaded dark and
white plumage and flippers for swimming. Most penguins feed on krill, fish, squid and other forms of sea life which they catch while swimming
underwater. They spend roughly half of their lives on land and the other half in the sea.
Although almost all penguin species are native to the Southern Hemisphere, they are not found only in cold climates, such as Antarctica. In fact, only a
few species of penguin live so far south. Several species are found in the temperate zone, but one species, the Galápagos penguin, lives near the equator.
The largest living species is the emperor penguin (Aptenodytes forsteri):[1] on average, adults are about 1.1 m (3 ft 7 in) tall and weigh 35 kg (77 lb). The
smallest penguin species is the little blue penguin (Eudyptula minor), also known as the fairy penguin, which stands around 33 cm (13 in) tall and weighs
1 kg (2.2 lb).[2] Among extant penguins, larger penguins inhabit colder regions, while smaller penguins are generally found in temperate or even tropical
climates. Some prehistoric species attained enormous sizes, becoming as tall or as heavy as an adult human. These were not restricted to Antarctic
regions; on the contrary, subantarctic regions harboured high diversity, and at least one giant penguin occurred in a region around 2,000 km south of the
equato
Penguins (order Sphenisciformes, family Spheniscidae) are a group of aquatic flightless birds. They live almost exclusively in the Southern Hemisphere
, with only one species, the Galápagos penguin, found north of the equator. Highly adapted for life in the water, penguins have countershaded dark and
white plumage and flippers for swimming. Most penguins feed on krill, fish, squid and other forms of sea life which they catch while swimming
underwater. They spend roughly half of their lives on land and the other half in the sea.
Although almost all penguin species are native to the Southern Hemisphere, they are not found only in cold climates, such as Antarctica. In fact, only a
few species of penguin live so far south. Several species are found in the temperate zone, but one species, the Galápagos penguin, lives near the equator.
The largest living species is the emperor penguin (Aptenodytes forsteri):[1] on average, adults are about 1.1 m (3 ft 7 in) tall and weigh 35 kg (77 lb). The
smallest penguin species is the little blue penguin (Eudyptula minor), also known as the fairy penguin, which stands around 33 cm (13 in) tall and weighs
1 kg (2.2 lb).[2] Among extant penguins, larger penguins inhabit colder regions, while smaller penguins are generally found in temperate or even tropical
climates. Some prehistoric species attained enormous sizes, becoming as tall or as heavy as an adult human. These were not restricted to Antarctic
regions; on the contrary, subantarctic regions harboured high diversity, and at least one giant penguin occurred in a region around 2,000 km south of the
equato
Penguins (order Sphenisciformes, family Spheniscidae) are a group of aquatic flightless birds. They live almost exclusively in the Southern Hemisphere
, with only one species, the Galápagos penguin, found north of the equator. Highly adapted for life in the water, penguins have countershaded dark and
white plumage and flippers for swimming. Most penguins feed on krill, fish, squid and other forms of sea life which they catch while swimming
underwater. They spend roughly half of their lives on land and the other half in the sea.
Although almost all penguin species are native to the Southern Hemisphere, they are not found only in cold climates, such as Antarctica. In fact, only a
few species of penguin live so far south. Several species are found in the temperate zone, but one species, the Galápagos penguin, lives near the equator.
The largest living species is the emperor penguin (Aptenodytes forsteri):[1] on average, adults are about 1.1 m (3 ft 7 in) tall and weigh 35 kg (77 lb). The
smallest penguin species is the little blue penguin (Eudyptula minor), also known as the fairy penguin, which stands around 33 cm (13 in) tall and weighs
1 kg (2.2 lb).[2] Among extant penguins, larger penguins inhabit colder regions, while smaller penguins are generally found in temperate or even tropical
climates. Some prehistoric species attained enormous sizes, becoming as tall or as heavy as an adult human. These were not restricted to Antarctic
regions; on the contrary, subantarctic regions harboured high diversity, and at least one giant penguin occurred in a region around 2,000 km south of the
equato
Penguins (order Sphenisciformes, family Spheniscidae) are a group of aquatic flightless birds. They live almost exclusively in the Southern Hemisphere
, with only one species, the Galápagos penguin, found north of the equator. Highly adapted for life in the water, penguins have countershaded dark and
white plumage and flippers for swimming. Most penguins feed on krill, fish, squid and other forms of sea life which they catch while swimming
underwater. They spend roughly half of their lives on land and the other half in the sea.
Although almost all penguin species are native to the Southern Hemisphere, they are not found only in cold climates, such as Antarctica. In fact, only a
few species of penguin live so far south. Several species are found in the temperate zone, but one species, the Galápagos penguin, lives near the equator.
The largest living species is the emperor penguin (Aptenodytes forsteri):[1] on average, adults are about 1.1 m (3 ft 7 in) tall and weigh 35 kg (77 lb). The
smallest penguin species is the little blue penguin (Eudyptula minor), also known as the fairy penguin, which stands around 33 cm (13 in) tall and weighs
1 kg (2.2 lb).[2] Among extant penguins, larger penguins inhabit colder regions, while smaller penguins are generally found in temperate or even tropical
climates. Some prehistoric species attained enormous sizes, becoming as tall or as heavy as an adult human. These were not restricted to Antarctic
regions; on the contrary, subantarctic regions harboured high diversity, and at least one giant penguin occurred in a region around 2,000 km south of the
equato
You might also like
- Order Birds Southern Hemisphere Galápagos Penguin Krill Fish Temperate Little Blue Penguin Prehistoric Subantarctic EquatoDocument12 pagesOrder Birds Southern Hemisphere Galápagos Penguin Krill Fish Temperate Little Blue Penguin Prehistoric Subantarctic EquatoAngelo AstudilloNo ratings yet
- Order Family Aquatic Flightless Birds Southern Hemisphere Antarctica Countershaded Flippers Krill Fish Squid SealifeDocument1 pageOrder Family Aquatic Flightless Birds Southern Hemisphere Antarctica Countershaded Flippers Krill Fish Squid SealifeGomathiRachakondaNo ratings yet
- PenguinDocument1 pagePenguinSachin ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Penguins (Sphenisciformes, Spheniscidae) Are A GroupDocument1 pagePenguins (Sphenisciformes, Spheniscidae) Are A GroupsandeshshivaNo ratings yet
- REPORTDocument3 pagesREPORTMandaNo ratings yet
- Dok 2Document1 pageDok 2lexterhunter1No ratings yet
- Polar BearDocument2 pagesPolar BearRajeshNo ratings yet
- Name Aimen Sabir Reg 2008-Ag-2808 Roll No. 601 Submitted T DR - Khurum AshfaqDocument14 pagesName Aimen Sabir Reg 2008-Ag-2808 Roll No. 601 Submitted T DR - Khurum AshfaqfoqajuttNo ratings yet
- New Microsoft Office Word DocumentDocument5 pagesNew Microsoft Office Word Documentsnip3r45No ratings yet
- My First Book about the Animal Alphabet of Antarctica: Amazing Animal Books - Children's Picture BooksFrom EverandMy First Book about the Animal Alphabet of Antarctica: Amazing Animal Books - Children's Picture BooksNo ratings yet
- Penguins (Document6 pagesPenguins (kimgNo ratings yet
- Endangered SpeciesDocument7 pagesEndangered SpeciesDaryll Anne LagtaponNo ratings yet
- Antarctic PenguinsDocument16 pagesAntarctic Penguinsavncntn100% (1)
- Penguins of The WorldDocument4 pagesPenguins of The WorldMicu RobertNo ratings yet
- Pingüino 1 en-USDocument3 pagesPingüino 1 en-USlalo 3 lalo3No ratings yet
- Report Text About PenguinDocument2 pagesReport Text About PenguinMuhammad Audi Arya PratamaNo ratings yet
- Little PenguinsDocument5 pagesLittle PenguinsPriscila Torres ConradoNo ratings yet
- Penguins Like Warm Climates Too! Animal Books for Kids 9-12 | Children's Animal BooksFrom EverandPenguins Like Warm Climates Too! Animal Books for Kids 9-12 | Children's Animal BooksNo ratings yet
- Penguin PDFDocument2 pagesPenguin PDFDaniel CarringtonNo ratings yet
- Cetaceans ReportDocument49 pagesCetaceans ReportArianeManlangitNo ratings yet
- Penguin: 2 Systematics and EvolutionDocument15 pagesPenguin: 2 Systematics and EvolutionMsKaroly100% (1)
- Island-Dwellers Emperor Adélie Chinstrap Gentoo Blubber: Life On LandDocument3 pagesIsland-Dwellers Emperor Adélie Chinstrap Gentoo Blubber: Life On LandZonny Zivins PresentsNo ratings yet
- Cahya Hidayat - XI AcpDocument2 pagesCahya Hidayat - XI AcpdedeNo ratings yet
- What Are Penguins?Document1 pageWhat Are Penguins?AngelNo ratings yet
- Answer 1. Text PenguinsDocument3 pagesAnswer 1. Text PenguinsRikudo AmubaNo ratings yet
- Bony FishesDocument70 pagesBony FishesJigar PatelNo ratings yet
- Wild Life of AntarcticaDocument5 pagesWild Life of Antarcticaapi-239805072No ratings yet
- Handy Pocket Guide to Tropical Coral Reef FishesFrom EverandHandy Pocket Guide to Tropical Coral Reef FishesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- AntarcticaDocument13 pagesAntarcticaPetra BalázsyNo ratings yet
- Polar Bear Habitat PresentationDocument10 pagesPolar Bear Habitat PresentationAhmad Usman KhanNo ratings yet
- Food Web of The ArcticDocument9 pagesFood Web of The ArcticAnna SkullHong ChullyHeenimNo ratings yet
- Penguin ReportDocument8 pagesPenguin ReportFelicia FerentinosNo ratings yet
- Tugas Bahasa InggrisDocument2 pagesTugas Bahasa InggrisCamel TzyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Snakes of Papua New GuineaDocument23 pagesChapter 2 Snakes of Papua New GuineaIrfan Haidar BasyirNo ratings yet
- Ingles T.P.Document4 pagesIngles T.P.Arai Ortiz EsquivelNo ratings yet
- Penguin Characterized Feathers Galapagos IslandsDocument2 pagesPenguin Characterized Feathers Galapagos IslandsHana HafizaNo ratings yet
- Galapagos Iguanas and LizardsDocument16 pagesGalapagos Iguanas and LizardsHostage MurdererNo ratings yet
- Text Report Tentang Binatang Hewan Laut (Marine Life)Document1 pageText Report Tentang Binatang Hewan Laut (Marine Life)Nur Idhofi RahmadNo ratings yet
- Notemaking Worksheet With AnswerDocument2 pagesNotemaking Worksheet With Answershubh100% (1)
- Antarctica Food ChainDocument12 pagesAntarctica Food Chainapi-263658859No ratings yet
- Foca AnilladaDocument5 pagesFoca AnilladaPaula SolerNo ratings yet
- Aquatic MammalsDocument4 pagesAquatic MammalsNarasimha MurthyNo ratings yet
- HumboldtPenguin PDFDocument3 pagesHumboldtPenguin PDFAndrew LiebermannNo ratings yet
- Penguins Are BirdsDocument4 pagesPenguins Are BirdsAnonymous 6MSekAxCnZNo ratings yet
- Everything That You Need to Know about Our Fishy Friends - Animal Book Age 5 | Children's Animal BooksFrom EverandEverything That You Need to Know about Our Fishy Friends - Animal Book Age 5 | Children's Animal BooksNo ratings yet
- Cetmar No.11 Teacher Mariana López Gutiérrez English II Redaction Project Student: Torres Martinez RubenDocument5 pagesCetmar No.11 Teacher Mariana López Gutiérrez English II Redaction Project Student: Torres Martinez RubenRUBEN TORRES MARTINEZNo ratings yet
- Emperor PenguinDocument1 pageEmperor PenguinHilda Calva PerezNo ratings yet
- Cetmar No.11 Teacher Mariana López Gutiérrez English II Redaction Project Student: Torres Martinez RubenDocument5 pagesCetmar No.11 Teacher Mariana López Gutiérrez English II Redaction Project Student: Torres Martinez RubenRUBEN TORRES MARTINEZNo ratings yet
- Bigcats DivitDocument19 pagesBigcats DivitdivitsmathurNo ratings yet
- SharksDocument3 pagesSharkslee35No ratings yet
- Wildlife Fact File - Birds - 81-90Document20 pagesWildlife Fact File - Birds - 81-90ClearMind84No ratings yet
- Pelican: Submitted By: Hassan Saeed Submitted To: Dr. Zubair AnjumDocument3 pagesPelican: Submitted By: Hassan Saeed Submitted To: Dr. Zubair AnjumDr-Hassan SaeedNo ratings yet
- Artic PenguinDocument2 pagesArtic PenguinFaisal YudhaNo ratings yet
- Factual Report Sea SnakeDocument2 pagesFactual Report Sea SnakeHarahassNo ratings yet
- Extant Species Genus Wild Boar Solitary But Social Habitat Eastern Anatolia Region Himalayas Bali Sunda Western South Asia Siberian TeDocument10 pagesExtant Species Genus Wild Boar Solitary But Social Habitat Eastern Anatolia Region Himalayas Bali Sunda Western South Asia Siberian TeAngelo AstudilloNo ratings yet
- For Other Uses, See,, and .: Bat (Disambiguation) BAT (Disambiguation) Bats (Disambiguation)Document12 pagesFor Other Uses, See,, and .: Bat (Disambiguation) BAT (Disambiguation) Bats (Disambiguation)Angelo AstudilloNo ratings yet
- For Other Uses, See .: Lion (Disambiguation)Document9 pagesFor Other Uses, See .: Lion (Disambiguation)Angelo AstudilloNo ratings yet
- DummyDocument1 pageDummyAngelo AstudilloNo ratings yet
- Sea OtterDocument22 pagesSea OtterAngelo AstudilloNo ratings yet
- DummyDocument1 pageDummyAngelo AstudilloNo ratings yet
- Extraction and Purification of Nucleic Acid Using CBNP & PCIA TechniqueDocument4 pagesExtraction and Purification of Nucleic Acid Using CBNP & PCIA TechniqueAngelo AstudilloNo ratings yet
- Extraction and Purification of Nucleic Acid Using CBNP & PCIA TechniqueDocument4 pagesExtraction and Purification of Nucleic Acid Using CBNP & PCIA TechniqueAngelo AstudilloNo ratings yet
- Isolation of Nucleic AcidsDocument8 pagesIsolation of Nucleic AcidsAngelo AstudilloNo ratings yet
- Isolation of Nucleic Acids: Methods in Molecular Biology February 2006Document8 pagesIsolation of Nucleic Acids: Methods in Molecular Biology February 2006Angelo AstudilloNo ratings yet
- Splices LAS 3rd Quarter Week 1Document6 pagesSplices LAS 3rd Quarter Week 1Winnielyn Quarteros BarreraNo ratings yet
- Interventional Studies 2Document28 pagesInterventional Studies 2Abdul RazzakNo ratings yet
- Exploring Nurses' Knowledge of The Glasgow Coma Scale in Intensive Care and Emergency Departments at A Tertiary Hospital in Riyadh City, Saudi ArabiaDocument9 pagesExploring Nurses' Knowledge of The Glasgow Coma Scale in Intensive Care and Emergency Departments at A Tertiary Hospital in Riyadh City, Saudi Arabianishu thapaNo ratings yet
- Full Download Bontragers Textbook of Radiographic Positioning and Related Anatomy 9th Edition Lampignano Test BankDocument36 pagesFull Download Bontragers Textbook of Radiographic Positioning and Related Anatomy 9th Edition Lampignano Test Bankjohn5kwillis100% (22)
- Contemp Module 56Document5 pagesContemp Module 56crisanta pizonNo ratings yet
- Bridging The Divide Between Saas and Enterprise Datacenters: An Oracle White Paper Feb 2010Document18 pagesBridging The Divide Between Saas and Enterprise Datacenters: An Oracle White Paper Feb 2010Danno NNo ratings yet
- The Life Cycle of Brent FieldDocument21 pagesThe Life Cycle of Brent FieldMalayan AjumovicNo ratings yet
- Mod 2 MC - GSM, GPRSDocument61 pagesMod 2 MC - GSM, GPRSIrene JosephNo ratings yet
- 60 Plan of DepopulationDocument32 pages60 Plan of DepopulationMorena Eresh100% (1)
- Thesis Preliminary PagesDocument8 pagesThesis Preliminary Pagesukyo0801No ratings yet
- Sheridan Specialized Building Products LLC - Queue Solutions Commercial Proposal by SeQure TechnologiesDocument6 pagesSheridan Specialized Building Products LLC - Queue Solutions Commercial Proposal by SeQure Technologiessailesh psNo ratings yet
- Family Planning MethodsDocument20 pagesFamily Planning MethodsRoel Marcial100% (2)
- RF Based Dual Mode RobotDocument17 pagesRF Based Dual Mode Robotshuhaibasharaf100% (2)
- Syllabus: Cambridge IGCSE (9-1) Art & Design 0989Document27 pagesSyllabus: Cambridge IGCSE (9-1) Art & Design 0989Jashan LoombaNo ratings yet
- LC 67002000 B Hr-Jumbo enDocument2 pagesLC 67002000 B Hr-Jumbo enJulio OrtegaNo ratings yet
- CV - Mohsin FormatDocument2 pagesCV - Mohsin FormatMuhammad Junaid IqbalNo ratings yet
- JSSC JDLCCE 2021 (Civil Engineering) Official Pape 230615 233342Document39 pagesJSSC JDLCCE 2021 (Civil Engineering) Official Pape 230615 233342Bhuban KumbhakarNo ratings yet
- What Role Does Imagination Play in Producing Knowledge About The WorldDocument1 pageWhat Role Does Imagination Play in Producing Knowledge About The WorldNathanael Samuel KuruvillaNo ratings yet
- Prelims CB em Ii5Document21 pagesPrelims CB em Ii5Ugaas SareeyeNo ratings yet
- Leonard Nadler' ModelDocument3 pagesLeonard Nadler' ModelPiet Gabz67% (3)
- 2019 Auto Truck Key Blank Reference PDFDocument188 pages2019 Auto Truck Key Blank Reference PDFAlbert RodaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Cobit Framework - Week 3Document75 pagesIntroduction To Cobit Framework - Week 3Teddy HaryadiNo ratings yet
- GRADE 302: Element Content (%)Document3 pagesGRADE 302: Element Content (%)Shashank Saxena100% (1)
- First Semester-NOTESDocument182 pagesFirst Semester-NOTESkalpanaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry For Changing Times 14th Edition Hill Mccreary Solution ManualDocument24 pagesChemistry For Changing Times 14th Edition Hill Mccreary Solution ManualElaineStewartieog100% (50)
- Dadm Assesment #2: Akshat BansalDocument24 pagesDadm Assesment #2: Akshat BansalAkshatNo ratings yet
- Property Case Digest DonationDocument13 pagesProperty Case Digest DonationJesselle Maminta100% (1)
- You'Re My Everything - Glenn FredlyDocument2 pagesYou'Re My Everything - Glenn FredlyTommy Juliansyah MarsenoNo ratings yet
- 184 Учебная программа Английский язык 10-11 кл ОГНDocument44 pages184 Учебная программа Английский язык 10-11 кл ОГНзульфираNo ratings yet
- An Overview of Marketing - Week 1Document7 pagesAn Overview of Marketing - Week 1Jowjie TVNo ratings yet