0% found this document useful (0 votes)
132 views14 pagesCMOS Inverter Design and Characteristics
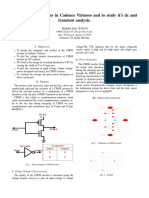
1. The document discusses CMOS inverters and compares them to NMOS inverters.
2. CMOS inverters use both PMOS and NMOS transistors which allows one transistor to be always off, reducing static power consumption.
3. The key advantages of CMOS inverters are high noise immunity and low static power consumption compared to NMOS inverters which dissipate power in their resistive load.
Uploaded by
Sandeep LocharlaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
132 views14 pagesCMOS Inverter Design and Characteristics
1. The document discusses CMOS inverters and compares them to NMOS inverters.
2. CMOS inverters use both PMOS and NMOS transistors which allows one transistor to be always off, reducing static power consumption.
3. The key advantages of CMOS inverters are high noise immunity and low static power consumption compared to NMOS inverters which dissipate power in their resistive load.
Uploaded by
Sandeep LocharlaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd