Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Newton Raphson: Numerical Solving Method
Uploaded by
Kundan Anand0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views5 pagesOriginal Title
Newton Raphson
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views5 pagesNewton Raphson: Numerical Solving Method
Uploaded by
Kundan AnandCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 5
Newton Raphson
Numerical Solving Method
Introduction
• Introduction to Iterative methods: There are number of iterative
methods typically generate a sequence of estimates of the solution
which is expected to converge to the true solution. Newton-Raphson
method is also one of the iterative methods which are used to find
the roots of given expression.
MATLAB Code
clc;
close all;
clear all;
syms x;
f=x^3 - x - 1; %Enter the Function here
g=diff(f); %The Derivative of the Function
n=input('Enter the number of decimal places:');
epsilon = 5*10^-(n+1)
x0 = input('Enter the initial approximation:');
for i=1:100
f0=vpa(subs(f,x,x0)); %Calculating the value of function at x0
f0_der=vpa(subs(g,x,x0)); %Calculating the value of function derivative at x0
y=x0-f0/f0_der; %3 The Formula
err=abs(y-x0);
if err<epsilon %checking the 5amount of error at each iteration
break
end
x0=y;
end
y = y - rem(y,10^-n); %Displaying upto required decimal places
fprintf('The Root is : %f \n',y);
fprintf('No. of Iterations : %d\n',i);
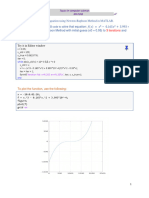
Output
Enter the number of decimal places:4
epsilon =
5.0000e-05
Enter the initial approximation:0.003
The Root is : 1.324700
No. of Iterations : 24
You might also like
- Math IV Lab: Different Methods To Find RootsDocument9 pagesMath IV Lab: Different Methods To Find RootsMuhammad Usama 796-FET/BSME/F18No ratings yet
- Lap Report On Newton Raphson MethodDocument9 pagesLap Report On Newton Raphson MethodSamixa TimalcenaNo ratings yet
- Matlab Newton-Raphson Root Finding CodeDocument2 pagesMatlab Newton-Raphson Root Finding CodeDeema AbuzaidNo ratings yet
- COMPARING NUMERICAL METHODSDocument8 pagesCOMPARING NUMERICAL METHODSSohaib Raja RajaNo ratings yet
- Bisection Method AlgorithmDocument10 pagesBisection Method AlgorithmSyed TuhinNo ratings yet
- NewtDocument2 pagesNewtch8fzk5v74No ratings yet
- Roots of Equations: 1.0.1 Newton's MethodDocument20 pagesRoots of Equations: 1.0.1 Newton's MethodMahmoud El-MahdyNo ratings yet
- Lab 01 Bisection Regula-Falsi and Newton-RaphsonDocument12 pagesLab 01 Bisection Regula-Falsi and Newton-RaphsonUmair Ali ShahNo ratings yet
- Numerical Methods for Solving EquationsDocument22 pagesNumerical Methods for Solving EquationsarafatasgharNo ratings yet
- Numerical Analysis All Lab ReportsDocument23 pagesNumerical Analysis All Lab ReportsZia JanNo ratings yet
- Nonlinear 1 PDFDocument11 pagesNonlinear 1 PDFمرتضى عباسNo ratings yet
- School of Chemical Engineering and Physical SciencesDocument7 pagesSchool of Chemical Engineering and Physical SciencesKoshika KoyyanaNo ratings yet
- Nonlinear EquationsDocument12 pagesNonlinear EquationsElőd JobbNo ratings yet
- Numerical Methods Roots of Equation Chapter OneDocument5 pagesNumerical Methods Roots of Equation Chapter Oneadnan-651358No ratings yet
- CM FileDocument15 pagesCM Fileprashantmahawar7546No ratings yet
- Nonlinear Equations MatlabDocument18 pagesNonlinear Equations MatlabRamakrishna_Ch_7716No ratings yet
- Numerical Methods-Lab-ManualDocument52 pagesNumerical Methods-Lab-Manualapi-31548536783% (6)
- Mix Achar Numerical MatlabDocument4 pagesMix Achar Numerical MatlabMuhammad MaazNo ratings yet
- Secent Method MATLAB CodeDocument4 pagesSecent Method MATLAB Codeasad malikNo ratings yet
- LABORATORY ACTIVITY 1 Puno 2Document8 pagesLABORATORY ACTIVITY 1 Puno 2Philip MiguelNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 PDFDocument3 pagesLecture 3 PDFAli MahmoudNo ratings yet
- Newton-Raphson MethodDocument9 pagesNewton-Raphson MethodMor DepRzNo ratings yet
- Book BindDocument79 pagesBook BindFaye YturraldeNo ratings yet
- Newton Raphson MethodDocument4 pagesNewton Raphson MethodLn Amitav BiswasNo ratings yet
- Algorithm:: Experiment No: 03 Experiment Name: Write A Program Implementation of AimDocument3 pagesAlgorithm:: Experiment No: 03 Experiment Name: Write A Program Implementation of AimRasel MadberNo ratings yet
- Newton-Raphson Root Finding LabDocument6 pagesNewton-Raphson Root Finding Labqais alnawafahNo ratings yet
- Lab NMDocument16 pagesLab NMrojandahal99No ratings yet
- Assignment 3 Open MethodDocument5 pagesAssignment 3 Open MethodPaolo ValdezNo ratings yet
- Idoc - Pub - Ccodechamp Com C Program of Newton Raphson Method C Code Cha PDFDocument7 pagesIdoc - Pub - Ccodechamp Com C Program of Newton Raphson Method C Code Cha PDFPrincess NobleNo ratings yet
- Numerical Method (Secant Method)Document20 pagesNumerical Method (Secant Method)Bhuwan DahalNo ratings yet
- MATLAB TipsDocument9 pagesMATLAB TipsAlejandra MorantesNo ratings yet
- Matlab CodeDocument2 pagesMatlab CodeMP INTERNATIONAL EXPORT PVT. LTD.No ratings yet
- Chbe 553 Notes 1Document6 pagesChbe 553 Notes 1सुबेदी गौरवNo ratings yet
- Solving Equations (Finding Zeros)Document20 pagesSolving Equations (Finding Zeros)nguyendaibkaNo ratings yet
- Siddhant CM FileDocument37 pagesSiddhant CM Filemysteriousjohn009No ratings yet
- 1.to Find The Roots of Non-Linear Equation Using Newton Raphson's MethodDocument2 pages1.to Find The Roots of Non-Linear Equation Using Newton Raphson's Methodmanjula mandavaNo ratings yet
- Aryasatya Wicaksono - 5008211047 - Modul 2 Final ReportDocument15 pagesAryasatya Wicaksono - 5008211047 - Modul 2 Final Reportdhani7No ratings yet
- Homework Set No. 5, Numerical Computation: 1. Bisection MethodDocument4 pagesHomework Set No. 5, Numerical Computation: 1. Bisection MethodkelbmutsNo ratings yet
- Individual AssignmentDocument5 pagesIndividual AssignmentAcik SulieSolNo ratings yet
- Complete NMCP FileDocument29 pagesComplete NMCP FileMEB05 Kishyon KumarNo ratings yet
- MATH 130 NUMERICAL SOLUTION TO CE PROBLEMSDocument10 pagesMATH 130 NUMERICAL SOLUTION TO CE PROBLEMSMia ManguiobNo ratings yet
- School of Chemical Engineering Winter Semester - 2020 / 21 Che3001 - Computational Methods in Process Engineering Experiment 1Document7 pagesSchool of Chemical Engineering Winter Semester - 2020 / 21 Che3001 - Computational Methods in Process Engineering Experiment 1Sisay AmareNo ratings yet
- Loops in MATLAB - Summing Numbers and Filtering VectorsDocument18 pagesLoops in MATLAB - Summing Numbers and Filtering Vectorslucky bhasinNo ratings yet
- Numerical Method 1 PDFDocument2 pagesNumerical Method 1 PDFGagan DeepNo ratings yet
- Newton Raphson ApoorwaDocument16 pagesNewton Raphson Apoorwaprashantnarayandubey1No ratings yet
- '''MatlabDocument2 pages'''Matlabsurafel123emiruNo ratings yet
- Newton's Raphson Method Lab ReportDocument4 pagesNewton's Raphson Method Lab Reportmuzahir.ali.baloch2021No ratings yet
- CheatsDocument11 pagesCheatsDEBJITROXX GAMINGNo ratings yet
- Implementation in Matlab of Differential EvolutionDocument26 pagesImplementation in Matlab of Differential EvolutionJuan Alex Arequipa ChecaNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1Document2 pagesExperiment 1Shubham SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Week 1Document13 pagesWeek 1IsmaelNo ratings yet
- Summary - Python Numerical MethodsDocument2 pagesSummary - Python Numerical MethodsBetter Than Ur LVNo ratings yet
- 1 ProblemsDocument7 pages1 ProblemsKAAVIYA R 20BEC0183No ratings yet
- Roots of EquationsDocument51 pagesRoots of EquationsMahesh JawaleNo ratings yet
- Session 03Document6 pagesSession 03Just SomebodyNo ratings yet
- A-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (8)
- A Brief Introduction to MATLAB: Taken From the Book "MATLAB for Beginners: A Gentle Approach"From EverandA Brief Introduction to MATLAB: Taken From the Book "MATLAB for Beginners: A Gentle Approach"Rating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (2)