Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 02 BCO
Uploaded by
Jeterine AriasOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 02 BCO
Uploaded by
Jeterine AriasCopyright:
Available Formats
CCoommppuutterer FFununddaammenenttaallss:: PPrradadeeeepp
KK.. SSiinhnhaa && PPrriititi SSiinhanha
Computer Fundamentals: Pradeep K. Sinha & Priti Sinha
Learning Objectives
In this chapter you will learn about:
Basic operations performed by all types of computer
systems
Basic organization of a computer system
Input unit and its functions
Output unit and its functions
Storage unit and its functions
Types of storage used in a computer system
(Continued on next slide)
Ref. Page 15 Chapter 2: Basic Computer Organization Slide 2/16
Computer Fundamentals: Pradeep K. Sinha & Priti Sinha
Learning Objectives
(Continued from previous slide..)
Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU)
Control Unit (CU)
Central Processing Unit (CPU)
Computer as a system
Ref. Page 15 Chapter 2: Basic Computer Organization Slide 3/16
Computer Fundamentals: Pradeep K. Sinha & Priti Sinha
The Five Basic Operations of a Computer System
Inputting. The process of entering data and instructions
into the computer system
Storing. Saving data and instructions to make them
readily available for initial or additional processing
whenever required
Processing. Performing arithmetic operations (add,
subtract, multiply, divide, etc.) or logical operations
(comparisons like equal to, less than, greater than, etc.)
on data to convert them into useful information
(Continued on next slide)
Ref. Page 15 Chapter 2: Basic Computer Organization Slide 4/16
Computer Fundamentals: Pradeep K. Sinha & Priti Sinha
The Five Basic Operations of a Computer System
Outputting. The process of producing useful information
or results for the user such as a printed report or visual
display
Controlling. Directing the manner and sequence in which
all of the above operations are performed
Ref. Page 15 Chapter 2: Basic Computer Organization Slide 5/16
Computer Fundamentals: Pradeep K. Sinha & Priti Sinha
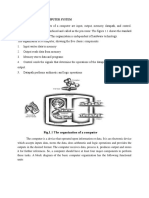
Basic Organization of a Computer System
Storage Unit
Secondary
Storage
Program Information
Input Output
and (Results)
Unit Unit
Data Primary
Storage
Control
Unit
Indicates flow of
instructions and data
Arithmetic Indicates the control
Logic exercised by the
Unit control unit
Central Processing Unit (CPU)
Ref. Page 16 Chapter 2: Basic Computer Organization Slide 6/16
Computer Fundamentals: Pradeep K. Sinha & Priti Sinha
Input Unit
An input unit of a computer system performs the
following functions:
1. It accepts (or reads) instructions and data from outside
world
2. It converts these instructions and data in computer
acceptable form
3. It supplies the converted instructions and data to the
computer system for further processing
Ref. Page 16 Chapter 2: Basic Computer Organization Slide 7/16
Computer Fundamentals: Pradeep K. Sinha & Priti Sinha
Output Unit
An output unit of a computer system performs the
following functions:
1. It accepts the results produced by the computer, which
are in coded form and hence, cannot be easily
understood by us
2. It converts these coded results to human acceptable
(readable) form
3. It supplies the converted results to outside world
Ref. Page 16 Chapter 2: Basic Computer Organization Slide 8/16
Computer Fundamentals: Pradeep K. Sinha & Priti Sinha
Storage Unit
The storage unit of a computer system holds (or stores)
the following :
1. Data and instructions required for processing (received
from input devices)
2. Intermediate results of processing
3. Final results of processing, before they are released to
an output device
Ref. Page 17 Chapter 2: Basic Computer Organization Slide 9/16
Computer Fundamentals: Pradeep K. Sinha & Priti Sinha
Two Types of Storage
Primary storage
Used to hold running program instructions
Used to hold data, intermediate results, and
results of ongoing processing of job(s)
Fast in operation
Small Capacity
Expensive
Volatile (looses data on power dissipation)
(Continued on next slide)
Ref. Page 17 Chapter 2: Basic Computer Organization Slide 10/16
Computer Fundamentals: Pradeep K. Sinha & Priti Sinha
Two Types of Storage
(Continued from previous slide..)
Secondary storage
Used to hold stored program instructions
Used to hold data and information of stored jobs
Slower than primary storage
Large Capacity
Lot cheaper that primary storage
Retains data even without power
Ref. Page 17 Chapter 2: Basic Computer Organization Slide 11/16
Computer Fundamentals: Pradeep K. Sinha & Priti Sinha
Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU)
Arithmetic Logic Unit of a computer system is the place
where the actual executions of instructions takes place during
processing operation
Ref. Page 18 Chapter 2: Basic Computer Organization Slide 12/16
Computer Fundamentals: Pradeep K. Sinha & Priti Sinha
CCoontrol Unit (CU)
Control Unit of a computer system manages and coordinates
the operations of all other components of the computer
system
Ref. Page 18 Chapter 2: Basic Computer Organization Slide 13/16
Computer Fundamentals: Pradeep K. Sinha & Priti Sinha
CCeentral Processing Unit (CPU)
Arithmetic Central
Logic Control Unit = Processing
+ (CU)
Unit Unit
(ALU) (CPU)
It is the brain of a computer system
It is responsible for controlling the operations of
all other units of a computer system
Ref. Page 18 Chapter 2: Basic Computer Organization Slide 14/16
Computer Fundamentals: Pradeep K. Sinha & Priti Sinha
The System Concept
A system has following three characteristics:
1. A system has more than one element
2. All elements of a system are logically related
3. All elements of a system are controlled in a manner to
achieve the system goal
A computer is a system as it comprises of integrated
components (input unit, output unit, storage unit, and
CPU) that work together to perform the steps called for in
the executing program
Ref. Page 18 Chapter 2: Basic Computer Organization Slide 15/16
Computer Fundamentals: Pradeep K. Sinha & Priti Sinha
Key Words/Phrases
Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU) Output interface
Auxiliary storage Output unit
Central Processing Unit (CPU) Outputting
Computer system Primate storage
Control Unit (CU) Processing
Controlling Secondary storage
Input interface Storage unit
Input unit Storing
Inputting System
Main memory
Ref. Page 19 Chapter 2: Basic Computer Organization Slide 16/16
You might also like
- 2.basic Computer OrganisationDocument16 pages2.basic Computer OrganisationkhankhanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 BCO 2opDocument10 pagesChapter 2 BCO 2opBalkrishan GoswamiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 02 BCODocument16 pagesChapter 02 BCOUdita BadolaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2Document15 pagesLecture 2Priyam ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- 2 Module 2.1 - BcoDocument15 pages2 Module 2.1 - BcovivekparasharNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Basic Computer OrganisationDocument5 pagesChapter 2 Basic Computer OrganisationHimanshu GamingNo ratings yet
- Chapter IiiDocument5 pagesChapter IiiYsha FernNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14-OS-2oP PDFDocument37 pagesChapter 14-OS-2oP PDFBalkrishan GoswamiNo ratings yet
- Puter OrganisationDocument27 pagesPuter Organisationluynaaaaa75No ratings yet
- 2 Computer OrganisationDocument39 pages2 Computer Organisationarunbalaji2020No ratings yet
- Introduction To Personal Computer ComponentsDocument18 pagesIntroduction To Personal Computer ComponentsMohammadreza FasihiNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Computer: Department of Computer & Software Technology by Kiramat RahmanDocument16 pagesIntroduction To Computer: Department of Computer & Software Technology by Kiramat RahmandangermanNo ratings yet
- Computer Organization & Architecture: Instructor Engr. Zeeshan RazaDocument35 pagesComputer Organization & Architecture: Instructor Engr. Zeeshan RazaMeena ShahNo ratings yet
- Computer System Computer ArchitectureDocument7 pagesComputer System Computer ArchitectureSuman Samal MagarNo ratings yet
- L-2 Basic Computer OrganizationDocument14 pagesL-2 Basic Computer OrganizationSakib AhmedNo ratings yet
- Topic 3 Basic Computer OrganizationDocument15 pagesTopic 3 Basic Computer OrganizationShwe Eain LinnNo ratings yet
- Mba (1 Semester) Computer Fundamental Mba Unit - I: Secondary StorageDocument12 pagesMba (1 Semester) Computer Fundamental Mba Unit - I: Secondary Storageshashi shekhar dixitNo ratings yet
- Explain Block Diagram of Computer and Its ComponentsDocument7 pagesExplain Block Diagram of Computer and Its ComponentsGame ChangerNo ratings yet
- Cite1004 Activity 1 MidtermDocument3 pagesCite1004 Activity 1 MidtermJoshua LimbagaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14-OSDocument54 pagesChapter 14-OSShikha MaheshwariNo ratings yet
- Computer Organization 2022-23Document156 pagesComputer Organization 2022-23Kakashi Hatake100% (1)
- Components CFDocument15 pagesComponents CFankudubeyNo ratings yet
- Computer - ComponentsDocument2 pagesComputer - ComponentsジョージNo ratings yet
- CAO Unit 1Document13 pagesCAO Unit 1mdmomin7517No ratings yet
- Cite1004 Activity 1 MidtermDocument3 pagesCite1004 Activity 1 MidtermJoshua LimbagaNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 - Basic Computer EngineeringDocument27 pagesUnit 1 - Basic Computer Engineeringgenokol858No ratings yet
- cls-01 PDF Computer and Its GenerationDocument27 pagescls-01 PDF Computer and Its GenerationHabiba ShifaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 02 Introduction To ComputingDocument16 pagesLecture 02 Introduction To ComputingHuzaifa QamashNo ratings yet
- ch01 ComputerBasic PDFDocument131 pagesch01 ComputerBasic PDFAbdreyll GerardNo ratings yet
- Lecture - 1 (Computer and Web Skills - I)Document59 pagesLecture - 1 (Computer and Web Skills - I)Qaisar Mehmood100% (1)
- Unit 1Document73 pagesUnit 1Rohan MehraNo ratings yet
- Q What Are The Essential Components of ComputersDocument3 pagesQ What Are The Essential Components of Computersgurdeep360100% (1)
- Unit 1 - Basic Computer EngineeringDocument27 pagesUnit 1 - Basic Computer EngineeringVikas JainNo ratings yet
- Intro To Computers and Se Chapter 2Document9 pagesIntro To Computers and Se Chapter 2amirNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document77 pagesUnit 1ladukhushi09No ratings yet
- Rajagiri School of Engineering and TechnologyDocument44 pagesRajagiri School of Engineering and TechnologyBennet MathewNo ratings yet
- Quantum COADocument293 pagesQuantum COAAnshika Chauhan88% (16)
- Computer ApplicationssDocument29 pagesComputer ApplicationssFatima SarwarNo ratings yet
- Components of A ComputerDocument5 pagesComponents of A ComputersoujanaNo ratings yet
- Components of Computer System: Input, Output, Processor and StorageDocument10 pagesComponents of Computer System: Input, Output, Processor and StorageMmaNo ratings yet
- Module - 01 - Computer FundamentalsDocument18 pagesModule - 01 - Computer FundamentalsRide RelaxNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2Document17 pagesLecture 2MD AZIZUL HOQUENo ratings yet
- Control Processing Unit (CPU) : AssignmentDocument5 pagesControl Processing Unit (CPU) : AssignmentBlackBeardNo ratings yet
- 5 Basic Operations Performed by Computer SystemDocument5 pages5 Basic Operations Performed by Computer SystemNuj Wehtam Inairam100% (7)
- Block Diagram of Computer (MBA-I)Document10 pagesBlock Diagram of Computer (MBA-I)Gurinder DeolNo ratings yet
- Computer COMPONENTDocument6 pagesComputer COMPONENTwowafer745No ratings yet
- Unit 1Document45 pagesUnit 1aryan93165No ratings yet
- Components of A Computer SystemDocument26 pagesComponents of A Computer SystemheheheheNo ratings yet
- Computer Fundamental, Organization and ArchitectureDocument19 pagesComputer Fundamental, Organization and Architecturepradhumnyadav756No ratings yet
- Data Is Raw Material Used As Input and Information Is Processed Data ObtainedDocument2 pagesData Is Raw Material Used As Input and Information Is Processed Data ObtainedHimanshuRanaNo ratings yet
- The Basic Architecture of Computer SystemDocument30 pagesThe Basic Architecture of Computer SystemAnnie GloryNo ratings yet
- Module 2 - Computer SystemDocument12 pagesModule 2 - Computer SystemKarl Steven Adalem MaddelaNo ratings yet
- A Computer Can Process DataDocument3 pagesA Computer Can Process DataMario ToloNo ratings yet
- FunctionalunitsofcomputerDocument6 pagesFunctionalunitsofcomputerMEGHA SASINo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document15 pagesUnit 1Aryan AnandNo ratings yet
- The Computer System: Function & InterconnectionsDocument46 pagesThe Computer System: Function & Interconnectionsjulius opolotNo ratings yet
- COAL Lecture 04Document31 pagesCOAL Lecture 04muhammad amirNo ratings yet
- PlayStation 2 Architecture: Architecture of Consoles: A Practical Analysis, #12From EverandPlayStation 2 Architecture: Architecture of Consoles: A Practical Analysis, #12No ratings yet
- Electrical Circuits Ii Direction: Read Each Item Carefully and Chose The BEST Answer From The Given Choices. Write YourDocument4 pagesElectrical Circuits Ii Direction: Read Each Item Carefully and Chose The BEST Answer From The Given Choices. Write YourJeterine AriasNo ratings yet
- Signals and Systems TutorialDocument62 pagesSignals and Systems TutorialJeterine AriasNo ratings yet
- Chapter 01 IntroductionDocument17 pagesChapter 01 IntroductionJeterine AriasNo ratings yet
- CapacitorsDocument44 pagesCapacitorsnoah williamsNo ratings yet
- R R R V: Voltage DividerDocument8 pagesR R R V: Voltage DividerNajmusNo ratings yet
- Conversiazecimalbinar KawDocument7 pagesConversiazecimalbinar KawOctavian MihaiNo ratings yet
- Eroarea de Trunchiere - KawDocument6 pagesEroarea de Trunchiere - KawOctavian MihaiNo ratings yet
- Cassy Baking Tools and Equipment - EditedDocument20 pagesCassy Baking Tools and Equipment - EditedJeterine AriasNo ratings yet
- 1-2 Measuring ErrorDocument15 pages1-2 Measuring ErrorJeterine AriasNo ratings yet
- History of CommunicationDocument2 pagesHistory of CommunicationJeterine AriasNo ratings yet
- Magnitude ComparatorDocument15 pagesMagnitude ComparatorJeterine AriasNo ratings yet
- CommunicationDocument4 pagesCommunicationJeterine AriasNo ratings yet
- Cassy Baking Tools and Equipment - EditedDocument20 pagesCassy Baking Tools and Equipment - EditedJeterine AriasNo ratings yet
- Cover PageDocument1 pageCover PageJeterine AriasNo ratings yet
- MA Premiere Pro Instructions PDFDocument1 pageMA Premiere Pro Instructions PDFSaim ShahzadNo ratings yet
- Section 8Document2 pagesSection 8Jeterine AriasNo ratings yet
- Ojt Endorsement LetterDocument1 pageOjt Endorsement LetterJeterine AriasNo ratings yet
- StubDocument18 pagesStubJeterine AriasNo ratings yet
- TitlesDocument4 pagesTitlesJeterine AriasNo ratings yet
- Ojt Endorsement LetterDocument1 pageOjt Endorsement LetterJeterine AriasNo ratings yet
- Section 24Document1 pageSection 24Jeterine AriasNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Properties of Materials DocsDocument6 pagesMagnetic Properties of Materials DocsJeterine AriasNo ratings yet
- Section 24Document1 pageSection 24Jeterine AriasNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 (Section 6) : Acoustics FundamentalsDocument3 pagesChapter 2 (Section 6) : Acoustics FundamentalsJeterine AriasNo ratings yet
- Section 8Document2 pagesSection 8Jeterine AriasNo ratings yet
- 01 B.Tech CSE Syllabus FinalDocument79 pages01 B.Tech CSE Syllabus FinalSamir KarNo ratings yet
- Computer Architecture and Organization: Adigrat University Electrical and Computer Engineering Dep'tDocument35 pagesComputer Architecture and Organization: Adigrat University Electrical and Computer Engineering Dep'tmillionNo ratings yet
- II r20 Aids SyllabusDocument45 pagesII r20 Aids SyllabusPavan GNo ratings yet
- ICT SyllabusDocument38 pagesICT SyllabusKashmi Sultana100% (1)
- NaCl SFIDocument11 pagesNaCl SFIvidhyapriyadharshneeNo ratings yet
- ACM - Step-By-Step Design and Simulation of A Simple CPU ArchitectureDocument5 pagesACM - Step-By-Step Design and Simulation of A Simple CPU ArchitectureGabriella Moreno100% (1)
- Reserved: Basic Structure of Computers and Instruction SetDocument20 pagesReserved: Basic Structure of Computers and Instruction SetJuanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 04 Processors and Memory HierarchyDocument50 pagesChapter 04 Processors and Memory Hierarchyশেখ আরিফুল ইসলাম75% (8)
- R18B Tech CSE (CyberSecurity) IIYearSyllabusDocument34 pagesR18B Tech CSE (CyberSecurity) IIYearSyllabusFareedNo ratings yet
- Computer OrganizationDocument22 pagesComputer OrganizationSuresh Reddy PolinatiNo ratings yet
- CAO PPT Unit 1Document16 pagesCAO PPT Unit 1mdmomin7517No ratings yet
- Mdu, B.tech (ECE) 5th and 6th Sem New SyllabusDocument23 pagesMdu, B.tech (ECE) 5th and 6th Sem New SyllabusAshish Singh50% (2)
- UNIT-1: Introduction To Computer OrganizationDocument51 pagesUNIT-1: Introduction To Computer OrganizationSoftNo ratings yet
- Amd Jaguar (Microarchitecture)Document4 pagesAmd Jaguar (Microarchitecture)Alexis Enrique Vicent RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Lec 6 CO & AL - CADocument34 pagesLec 6 CO & AL - CAUmar ZamanNo ratings yet
- Computer Organization - University QuestionsDocument7 pagesComputer Organization - University QuestionsSirisha VamsiNo ratings yet
- Design Issues and Preformance of ComputerDocument7 pagesDesign Issues and Preformance of ComputerDhruwa Bhatt0% (1)
- Chap2 SlidesDocument127 pagesChap2 SlidesDhara RajputNo ratings yet
- Chapter 04 Processors and Memory Hierarchy PDFDocument50 pagesChapter 04 Processors and Memory Hierarchy PDFgayathriNo ratings yet
- CH 5Document46 pagesCH 5Vijaya GoelNo ratings yet
- Computer Organization MCQ - 5Document2 pagesComputer Organization MCQ - 5Tarun Saini100% (1)
- Computer Rganization-And-Architecture-302Document2 pagesComputer Rganization-And-Architecture-302yashiupadhyay111No ratings yet
- Com OrgDocument5 pagesCom Orgarmie valenciaNo ratings yet
- CSC 2304 01 - Syllabus - Computer ArchitectureDocument4 pagesCSC 2304 01 - Syllabus - Computer ArchitectureAmine NaitlhoNo ratings yet
- The 5 Love Languages of Children by Gary Chapman and Ross CampbellDocument89 pagesThe 5 Love Languages of Children by Gary Chapman and Ross Campbellaysteph3No ratings yet
- Module 4 - Instruction Set Architecture (ISA) v2 (Student) PDFDocument49 pagesModule 4 - Instruction Set Architecture (ISA) v2 (Student) PDFnedunilavanNo ratings yet
- Intel's Haswell CPU MicroarchitectureDocument17 pagesIntel's Haswell CPU Microarchitectureterrys_85No ratings yet
- EE 320 (CS 320) - Computer Organization and Assembly - Jahangir IkramDocument4 pagesEE 320 (CS 320) - Computer Organization and Assembly - Jahangir IkramSheikh AsherNo ratings yet
- 01 Laboratory Exercise 1 - Computer Organization BasicsDocument3 pages01 Laboratory Exercise 1 - Computer Organization BasicsNice MoveNo ratings yet
- Computer Organization NotesDocument126 pagesComputer Organization NotesPriyadarsini karthikNo ratings yet