Professional Documents
Culture Documents
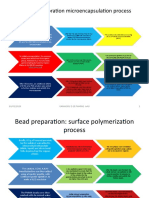
Solvent Evaporation Microencapsulation Process
Uploaded by
Gamachu Diba0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
24 views2 pagesOriginal Title
Solvent evaporation microencapsulation process
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
24 views2 pagesSolvent Evaporation Microencapsulation Process
Uploaded by
Gamachu DibaCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
Solvent evaporation microencapsulation process
an inner aqueous phase was
made by dissolving an appropriate
After the PVA was dissolved fully, ferrous
amount ofPVA 2( inner aqueous phase) ammonium sulfate was dissolved to
The oil phase was obtained by dissolving
dependent on the required particle size 5% w/w PMMA in dichloromethane
make a 0.07M ferrous ammonium
(DCM).
(2% w/v for 50–100 and 100–250, and solution (as the inner aqueous phase).
6% w/v for 250–500 micrometer) in de-
ionized water
To initiate encapsulation, the aqueous with continuous agitation by an RW-16
basic overhead mechanical stirrer at
phase was added into the organic speeds ranging from 100 rpm to 600
phase, followed by 2 minutes with Each W/O emulsion was then poured
rpm (dependent on the desired particle
into 2% w/w PVA solution (outer
gentle shaking by hand to make a size; 200 rpm for microcapsules of 250–
aqueous phase),
Water-in Oil (W/O) emulsion 500 mm; 600 rpm for microcapsules of
50–100 mm) to form the final
(5%w/w+DCM)) water/oil/water (W/O/W) emulsions.
After microencapsulation, each mixture
After 30minutes, an additional 100mL was centrifuged at 5000 rpm for
5minutes. All microcapsules were oven dried (60 C)
of 0.5% w/w PVA solution was added and weighed before measuring the
The microcapsules were then washed percentage encapsulation efficiency
to further stabilize and solidify the with de-ionized water three times to
microcapsules (%EE).
remove the non-encapsulated ferrous
ammonium complex and residual PVA
09/02/2020 GAMACHU D.(B.PHARM) AAU 1
Bead preparation: surface polymerization
process
Briefly, 0.5 g of benzoyl peroxide
(as the initiator) was added to
10mLmethylmethacrylate Simultaneously, the 0.07M ferrous The two phases were combined
(MMA, liquid) and stirred until ammonium aqueous phase was with gentle agitation using a plastic
fully dissolved (as the organic prepared with 6% w/w PVA. rod (1:10, aqueous: organic).
phase).
.
The catalyst, 0.2mL 4,N,N- A low agitation speed (<150 rpm)
After the beads were formed, the
trimethylaniline was then added was maintained to ensure that the
whole mixture was agitated at 200
W/O droplets stayed at the surface
using a transfer pipette, with of the solution for the
rpm for another 30 minutes to
continued gentle agitation, to further stabilize and solidify the
polymerization procedure to occur
PMMA beads.
make a W/O emulsion (no higher than 150 rpm).
All PMMA beads were then dried in
The PMMA beads were then an oven overnight at 60 C.
Unlike solvent evaporation
washed with de-ionized water microencapsulation, a wide range After drying, the PMMA beads were
three times to remove the non- (250 mm to 4mm in diameter) of sieved and separated using US
encapsulated ferrous PMMA beads can be obtained from standard sieves (three size ranges:
a single batch using the surface 0.5–1, 1–2, and 2–3mm) and
ammonium complex and polymerization process. weighed before measuring the %EE.
residual PVA.
09/02/2020 GAMACHU D.(B.PHARM) AAU 2
You might also like
- Properties of EVM Compounds in Relation To The Vinyl Acetate Content of The PolymerDocument10 pagesProperties of EVM Compounds in Relation To The Vinyl Acetate Content of The PolymerabiliovieiraNo ratings yet
- Process Plant Estimating StandardsDocument15 pagesProcess Plant Estimating StandardsCarl Williams75% (4)
- Reliance Industries Limited Reliance Industries Limited: Chemical EORDocument21 pagesReliance Industries Limited Reliance Industries Limited: Chemical EORmexx4u2nvNo ratings yet
- Developments in the Interpretation of Power Transformer Dissolved Gas Analysis Results 论文Document162 pagesDevelopments in the Interpretation of Power Transformer Dissolved Gas Analysis Results 论文Jicheng PiaoNo ratings yet
- Waste ManagementDocument43 pagesWaste Managementالدنيا ساعة فاجعلها طاعةNo ratings yet
- Membrane SeparationDocument18 pagesMembrane SeparationIteoluwakiishi AberuagbaNo ratings yet
- Membrane Processes: Reverse Osmosis Ultrafiltration MicrofiltrationDocument18 pagesMembrane Processes: Reverse Osmosis Ultrafiltration MicrofiltrationssgentisNo ratings yet
- DM PlantDocument2 pagesDM PlantDarakhshan Sheikh100% (1)
- Croda Eseminar Coatings Polymers Mar 312010Document32 pagesCroda Eseminar Coatings Polymers Mar 312010Giovanna Guerrero100% (1)
- Design, Properties and Applications of Porous Materials Obtained in Highly Concentrated EmulsionsDocument72 pagesDesign, Properties and Applications of Porous Materials Obtained in Highly Concentrated EmulsionsDrMohammed Al MamooryNo ratings yet
- Huang Li Annex18 Freiburg Nov052008Document16 pagesHuang Li Annex18 Freiburg Nov052008Jane LouisNo ratings yet
- TB 9 Emulsions and Emulsification - LowresDocument5 pagesTB 9 Emulsions and Emulsification - LowresмарияNo ratings yet
- Membrane Technology: Reverse Osmosis Ultrafiltration MicrofiltrationDocument66 pagesMembrane Technology: Reverse Osmosis Ultrafiltration MicrofiltrationShivani MunishwarNo ratings yet
- Emulsions: - Part 1 Preparation Methods (Some) PropertiesDocument52 pagesEmulsions: - Part 1 Preparation Methods (Some) PropertieschandramohanNo ratings yet
- PMMA Data SheetDocument8 pagesPMMA Data SheetLibertadNo ratings yet
- 2016-01-26 - Nuplex - Enhancing The Performance of Waterborne Coatings Through The Polymerization of Super Hydrophobic MonomersDocument26 pages2016-01-26 - Nuplex - Enhancing The Performance of Waterborne Coatings Through The Polymerization of Super Hydrophobic MonomerselgendawyNo ratings yet
- Gemini Column CareDocument3 pagesGemini Column CareLee MingTingNo ratings yet
- Suzuki 1994Document7 pagesSuzuki 1994Ppa Gpat AmitNo ratings yet
- Aerogel de Bambu Blanco MicroficrillaDocument14 pagesAerogel de Bambu Blanco MicroficrillaLucia MaribelNo ratings yet
- Membrane ProcessesDocument18 pagesMembrane Processestatchanok1525No ratings yet
- Pinacci 2002Document3 pagesPinacci 2002LeonardoNo ratings yet
- Development and Characterization of Sulfonated Polysulfone Membranes For Direct Methanol Fuel CellsDocument3 pagesDevelopment and Characterization of Sulfonated Polysulfone Membranes For Direct Methanol Fuel CellsKaustubhNo ratings yet
- Investigation of Effect of Pour Point Depressant On Wax DepositionDocument3 pagesInvestigation of Effect of Pour Point Depressant On Wax DepositionAfzal AktharNo ratings yet
- 3-2015 - Ultrasound Assisted Manufacturing of Paraffin Wax Nanoemulsions Process OptimizationDocument7 pages3-2015 - Ultrasound Assisted Manufacturing of Paraffin Wax Nanoemulsions Process OptimizationIITRANANDJADHAVNo ratings yet
- Eshmuno S ResinDocument4 pagesEshmuno S ResinTuyền KimNo ratings yet
- Hypothesis Review: NanoemulsionsDocument5 pagesHypothesis Review: NanoemulsionsRAPPORTS DE PHARMACIENo ratings yet
- Continuous Electrostatic Dehydrator 에 의한 Water-in -Crude oil Emulsions 의 DemulsificationDocument5 pagesContinuous Electrostatic Dehydrator 에 의한 Water-in -Crude oil Emulsions 의 DemulsificationYoga WiranotoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4Document41 pagesLecture 4Yasemin KaradağNo ratings yet
- Nanoencapsulation of Intercalated Montmorillonite-Urea Within PVA Nanofibers: Hydrogel Fertilizer NanocompositeDocument10 pagesNanoencapsulation of Intercalated Montmorillonite-Urea Within PVA Nanofibers: Hydrogel Fertilizer NanocompositeRenato Diaz Frigerio100% (1)
- Silicon Carbide Membranes: P R O D U C T B U L L E T I NDocument2 pagesSilicon Carbide Membranes: P R O D U C T B U L L E T I NGabriel Montoya CorreaNo ratings yet
- Cherng-Yuan Lin, Chang-Ting Tsai: Highlights GraphicalDocument7 pagesCherng-Yuan Lin, Chang-Ting Tsai: Highlights GraphicalNaud Avendaño RodríguezNo ratings yet
- (CCS) Product Specification Acclaim Mixed Mode WCX-1Document8 pages(CCS) Product Specification Acclaim Mixed Mode WCX-1tamiaNo ratings yet
- Fabrication and Performance Analysis of PVA/PVC Composite Membrane To Remove Total Dissolved Solids From Liming/unhairing WastewaterDocument17 pagesFabrication and Performance Analysis of PVA/PVC Composite Membrane To Remove Total Dissolved Solids From Liming/unhairing Wastewater17044 AZMAIN IKTIDER AKASHNo ratings yet
- Nano-Emulsion Formation by Emulsion Phase Inversion PDFDocument6 pagesNano-Emulsion Formation by Emulsion Phase Inversion PDFPpa Gpat AmitNo ratings yet
- Indion 850 Resin Engg Data SheetDocument6 pagesIndion 850 Resin Engg Data SheetsoumitrabanNo ratings yet
- 2017 Rafa Polar PesticidesDocument1 page2017 Rafa Polar PesticidesluuphuongNo ratings yet
- Slab High Resilience FoamDocument6 pagesSlab High Resilience FoamJina S. BeerNo ratings yet
- Double Emulsions of Water in Oil in Water StabilizedDocument7 pagesDouble Emulsions of Water in Oil in Water StabilizedMarceta BrankicaNo ratings yet
- Electrospun Crosslinked Polyvinyl Alcohol Membrane 2008 Materials LettersDocument3 pagesElectrospun Crosslinked Polyvinyl Alcohol Membrane 2008 Materials LettersrukwavuNo ratings yet
- Microemulsion Polymerization: Presented by Ashish Dixit SR - No.:-252/07 3 B.Tech - Plastic Tech. H.B.T.I.KanpurDocument35 pagesMicroemulsion Polymerization: Presented by Ashish Dixit SR - No.:-252/07 3 B.Tech - Plastic Tech. H.B.T.I.KanpurNitin GuptaNo ratings yet
- Formation of Nano EmulsionDocument9 pagesFormation of Nano EmulsionHariom RajputNo ratings yet
- Formation of Nano Emulsion (1) Hariom Rajput Mr. SahilDocument9 pagesFormation of Nano Emulsion (1) Hariom Rajput Mr. SahilHariom RajputNo ratings yet
- Largest Power Plant in Philippines Uses Membrane Desalination For Purified WaterDocument2 pagesLargest Power Plant in Philippines Uses Membrane Desalination For Purified WaterPhilip Jay-ar DimailigNo ratings yet
- EUROWATER RO Units LeafletDocument4 pagesEUROWATER RO Units LeafletNoah MusundiNo ratings yet
- p190035 en Versalink-Brochure NR RZ WebDocument4 pagesp190035 en Versalink-Brochure NR RZ Webyilong luoNo ratings yet
- Formation of Vitamin e Enriched Nano EmulsionDocument20 pagesFormation of Vitamin e Enriched Nano Emulsionayush barikNo ratings yet
- Mini Prep Cell and Model 491 Prep Cell Starter Kit InstructionsDocument2 pagesMini Prep Cell and Model 491 Prep Cell Starter Kit InstructionsdnajenNo ratings yet
- Puma Bitumen Bitumen EmulsionsDocument15 pagesPuma Bitumen Bitumen EmulsionsKushnappa BkNo ratings yet
- Exterior White Paint 37% PVCDocument1 pageExterior White Paint 37% PVCAPEX SONNo ratings yet
- Dowex Marathon MSA 2 LDocument11 pagesDowex Marathon MSA 2 LBrianNo ratings yet
- Criating NanoDocument7 pagesCriating NanoJaynish IdhariyaNo ratings yet
- Aquafilm ™ Af-3U: Afff Foam Concentrate (3%)Document2 pagesAquafilm ™ Af-3U: Afff Foam Concentrate (3%)Indopura GroupNo ratings yet
- Cellulose Acetate Membrane / Asymmetric MembraneDocument8 pagesCellulose Acetate Membrane / Asymmetric MembraneHafiz M FaheemNo ratings yet
- Properties of Modified Poly (Vinyl Alcohol) Membranes Prepared by The Grafting of New Polyelectrolyte Copolymers For Water-Ethanol Mixture SeparationDocument6 pagesProperties of Modified Poly (Vinyl Alcohol) Membranes Prepared by The Grafting of New Polyelectrolyte Copolymers For Water-Ethanol Mixture SeparationViraj EdirisingheNo ratings yet
- RSC Advances: CommunicationDocument4 pagesRSC Advances: CommunicationSHREYANo ratings yet
- Nanoemulsion: A ReviewDocument23 pagesNanoemulsion: A ReviewfikriNo ratings yet
- Mag Beads Swab & Saliva Genomic DNA Extraction KitDocument3 pagesMag Beads Swab & Saliva Genomic DNA Extraction KitangelinaNo ratings yet
- FF IP Engg DataDocument10 pagesFF IP Engg DataKpm MuthuNo ratings yet
- Effect of Amine Solubizer Structure of Cured Film Properties of Water Reducible Thermoset ResinsDocument8 pagesEffect of Amine Solubizer Structure of Cured Film Properties of Water Reducible Thermoset ResinsogzlemNo ratings yet
- Hydrophilic-Lipophilic BalanceDocument6 pagesHydrophilic-Lipophilic BalanceChantelle MeaNo ratings yet
- Advances in Desalination Energy RecoveryDocument5 pagesAdvances in Desalination Energy RecoveryMurali K oe16d017No ratings yet
- Clariant File Reactive Emulsifiers Guide Formulation Styrene AcrylicDocument1 pageClariant File Reactive Emulsifiers Guide Formulation Styrene AcrylicSanjaya Bandara100% (1)
- Oral AdministrationDocument2 pagesOral AdministrationGamachu DibaNo ratings yet
- Solvent Evaporation Microencapsulation ProcessDocument2 pagesSolvent Evaporation Microencapsulation ProcessGamachu DibaNo ratings yet
- Size Discrimination in Rat and Mouse Gastric Emptying: Biopharmaceutics AssignmentDocument15 pagesSize Discrimination in Rat and Mouse Gastric Emptying: Biopharmaceutics AssignmentGamachu DibaNo ratings yet
- Vaginal Drug Delivery SystemDocument27 pagesVaginal Drug Delivery SystemGamachu DibaNo ratings yet
- College of Health Sciences School of Pharmacy Department of Pharmaceutics and Social Pharmacy Novel Drug Delivery SystemsDocument33 pagesCollege of Health Sciences School of Pharmacy Department of Pharmaceutics and Social Pharmacy Novel Drug Delivery SystemsGamachu DibaNo ratings yet
- College of Health Sciences School of Pharmacy Department of Pharmaceutics and Social Pharmacy Novel Drug Delivery SystemsDocument33 pagesCollege of Health Sciences School of Pharmacy Department of Pharmaceutics and Social Pharmacy Novel Drug Delivery SystemsGamachu DibaNo ratings yet
- College of Health Sciences School of Pharmacy Department of Pharmaceutics and Social PharmacyDocument33 pagesCollege of Health Sciences School of Pharmacy Department of Pharmaceutics and Social PharmacyGamachu DibaNo ratings yet
- Green Book SolutionDocument44 pagesGreen Book SolutionCaleb RaphaelNo ratings yet
- Submittal Package 74-07 46 46-00 - Mineral-Fiber Cement Siding NET - 230622Document56 pagesSubmittal Package 74-07 46 46-00 - Mineral-Fiber Cement Siding NET - 230622Apple CabreraNo ratings yet
- Product Data Sheet: Butyl AcetateDocument1 pageProduct Data Sheet: Butyl AcetateHemant RathvaNo ratings yet
- NSCPDocument3 pagesNSCPJulius Christian PerezNo ratings yet
- Final Report FB-2018-1 PDFDocument75 pagesFinal Report FB-2018-1 PDFRatik GaonkarNo ratings yet
- Design and Analysis of Go Kart Chasis PDFDocument6 pagesDesign and Analysis of Go Kart Chasis PDFPushparaj MariaNo ratings yet
- Ocused Ion Beam Microscopy and Micromachining: C.A. Volkert and A.M. Minor, Guest EditorsDocument11 pagesOcused Ion Beam Microscopy and Micromachining: C.A. Volkert and A.M. Minor, Guest EditorsrmehfuzNo ratings yet
- Aloha Flight 243 A New DirectionDocument45 pagesAloha Flight 243 A New DirectionBhavani PrasadNo ratings yet
- 4 - Class Notes (CH-101 &CH-201) Module-4 - PolymerizationDocument9 pages4 - Class Notes (CH-101 &CH-201) Module-4 - PolymerizationMtabazi SahiniNo ratings yet
- Extra Item Rates AnalysisDocument18 pagesExtra Item Rates AnalysisAnish DhillonNo ratings yet
- Stellar OpacityDocument6 pagesStellar OpacityJay SunNo ratings yet
- 324-Chapter 1 Rock Bit Interactions PDFDocument42 pages324-Chapter 1 Rock Bit Interactions PDFBilge KaanNo ratings yet
- Sustainable Post-Consumer Diaper Recycler: Designer: Bei-Ren Wu, Miley Tsai, Sz-Chwun John HwangDocument22 pagesSustainable Post-Consumer Diaper Recycler: Designer: Bei-Ren Wu, Miley Tsai, Sz-Chwun John HwangluisNo ratings yet
- Mamufacturing of Potassium ChlorideDocument16 pagesMamufacturing of Potassium Chloriderajesh100% (1)
- A Description Is Given of The Assessment of The CreasingDocument8 pagesA Description Is Given of The Assessment of The CreasingRusted BoyNo ratings yet
- Air Quality Meter Gasman-H2S Hydrogen Sulfide - PCE InstrumentsDocument3 pagesAir Quality Meter Gasman-H2S Hydrogen Sulfide - PCE InstrumentsSalman HaroonNo ratings yet
- TPSA US (English)Document7 pagesTPSA US (English)Henrique OliveiraNo ratings yet
- Rendercon ChemDocument4 pagesRendercon ChemHarshvardhan PathakNo ratings yet
- Modul Soalan KonsepDocument4 pagesModul Soalan KonsepNormah MisparNo ratings yet
- 730 UlfmDocument4 pages730 UlfmTobias Alberto Gonzalez PeresNo ratings yet
- A Database For Shot Peening ProcessDocument9 pagesA Database For Shot Peening Processkayasimge595No ratings yet
- Cabochon Settings and Patterns UsingDocument27 pagesCabochon Settings and Patterns Usingodile lambNo ratings yet
- Destiladores BoecoDocument3 pagesDestiladores BoecoCamilo Andres Sarasty DiazNo ratings yet
- Alginate: DR Avreet SandhuDocument58 pagesAlginate: DR Avreet Sandhuwaheguru13he13No ratings yet
- A Tribological Study of Cobalt Chromium Molybdenum Alloys Used in Metal-On-Metal Resurfacing Hip ArthroplastyDocument8 pagesA Tribological Study of Cobalt Chromium Molybdenum Alloys Used in Metal-On-Metal Resurfacing Hip ArthroplastyGustavo Alonso Luévanos ArizmendiNo ratings yet
- Ktu Gte 1 Question CombinedDocument11 pagesKtu Gte 1 Question CombinedAshok Mathew0% (1)
- A. Introduction To WeldingDocument29 pagesA. Introduction To WeldingRonel LawasNo ratings yet