Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Organic Chemistry Alkanes and Alkenes
Uploaded by
Shahira0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views12 pagesAlkanes and alkenes undergo different reaction types. Alkanes undergo substitution reactions where hydrogen atoms are replaced, as well as combustion producing carbon dioxide, water, and heat. Alkenes undergo addition reactions and can be identified using bromine water, which turns colorless upon reaction with an alkene double bond. Both undergo additional reactions including hydrogenation, halogenation, hydration, and addition of hydrogen halides.
Original Description:
Notes on Alkanes vs. alkenes
Original Title
alkanes vs alkenes
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentAlkanes and alkenes undergo different reaction types. Alkanes undergo substitution reactions where hydrogen atoms are replaced, as well as combustion producing carbon dioxide, water, and heat. Alkenes undergo addition reactions and can be identified using bromine water, which turns colorless upon reaction with an alkene double bond. Both undergo additional reactions including hydrogenation, halogenation, hydration, and addition of hydrogen halides.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views12 pagesOrganic Chemistry Alkanes and Alkenes
Uploaded by
ShahiraAlkanes and alkenes undergo different reaction types. Alkanes undergo substitution reactions where hydrogen atoms are replaced, as well as combustion producing carbon dioxide, water, and heat. Alkenes undergo addition reactions and can be identified using bromine water, which turns colorless upon reaction with an alkene double bond. Both undergo additional reactions including hydrogenation, halogenation, hydration, and addition of hydrogen halides.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 12
Organic Chemistry
Alkanes and Alkenes
Combustion of Alkanes
• Alkanes burn in air or oxygen and produces clean, blue, non-smoky
flame .
• Burning/combustion of alkane produces carbon dioxide and water
and heat.
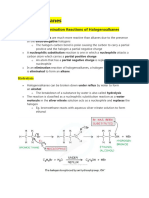
Alkanes- Substitution RXN
• In this rxn H atoms in alkane are replaced by other atoms. Eg. Halogen; Cl, Br, Fl, I
• Eg. Methane and Chlorine
Addition Rxns
• Hydrogenation
• Halogenation
• Hydration
• Addition of Hydrogen halides
• With acidified potassium manganite (IV) solution
• Polymerization
Testing for alkenes
• Bromine water is used to tell the difference
between an alkane and an alkene.
• An alkene will turn brown bromine water
colourless as it reacts with the double bond.
• Bromine water remains brown in the presence
of an alkane as there is no double bond.
• ADDITION OF acidified potassium manganate
(VII)
You might also like
- Organic Tests: AS ChemistryDocument26 pagesOrganic Tests: AS ChemistryDominika NowakNo ratings yet
- Hydrocarbon PDFDocument19 pagesHydrocarbon PDFPrincess Lou CarpenteroNo ratings yet
- 3.3 Reactions and Synthesis of Alkenes PPT 1Document16 pages3.3 Reactions and Synthesis of Alkenes PPT 1Vergil HashimotoNo ratings yet
- Hydrocarbon NotesDocument7 pagesHydrocarbon Notesl8627352No ratings yet
- 13.HYDROCARBONS Full Chapter 2021Document14 pages13.HYDROCARBONS Full Chapter 2021raziabegum03761No ratings yet
- Saturated and Unsaturated HydrocarbonsDocument4 pagesSaturated and Unsaturated HydrocarbonsgefegNo ratings yet
- AlkynesDocument16 pagesAlkynesMichael AttehNo ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument27 pagesChemistryAditya ChawlaNo ratings yet
- Hydroxy CompoundDocument37 pagesHydroxy CompoundZuhailimuna MudaNo ratings yet
- Alchohols Phenols and EthersDocument5 pagesAlchohols Phenols and EthersPritika Yamini SaiNo ratings yet
- Part 1 HCDocument22 pagesPart 1 HCGerald AquinoNo ratings yet
- Physical and Chemical Properties of AlcoholsDocument24 pagesPhysical and Chemical Properties of AlcoholsmeerasahibfarhanNo ratings yet
- Carboxylic Acid and Their DerivatesDocument10 pagesCarboxylic Acid and Their Derivatesvita iftitahiyahNo ratings yet
- Organic Compounds Containing Oxygen PDFDocument17 pagesOrganic Compounds Containing Oxygen PDFPrasant KumarNo ratings yet
- Alkynes 1Document4 pagesAlkynes 1Prazwal RegmiNo ratings yet
- HaloalkaneDocument116 pagesHaloalkaneSam.CareleoneNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Part 2Document9 pagesOrganic Chemistry Part 2AWESOME GENERAL VARUN nrjuNo ratings yet
- Discussion Exp 1Document6 pagesDiscussion Exp 1Dhirah Yuhans67% (3)
- Intro Exp1 chm301Document2 pagesIntro Exp1 chm301AHLA AMANI AHMAD SYAYUTHINo ratings yet
- POC LEcture1Document51 pagesPOC LEcture1quickflickesNo ratings yet
- Tests For Alkanes and Alkenes: More Lessons For IGCSE Chemistry Math WorksheetsDocument3 pagesTests For Alkanes and Alkenes: More Lessons For IGCSE Chemistry Math WorksheetsOdyNo ratings yet
- Alkynes: An Introduction To Organic SynthesisDocument9 pagesAlkynes: An Introduction To Organic Synthesisggwp21No ratings yet
- Chemistry Carbon To Carbon Double BondDocument2 pagesChemistry Carbon To Carbon Double BondJAYLEN TRACEYNo ratings yet
- Org 2Document30 pagesOrg 2rearachel25No ratings yet
- Haloalkanes and Haloarenes NotesDocument18 pagesHaloalkanes and Haloarenes NotesAnkitha shajiNo ratings yet
- Alcohols and Ethers CHM457Document51 pagesAlcohols and Ethers CHM457AIMAN IMAN SHAIFUDDINNo ratings yet
- Organic ChemistryDocument22 pagesOrganic ChemistryjhoyvanNo ratings yet
- Alcohols: N n+1 N 2n+2Document18 pagesAlcohols: N n+1 N 2n+2PrakharNo ratings yet
- Class 12 Chapter 10 Haloalkanes and Haloarenes-1Document75 pagesClass 12 Chapter 10 Haloalkanes and Haloarenes-1RK LegendsNo ratings yet
- BaeyerDocument1 pageBaeyerLivaashini NadarajanNo ratings yet
- of HydrocarbonsDocument45 pagesof HydrocarbonsSneha KediaNo ratings yet
- Some Reactions of HydrocarbonsDocument15 pagesSome Reactions of HydrocarbonsValli SankaranarayananNo ratings yet
- Reactions of AlkenesDocument22 pagesReactions of Alkenesdela2No ratings yet
- Alcohols Phenols & EtherDocument10 pagesAlcohols Phenols & EtherVipin AroraNo ratings yet
- Chap 4Document6 pagesChap 4Doris KimNo ratings yet
- HYDROCARBONSDocument56 pagesHYDROCARBONSAnsh ThakurNo ratings yet
- Hsslive-Xii-Chem-11. Alcohols Phenols and EthersDocument17 pagesHsslive-Xii-Chem-11. Alcohols Phenols and EthersHakim AbbasNo ratings yet
- LAB REPORT Reactions of Aliphatic HydrocarbonsDocument6 pagesLAB REPORT Reactions of Aliphatic HydrocarbonsSafwan Jamil62% (13)
- The Alchemy of Alcohols:: A Beginner's Guide in Organic ChemistryDocument17 pagesThe Alchemy of Alcohols:: A Beginner's Guide in Organic ChemistrypentojochaunceyNo ratings yet
- St. Joseph's College of Arts & Science (Autonomous)Document20 pagesSt. Joseph's College of Arts & Science (Autonomous)Reyadevi GNo ratings yet
- CIE AS Chemistry: 21.1 Organic SynthesisDocument17 pagesCIE AS Chemistry: 21.1 Organic SynthesisiceforgamingNo ratings yet
- Practical No. 2Document16 pagesPractical No. 2shahbazNo ratings yet
- Distinguish TestDocument1 pageDistinguish TestAnsia MeenazNo ratings yet
- Revision Notes On AlcoholsDocument15 pagesRevision Notes On AlcoholsSUSHMANo ratings yet
- FOR STUDENTS - Organic Reactions, Reagents, Conditions, Products SummaryDocument12 pagesFOR STUDENTS - Organic Reactions, Reagents, Conditions, Products Summaryh4rrywastakenNo ratings yet
- SC22b Reactions of Alkanes and AlkenesDocument14 pagesSC22b Reactions of Alkanes and AlkenesEmaadB EmaadBNo ratings yet
- Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers - WatermarkDocument44 pagesAlcohols, Phenols and Ethers - Watermarkasp212009No ratings yet
- Reactions of Alcohols, Phenols, Aldehydes and KetonesDocument44 pagesReactions of Alcohols, Phenols, Aldehydes and KetonesGlen Mangali100% (4)
- HalogenoalkanesDocument16 pagesHalogenoalkaneskudec2008No ratings yet
- Intro & Abstract of AlcoholDocument6 pagesIntro & Abstract of AlcoholgunaNo ratings yet
- Single Organic Test PDFDocument15 pagesSingle Organic Test PDFgreatNo ratings yet
- Postlab 3Document20 pagesPostlab 3Lyra Ane IlaganNo ratings yet
- ALKENEDocument27 pagesALKENEChane ReponteNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry N PolymersDocument82 pagesOrganic Chemistry N PolymersNot IsmdanNo ratings yet
- SKO3013 Aldehyde Ketone-Student NoteDocument51 pagesSKO3013 Aldehyde Ketone-Student NoteMike EzioNo ratings yet
- HYDROCARBONSDocument7 pagesHYDROCARBONSHarsh vardhan SinghNo ratings yet
- Identification of Unknown Organic CompoundsDocument10 pagesIdentification of Unknown Organic CompoundsabhinickyNo ratings yet
- AlkenesDocument120 pagesAlkenesVidhan PatniNo ratings yet
- BSN 1 Reporting Bio Chem 1Document14 pagesBSN 1 Reporting Bio Chem 1Reibenjay CamoralNo ratings yet