Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Power Electronics PPT by SSC
Uploaded by
shadan alam0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views17 pagesOriginal Title
power electronics ppt by ssc
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views17 pagesPower Electronics PPT by SSC
Uploaded by
shadan alamCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 17
SINGLE PHASE FULL - WAVE BRIDGE
CONVERTER WITH RLE LOAD
(Continuous Load Current)
PRESENTED BY : SHEETAL SINGH CHAUHAN
ROLL NO. : 16/IEE/052
CONTENT
Phase controlled rectifiers.
Types of rectifiers.
Single phase converter.
Single phase full- wave bridge converter.
Circuit diagram.
Explanation.
Output waveform.
Operation
PHASE CONTROLLED RECTIFIERS
Converts AC into DC.
Employs thyristors,diodes .
Used in battery charging ,speed control of DC motors,
HVDC,etc.
Need no commutation circuitry.
These are simple.
Less expensive.
Cont'd...
Widely used in industries where controlled DC power is
required.
These are of two types : single - phase and three - phase
converters.
TYPES OF RECTIFIERS
SINGLE PHASE CONVERTER
Phase controlled single - phase converters are primarily
of three types:-
1) Uncontrolled converters : It uses only diodesand the
level of dc output voltage cannot be controlled.
2) Half - controlled converters : It uses a mixture of diodes
and thyristors and there is a limited control over the level
of dc output voltage.
3) Fully - controlled converters : It uses SCRs only and
there is a wider control over the level of dc output
voltage.
SINGLE PHASE FULL WAVE BRIDGE
CONVERTER
Employs only thyristors.
Provides wider control over the level of DC output
voltage.
Level of the voltage can be regulated by varying the firing
angle α.
There is no effect of battery E on Vo in continuous load
current case.
CIRCUIT DIAGRAM
Fig.1.Single phase full converter bridge
RLE load.
EXPLANATION
It uses 4 SCR's i.e. T1,T2,T3,T4.
The load is assumed to be RLE type where E is the load
circuit emf.
Voltage E may be due to battery in the load circuit or may
be generated emf of a DC motor.
Thyristor pair T1,T2 is simultaneously triggered and π
radians later ,pair T3,T4 is gated together.
The current directions and voltage polarities shown in Fig.
are treated as positive.
Cont'd...
Here,
• vab= supply voltage when a is positive with respect to b.
• vba= supply voltage when b is positive with respect to a.
• vab= -vba
• io = load current or output current.
• vs = supply voltage.
• is = supply current.
• vo = voltage across load.
Con'd...
• α = firing angle.
• vT1,vT2,vT3,vT4 = terminal voltage across T1,T2,T3 and T4
respectively.
• iT1,iT2 = current through thyristor T1 and T2.
io is assumed to be continuous over the working range;
this means that load is always connected to the ac
voltage source through the thyristors.
OUTPUT WAVEFORM
Fig.2. Voltage and current waveforms for
continuous load current.
Cont'd...
Fig.3.Voltage and current waveforms
for continuous load current.
OPERATION
In continuous load current case : β = π + α.
Forward biased SCRs T1 and T2 are triggered at ωt = α
i.e. they get turned on. As a result , supply voltage VM sin
α immediately appears across thyristors T3,T4 as a
reverse bias.At the same time , load current io flowing
throughT3,T4 is transferred to T1,T2 at ωt = α.
Thyristors T1,T2 conduct from ωt = α to π + α i.e. T1,T2
conduct for π radians.
vT1 = vT2
Cont'd...
At ωt = π + α,forward biased SCRs T3,T4 are triggered.
The load current is transferred from T1,T2 to T3,T4.
vT3 = vT4
At the instant of triggering with firing angle α,each SCR is
subjected to a reverse voltage of Vm sin α.
Source current is shown positive when T1,T2 are
conducting and negative when T3,T4 are conducting.
During α to π, vs and is are positive,power therefore flows
from ac source to load.
Cont'd...
But during the interval π to π + α, vs is negative and is is
positive,the load therefore returns some of its energy to
the supply system.But the net power flow is from ac
source to dc load.'
This connection is also called as B-2 connection.
THANK YOU
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5806)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1091)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (842)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (589)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Pneumatic Vs Electric Cost CalculatorDocument7 pagesPneumatic Vs Electric Cost CalculatorCazacu AndreiNo ratings yet
- Subtle Energy and The Cosmos - Part 1 Yury KronnDocument10 pagesSubtle Energy and The Cosmos - Part 1 Yury KronnTyl3rNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics PPT by Atul Kumar PrajapatiDocument13 pagesPower Electronics PPT by Atul Kumar Prajapatishadan alamNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics PPT by DeveshDocument34 pagesPower Electronics PPT by Deveshshadan alamNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics PPT by HEMANTDocument9 pagesPower Electronics PPT by HEMANTshadan alamNo ratings yet
- Single Phase Semi ConverterDocument17 pagesSingle Phase Semi Convertershadan alamNo ratings yet
- "Single Phase Full Wave Rectifier": Power Point Presentation OnDocument12 pages"Single Phase Full Wave Rectifier": Power Point Presentation Onshadan alamNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics PPT by Shadan AlamDocument17 pagesPower Electronics PPT by Shadan Alamshadan alamNo ratings yet
- Seminar ReportDocument17 pagesSeminar Reportshadan alamNo ratings yet
- Assignment (1) Robust and Aduptive Cantrol Difference Between MRAC and STRDocument1 pageAssignment (1) Robust and Aduptive Cantrol Difference Between MRAC and STRshadan alamNo ratings yet
- Soft Computing Techniques Assignment1 PDFDocument14 pagesSoft Computing Techniques Assignment1 PDFshadan alamNo ratings yet
- Assignment (1) Robust and Aduptive Cantrol Difference Between MRAC and STRDocument1 pageAssignment (1) Robust and Aduptive Cantrol Difference Between MRAC and STRshadan alamNo ratings yet
- Biomedical and Instrumentation Lab FileDocument37 pagesBiomedical and Instrumentation Lab Fileshadan alamNo ratings yet
- Liquid FuelsDocument8 pagesLiquid FuelsCharles Bonn Kirby MayoNo ratings yet
- MTZ Wiring DiagramsDocument6 pagesMTZ Wiring Diagramsalexns84No ratings yet
- Sa Ami 460 Fcon 100702 - 1 1Document1 pageSa Ami 460 Fcon 100702 - 1 1tanyadeasis8No ratings yet
- Parcial Examen Final Quiz Validación Otro XDocument2 pagesParcial Examen Final Quiz Validación Otro XJuan De DiosNo ratings yet
- Chap 4 LectureDocument19 pagesChap 4 LectureMatamoros De La Cruz JorgeNo ratings yet
- Book Excerpt: 'We Have No Idea'Document6 pagesBook Excerpt: 'We Have No Idea'Here & NowNo ratings yet
- DC Microgrids Part II A Review of PowerDocument24 pagesDC Microgrids Part II A Review of PowerPedrito OrangeNo ratings yet
- Neumann KPG - Brochure PDFDocument2 pagesNeumann KPG - Brochure PDFromaoj671No ratings yet
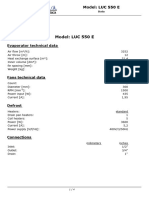
- Luc 550 eDocument4 pagesLuc 550 ealNo ratings yet
- Power Factor BasicsDocument13 pagesPower Factor BasicsAlaa RamadanNo ratings yet
- 17 Samss 516Document24 pages17 Samss 516FuzzzyLogNo ratings yet
- HVDC TransmissionDocument78 pagesHVDC Transmissiondhay aliNo ratings yet
- DNV - China LNG Final ReportDocument41 pagesDNV - China LNG Final ReportdensandsNo ratings yet
- Generators: Model: PDG25 25 KVA Available in Single Phase and Three PhaseDocument2 pagesGenerators: Model: PDG25 25 KVA Available in Single Phase and Three Phaseefmartin21No ratings yet
- Genadvisor Shaft Volt Current Mon PSPG b10244 00 7600 en LR Fina PDFDocument2 pagesGenadvisor Shaft Volt Current Mon PSPG b10244 00 7600 en LR Fina PDFSourav RanaNo ratings yet
- Bio EnergyDocument7 pagesBio EnergyVikram PorjeNo ratings yet
- Work Power Energy QuizDocument2 pagesWork Power Energy QuizMarilyn GarciaNo ratings yet
- Generador StanfordDocument8 pagesGenerador StanfordJuan Carlos Vivas GuioNo ratings yet
- Enl GW56Document2 pagesEnl GW56byrsNo ratings yet
- Energy EfficiencyDocument9 pagesEnergy Efficiencyjeffreydichos24No ratings yet
- Reciprocating CompressorDocument24 pagesReciprocating CompressorSANTHOSH NAGARAJA0% (1)
- Transient Step Response Specification of Z-Source DC-DC ConverterDocument5 pagesTransient Step Response Specification of Z-Source DC-DC ConverterijsretNo ratings yet
- Part 1. Background Material: Chapter 1. The Basics of Quantum MechanicsDocument94 pagesPart 1. Background Material: Chapter 1. The Basics of Quantum MechanicsKirby BurneaNo ratings yet
- DOE List of Power ContractsDocument9 pagesDOE List of Power Contractskonverg101No ratings yet
- Spiritual Dowsing WorkshopDocument13 pagesSpiritual Dowsing Workshopmoumona100% (3)
- Midterm Exam QuestionaireDocument2 pagesMidterm Exam QuestionaireJohn RivasNo ratings yet
- CW & AcwDocument1 pageCW & Acwrbdubey2020No ratings yet
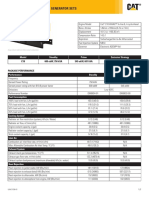
- Data Sheet C18 - 750kVA StandBy 2021Document2 pagesData Sheet C18 - 750kVA StandBy 2021Paulo dos SantosNo ratings yet