0% found this document useful (0 votes)
157 views81 pagesInfeksi Kulit: Staphylococcus & Streptococcus
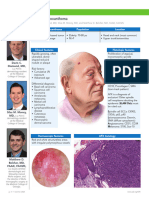
Impetigo and ecthyma are superficial bacterial skin infections caused by Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus pyogenes. They are characterized by crusted erosions or ulcers on the skin. Treatment involves incision and drainage of abscesses, along with a 7-10 day course of antibiotics such as dicloxacillin, cephalexin, or erythromycin to eliminate the bacterial infection.
Uploaded by
AtikaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
157 views81 pagesInfeksi Kulit: Staphylococcus & Streptococcus
Impetigo and ecthyma are superficial bacterial skin infections caused by Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus pyogenes. They are characterized by crusted erosions or ulcers on the skin. Treatment involves incision and drainage of abscesses, along with a 7-10 day course of antibiotics such as dicloxacillin, cephalexin, or erythromycin to eliminate the bacterial infection.
Uploaded by
AtikaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd