100% found this document useful (1 vote)
288 views32 pagesDr. Abdul Rashad Senior Lecturer DPT, Mphill (Opt) Mppta United College of Physical Therapy
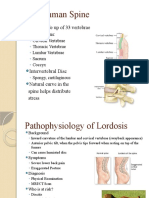
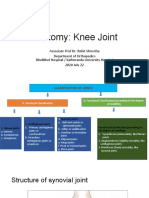
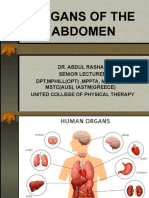
This document discusses various musculoskeletal disorders and their treatment. It covers common conditions like amputation, chronic back pain, carpal tunnel syndrome, arthritis, and osteoporosis. For each condition, it describes causes, signs and symptoms, and medical and nursing considerations for treatment. Surgical and non-surgical treatment options are provided. The document provides an overview of assessing, planning, and treating a variety of musculoskeletal problems.
Uploaded by
pashaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
100% found this document useful (1 vote)
288 views32 pagesDr. Abdul Rashad Senior Lecturer DPT, Mphill (Opt) Mppta United College of Physical Therapy
This document discusses various musculoskeletal disorders and their treatment. It covers common conditions like amputation, chronic back pain, carpal tunnel syndrome, arthritis, and osteoporosis. For each condition, it describes causes, signs and symptoms, and medical and nursing considerations for treatment. Surgical and non-surgical treatment options are provided. The document provides an overview of assessing, planning, and treating a variety of musculoskeletal problems.
Uploaded by
pashaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd