Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Gyroscope: Basic Definition and Types
Uploaded by
pericharla ravivarma0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views4 pagesOriginal Title
GYROSCOPE
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views4 pagesGyroscope: Basic Definition and Types
Uploaded by
pericharla ravivarmaCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
GYROSCOPE: BASIC DEFINITION AND TYPES
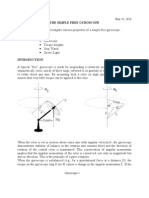
A gyroscope is a device used for measuring or maintaining
orientation and angular velocity. It is a spinning wheel or disc in
which the axis of rotation (spin axis) is free to assume any
orientation by itself.
There are three basic types of gyroscope:
•Rotary (classical) gyroscopes.
•Vibrating Structure Gyroscope.
•Optical Gyroscopes.
ROTARY GYROSCOPES
• These gyroscopes typically consist of a spinning disk or mass
on an axle, which is mounted on a series of gimbals. Each
gimbal offers the spinning disk an additional degree of rotational
freedom. The gimbals allow the rotor to spin without applying
any net external torque on the gyroscope.
Vibrating structure gyroscope
• The physical principle is that a vibrating object tends to
continue vibrating in the same plane even if its support rotates.
The Coriolis effect causes the object to exert a force on its
support, and by measuring this force the rate of rotation can be
determined.
Optical gyroscopes ( fibre- optic gyroscope)
• A fibre-optic gyroscope (FOG) senses changes in orientation using the
Sagnac effect, thus performing the function of a mechanical
gyroscope. However its principle of operation is instead based on the
interference of light which has passed through a coil of optical fibre,
which can be as long as 5 kilometres (3 mi).
You might also like
- Gyro PDFDocument165 pagesGyro PDFvineesh chandraNo ratings yet
- GYROSCOPIC INSTRUMENTS SYSTEM: GYROSCOPES AND GIMBALSDocument17 pagesGYROSCOPIC INSTRUMENTS SYSTEM: GYROSCOPES AND GIMBALSashwin pavithranNo ratings yet
- Gyroscope: For Other Uses and Non-Rotary Gyroscopes, SeeDocument3 pagesGyroscope: For Other Uses and Non-Rotary Gyroscopes, SeeFaiezKhanNo ratings yet
- Motorized Gyroscope Apparatus 1Document7 pagesMotorized Gyroscope Apparatus 1Rickson Viahul Rayan CNo ratings yet
- Shreyash Meshram (20030089) - 251: Governer BYDocument5 pagesShreyash Meshram (20030089) - 251: Governer BYShreyash MeshramNo ratings yet
- Gyroscope and Stabilizing: Presented To: Engr. Abu Bakar SBDocument32 pagesGyroscope and Stabilizing: Presented To: Engr. Abu Bakar SBGhulam MurtazaNo ratings yet
- Gyro CompassDocument36 pagesGyro CompassAfiq Abidin100% (1)
- GyroscopeDocument10 pagesGyroscopeMohammad Arslan YousafNo ratings yet
- Gyroscope Device Measures OrientationDocument11 pagesGyroscope Device Measures OrientationAnil durgamNo ratings yet
- Gyroscope Basics and ApplicationsDocument15 pagesGyroscope Basics and ApplicationsNisitha Tharushan DarmarathnaNo ratings yet
- Gyroscopic CoupleDocument19 pagesGyroscopic CoupleusmanNo ratings yet
- GyroscopeDocument99 pagesGyroscopeAntonioNo ratings yet
- Gyroscopes Tech TopicDocument10 pagesGyroscopes Tech TopicVy Kim LêNo ratings yet
- M11.5A 2 Gyroscopic Instrument OkDocument73 pagesM11.5A 2 Gyroscopic Instrument OkellysazainudinNo ratings yet
- Gyroscope: Navigation SearchDocument1 pageGyroscope: Navigation Searchjpalex1986100% (1)
- Gyroscopic CoupleDocument8 pagesGyroscopic CouplerR2CcNo ratings yet
- AlvinDocument15 pagesAlvinJhon Benedick Pando TajaNo ratings yet
- GyroscopeDocument7 pagesGyroscopeSNEHAJIT TALENo ratings yet
- What is a gyroscope in 40 charactersDocument7 pagesWhat is a gyroscope in 40 charactersSNEHAJIT TALENo ratings yet
- B2-13h Instruments Gyroscopic SRDocument104 pagesB2-13h Instruments Gyroscopic SRAlexander Mcfarlane100% (2)
- 02 Principles of Gyroscopic InstrumentsDocument18 pages02 Principles of Gyroscopic InstrumentsFurkan DuruNo ratings yet
- Gyroscope: For Other Uses and Non-Rotary Gyroscopes, SeeDocument17 pagesGyroscope: For Other Uses and Non-Rotary Gyroscopes, SeevigneshwaranNo ratings yet
- GyroscopesDocument34 pagesGyroscopesNikhil SinghNo ratings yet
- Bicycle Wheel Gyroscope DemonstrationDocument4 pagesBicycle Wheel Gyroscope Demonstrationneyemhey2348513No ratings yet
- Gyro Notes For 2ND MateDocument18 pagesGyro Notes For 2ND MateArchit Bhardwaj100% (1)
- Gyro Compass The Free GyroscopeDocument7 pagesGyro Compass The Free GyroscopeJJohn GGnanavelu100% (2)
- ReportDocument13 pagesReportMamta SindhuNo ratings yet
- ATPL Inst 3.1 PDFDocument10 pagesATPL Inst 3.1 PDFKoustubh VadalkarNo ratings yet
- Fabrication of Self Balancing Two Wheeler Using Gysroscope.02Document20 pagesFabrication of Self Balancing Two Wheeler Using Gysroscope.02milan mottaNo ratings yet
- GyroDocument6 pagesGyroLynton MenezesNo ratings yet
- What Is A Gyroscope?Document18 pagesWhat Is A Gyroscope?Famous GuyNo ratings yet
- Gyroscope and GyrocompassDocument26 pagesGyroscope and Gyrocompassdragonborn dragonbornNo ratings yet
- Gyro 110401032813 Phpapp01sdaDocument12 pagesGyro 110401032813 Phpapp01sdaAniket SankpalNo ratings yet
- Understanding Gyroscopes and Their ApplicationsDocument41 pagesUnderstanding Gyroscopes and Their ApplicationsMalhar NityanandNo ratings yet
- Gyroscopic Motion Presentation GCUFDocument15 pagesGyroscopic Motion Presentation GCUFAhmad ChNo ratings yet
- MECH-2210: Experiment 4: 3D Gyroscopic DynamicsDocument19 pagesMECH-2210: Experiment 4: 3D Gyroscopic DynamicsNamit JainNo ratings yet
- g6 Gyroscope 2of2Document10 pagesg6 Gyroscope 2of2rahul sharmaNo ratings yet
- Rotational Motion and its Applications in Everyday LifeDocument5 pagesRotational Motion and its Applications in Everyday LifeAmirul Syafiq KamalNo ratings yet
- What Is GyroscopeDocument15 pagesWhat Is GyroscopeHazrat BelalNo ratings yet
- GyroscopeDocument5 pagesGyroscopesande.norman21No ratings yet
- Application of gyroscopic principle in automobilesDocument3 pagesApplication of gyroscopic principle in automobilesANANDARAJ SNo ratings yet
- Gyroscope Lab ExperimentDocument5 pagesGyroscope Lab Experimentrhusseinpos4765No ratings yet
- MECA 324 Sensors & Actuators: Velocity and Acceleration SensorsDocument16 pagesMECA 324 Sensors & Actuators: Velocity and Acceleration SensorsArda GunayNo ratings yet
- Lab 11 ManualDocument6 pagesLab 11 Manualmubarik aliNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14 - GyroscopesDocument54 pagesChapter 14 - Gyroscopesnigatudesta21No ratings yet
- GyroscopesDocument27 pagesGyroscopesMadhan RajamanickamNo ratings yet
- Gyroscopic Stabilization and Kinematics of MachineryDocument21 pagesGyroscopic Stabilization and Kinematics of MachineryVenkatesh Mec100% (1)
- Gyroscope: Presenter: Muhammad Khurram Javed 2008-EP-17Document23 pagesGyroscope: Presenter: Muhammad Khurram Javed 2008-EP-17Abhishek SavnaniNo ratings yet
- How Gyros Work in Well SurveyingDocument2 pagesHow Gyros Work in Well SurveyingdaveNo ratings yet
- Availability and Irreversibility Gate Notes 201686837008983Document7 pagesAvailability and Irreversibility Gate Notes 201686837008983Somu SinghNo ratings yet
- Gyro Drift and Corrective Action of a Wellbore Navigation and Humphrey/Goodrich 1.50” Diameter Inertia GyroscopeDocument15 pagesGyro Drift and Corrective Action of a Wellbore Navigation and Humphrey/Goodrich 1.50” Diameter Inertia GyroscopecprobesNo ratings yet
- Gyros CopDocument25 pagesGyros CopMiguel Alejandro PérezNo ratings yet
- Group 6 GyroscopeDocument17 pagesGroup 6 GyroscopePhenias ManyashaNo ratings yet
- A Gyroscope-Based Inverted Pendulum With Application To Posture Stabilization of Bicycle VehicleDocument6 pagesA Gyroscope-Based Inverted Pendulum With Application To Posture Stabilization of Bicycle VehicleRitesh RajNo ratings yet
- Lecture36 37 GyroscopeDocument25 pagesLecture36 37 GyroscopeShivaniNo ratings yet
- Gyroscopic Stabilization of Unstable Vehicles Project PresentationDocument25 pagesGyroscopic Stabilization of Unstable Vehicles Project PresentationPratham JainNo ratings yet
- Gyroscope: Amit Kumar Sharma Mech. Engg. 17MED54 Iet Khandari, AgraDocument12 pagesGyroscope: Amit Kumar Sharma Mech. Engg. 17MED54 Iet Khandari, AgraAmit Kumar SharmaNo ratings yet
- The Inner Workings of a Watch - A Simple Guide for Enthusiasts of Clockwork MechanismsFrom EverandThe Inner Workings of a Watch - A Simple Guide for Enthusiasts of Clockwork MechanismsNo ratings yet
- Clapper Block PDFDocument2 pagesClapper Block PDFpericharla ravivarmaNo ratings yet
- PSG College of Technology, Coimbatore - 641004: Online Examinations - September 2020Document3 pagesPSG College of Technology, Coimbatore - 641004: Online Examinations - September 2020pericharla ravivarmaNo ratings yet
- Kinematics of Machinery – Chain Drive and Gyroscope TypesDocument8 pagesKinematics of Machinery – Chain Drive and Gyroscope Typespericharla ravivarmaNo ratings yet
- Group - 4 FinalDocument16 pagesGroup - 4 Finalpericharla ravivarmaNo ratings yet
- Steam Turbine: December 2012Document22 pagesSteam Turbine: December 2012pericharla ravivarmaNo ratings yet
- Batch 8 INDUSTRIAL METALLURGYDocument9 pagesBatch 8 INDUSTRIAL METALLURGYpericharla ravivarmaNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics Assignment PresentationDocument21 pagesThermodynamics Assignment Presentationpericharla ravivarmaNo ratings yet
- Main Parts of Steam TurbineDocument5 pagesMain Parts of Steam Turbinepericharla ravivarmaNo ratings yet
- Group-4 - Corporate Social ResponsibilityDocument6 pagesGroup-4 - Corporate Social Responsibilitypericharla ravivarmaNo ratings yet
- Fatigue and Fracture PDFDocument31 pagesFatigue and Fracture PDFpericharla ravivarmaNo ratings yet
- MP I - by - DR - RameshBabu Lecture 1Document20 pagesMP I - by - DR - RameshBabu Lecture 1pericharla ravivarmaNo ratings yet
- MP I - by - DR - RameshBabu Lecture 4Document61 pagesMP I - by - DR - RameshBabu Lecture 4pericharla ravivarmaNo ratings yet
- Gating and Risering PDFDocument16 pagesGating and Risering PDFpericharla ravivarmaNo ratings yet
- Auto PDFDocument31 pagesAuto PDFpericharla ravivarmaNo ratings yet
- Fatigue and Fracture PDFDocument31 pagesFatigue and Fracture PDFpericharla ravivarmaNo ratings yet
- Unit 3getting and RiseringDocument16 pagesUnit 3getting and Riseringrakesh shresthaNo ratings yet
- General Foundry PracticesDocument6 pagesGeneral Foundry Practicespericharla ravivarmaNo ratings yet
- Rolling ResistanceDocument3 pagesRolling Resistancepericharla ravivarmaNo ratings yet
- Friction WedgesDocument7 pagesFriction Wedgespericharla ravivarmaNo ratings yet