Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Dematerialisation
Uploaded by
Shreyansh Jain0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
24 views6 pagesOriginal Title
Dematerialisation.pptx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
24 views6 pagesDematerialisation
Uploaded by
Shreyansh JainCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 6
Dematerialisation
Dematerialisation (“Demat” in short form) signifies conversion of a share certificate
from its physical form to electronic form.
The term Demat, in India, refers to a dematerialised account for individual Indian
citizens to trade in listed stocks or debentures, as required by The Securities Exchange
Board of India (SEBI).
In a Demat account, shares and securities are held electronically instead of the investor
taking physical possession of certificates.
To convert his physical buildings of securities into the dematerialised form, the
investor makes an application to the DP in a dematerialisation request form (DRF).
While seven days, the DP (Depository Participants)forwards the form, along with the
security certificates, to issuer or its registrar and transfer agree after electronically
registering the request with the depository.
The depository electronically forwards the demat request to the respective issuer or its
registrar and transfer agent, who verities the validity of the security certificates as well
as the fact that the DRF has been made by a person recorded as a member in its
register of members.
After verification, the issuer or its registrar and transfer agent authorizes an electronic
credit for the security in favour of the client. Thereafter, the depository causes the
credit entries to be made in the account of the client.
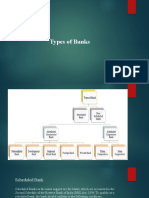
National Securities Depository Limited (NSDL)
The Indian capital market took a major step in its modernization when the National
Securities Depository Limited (NSDL) was set up as the first depository in India.
The NSDL, promoted by the Industrial Development Bank of India, the Unit of India
(UTI), the National Stock Exchange of India Limited (NSE), and the State Bank of
India (SBI) was registered on June 7, 1996, with the SEBI and commenced operations
in November 1996.
The NSDL is a public limited company formed under the Companies Act, 1956 with a
paid-up capital of Rs.105 crore.
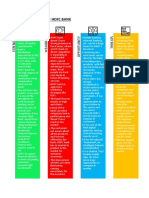
Services of NSDL:
Core services
1. Maintenance of individual investors ‘beneficial holdings in an electronic form.
2. Trade settlement
Special services
1. Automatic delivery of securities to the clearing corporation
2. Dematerialisation and rematerialisation of securities.
3. Account transfer for settlement of trades in electronic shares.
4. Allotments in the electronic form in case of initial public offerings.
5. Distribution of non-cash corporate actions (bonus
6. Facility for freezing/locking of investor accounts.
7. Facility for pledge and hypothecation of securities.
8. Demat of National Savings Certificates (NSC)/Kisan Vikas Patra (KVP);
9. Interest based services such as SPEED-e and IDeAS.
You might also like
- Environment Management NotesDocument12 pagesEnvironment Management NotesShreyansh JainNo ratings yet
- Scheduled BanksDocument21 pagesScheduled BanksShreyansh JainNo ratings yet
- Unit 5: Decision Making SystemDocument11 pagesUnit 5: Decision Making SystemShreyansh JainNo ratings yet
- Debt MarketDocument18 pagesDebt MarketShreyansh JainNo ratings yet
- Concepts Related To Secondary MarketDocument9 pagesConcepts Related To Secondary MarketShreyansh JainNo ratings yet
- Pamphlet - Assignments - Sem III - 2020-2021..Document29 pagesPamphlet - Assignments - Sem III - 2020-2021..Shreyansh JainNo ratings yet
- Inflation-Meaning and TypesDocument18 pagesInflation-Meaning and TypesShreyansh JainNo ratings yet
- CCIPL Online Supplement - 2018 19 - FinalDocument38 pagesCCIPL Online Supplement - 2018 19 - FinalShreyansh JainNo ratings yet
- Monopoly of Indian RailwaysDocument19 pagesMonopoly of Indian RailwaysShreyansh JainNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Pricing by Indian Railway-A Way To Customer Loss: April 2018Document13 pagesDynamic Pricing by Indian Railway-A Way To Customer Loss: April 2018Shreyansh JainNo ratings yet
- Industry ReportDocument32 pagesIndustry ReportShreyansh JainNo ratings yet
- Training & Development PresentationDocument36 pagesTraining & Development PresentationShreyansh JainNo ratings yet
- Industry ReportDocument38 pagesIndustry ReportShreyansh JainNo ratings yet
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Swot Analysis of HDFC BankDocument1 pageSwot Analysis of HDFC BankRishabh KumarNo ratings yet
- Audit and AssuranceDocument222 pagesAudit and AssuranceQudsia ZulfiqarNo ratings yet
- Contact List 2020Document14 pagesContact List 2020Crawford BoydNo ratings yet
- 2018 Portfolio Risk and Return: Part II: Test Code: R42 PRR2 Q-BankDocument14 pages2018 Portfolio Risk and Return: Part II: Test Code: R42 PRR2 Q-BankAhmed RiajNo ratings yet
- Cycle Test Ii AnswerDocument46 pagesCycle Test Ii Answersumitha ganesanNo ratings yet
- Compound IntrestDocument5 pagesCompound Intrestvenkata sureshNo ratings yet
- Application FormDocument5 pagesApplication FormSaurav BansalNo ratings yet
- Leveraging Digital Channels For Enhancing Customer Experience and Analysis of Micro MarketsDocument22 pagesLeveraging Digital Channels For Enhancing Customer Experience and Analysis of Micro MarketsTashioNo ratings yet
- Intercompany Inventory Transactions: Mcgraw-Hill/Irwin © 2008 The Mcgraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All Rights ReservedDocument22 pagesIntercompany Inventory Transactions: Mcgraw-Hill/Irwin © 2008 The Mcgraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All Rights ReservedFarhan Osman ahmedNo ratings yet
- Tree of WealthDocument121 pagesTree of WealthJoseAliceaNo ratings yet
- Account StatementDocument9 pagesAccount StatementMuhammad JavedNo ratings yet
- HOBA2019QUIZ1MCDocument10 pagesHOBA2019QUIZ1MCjasfNo ratings yet
- Ambrish Gupta - Financial Accounting For Management - An Analytical Perspective (2016, Pearson Education) PDFDocument759 pagesAmbrish Gupta - Financial Accounting For Management - An Analytical Perspective (2016, Pearson Education) PDFManirul100% (6)
- Cost Accounting MCQ With Answer PDFDocument3 pagesCost Accounting MCQ With Answer PDFMijanur Rahman100% (2)
- Project Report On Financial Statement Analysis of Bata Shoes and Servis ShoesDocument22 pagesProject Report On Financial Statement Analysis of Bata Shoes and Servis Shoessujit_ranjanNo ratings yet
- Loan AgreementDocument19 pagesLoan AgreementR GautamNo ratings yet
- June 2022 BoltDocument77 pagesJune 2022 BoltRambabu PalepoguNo ratings yet
- Reflection Paper 1Document2 pagesReflection Paper 1Dela Peña, Rey Igino K.No ratings yet
- BharatPe Corporate ProfileDocument5 pagesBharatPe Corporate Profileoneoceannetwork3No ratings yet
- The Mortgage Forgiveness Debt Relief Act and Debt CancellationDocument3 pagesThe Mortgage Forgiveness Debt Relief Act and Debt CancellationPeter Smothers100% (1)
- Statement DEC PDFDocument14 pagesStatement DEC PDFUmay Delisha0% (1)
- Company Profile HDFC BankDocument7 pagesCompany Profile HDFC Bankdominic wurdaNo ratings yet
- MBA-IB 2021-23: Pre-Read MaterialDocument17 pagesMBA-IB 2021-23: Pre-Read MaterialSIDDHI KANSAL MBA 2021-23 (Delhi)No ratings yet
- AML Fines UAE and World 2022Document5 pagesAML Fines UAE and World 2022Amit RajoriaNo ratings yet
- FINAL Examination - Applied Auditing 1 SY 2017-2018: College of Accounting EducationDocument17 pagesFINAL Examination - Applied Auditing 1 SY 2017-2018: College of Accounting EducationAiron Keith Along100% (1)
- T3TAAC - Arrangement Architecture - Core - R11.1Document163 pagesT3TAAC - Arrangement Architecture - Core - R11.1Sojanya KatareNo ratings yet
- PA2 X ESP HW9 G1 Revanza TrivianDocument9 pagesPA2 X ESP HW9 G1 Revanza TrivianRevan KonglomeratNo ratings yet
- Key Investor Information: Objectives and Investment PolicyDocument2 pagesKey Investor Information: Objectives and Investment PolicyGeorgio RomaniNo ratings yet
- BSAIS-InAc 213 Information Sheet 1Document11 pagesBSAIS-InAc 213 Information Sheet 1Reena BoliverNo ratings yet