Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Report. Stratman - Ferrer
Uploaded by
Joyce Anne Ferrer0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views7 pagesThis document discusses international strategy for multinational firms. It outlines key decisions around entry strategies, balancing local adaptation vs global integration. It then defines globalization and discusses factors affecting a nation's competitiveness. The document also outlines the main motivations for international expansion like increasing market size and arbitrage opportunities. Finally, it discusses potential risks of international expansion such as political, economic, counterfeiting and currency risks.
Original Description:
Original Title
REPORT. STRATMAN.FERRER.pptx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses international strategy for multinational firms. It outlines key decisions around entry strategies, balancing local adaptation vs global integration. It then defines globalization and discusses factors affecting a nation's competitiveness. The document also outlines the main motivations for international expansion like increasing market size and arbitrage opportunities. Finally, it discusses potential risks of international expansion such as political, economic, counterfeiting and currency risks.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views7 pagesReport. Stratman - Ferrer
Uploaded by
Joyce Anne FerrerThis document discusses international strategy for multinational firms. It outlines key decisions around entry strategies, balancing local adaptation vs global integration. It then defines globalization and discusses factors affecting a nation's competitiveness. The document also outlines the main motivations for international expansion like increasing market size and arbitrage opportunities. Finally, it discusses potential risks of international expansion such as political, economic, counterfeiting and currency risks.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 7
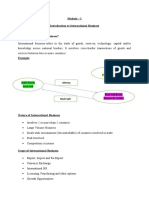
INTERNATIONAL STRATEGY
O Multinational firms are constantly faced with
many important decisions. These include entry
strategies; the dilemma of choosing between local
adaptation (in product offerings, locations,
advertising, and pricing) and global integration;
and others.
O This lesson will discuss how firms create value
and achieve competitive advantage in the global
marketplace.
Globalization - a term that has two meanings:
1. The increase in international exchange, including
trade in goods and services as well as exchange of
money, ideas, and information;
2. The growing similarity of laws, rules, norms,
values, and ideas across countries.
Factors Affecting Nation’s
Competitiveness
Motivations for
International Expansion
1. Increase Market Size
O To increase the size of potential markets for a firm‘s
products and services
2. Take Advantage of Arbitrage
O Arbitrage opportunities - an opportunity to profit by
buying and selling the same good in different markets.
3. Enhancing a Product’s Growth Potential
O Enhancing the growth rate of a product that is in its maturity
stage in a firm‘s home country but that has greater demand
potential elsewhere is another benefit of international
expansion.
4. Optimize the Location of Value-Chain Activities
O Optimizing the location for every activity in the value chain can yield
one or more of three strategic advantages: performance enhancement,
cost reduction, and risk reduction.
5. Learning Opportunities
O By expanding into new markets, corporations expose themselves to
differing market demands, R&D capabilities, functional skills,
organizational processes, and managerial practices
6. Explore Reverse Innovation
O Reverse innovation - new products developed by developed-country
multinational firms for emerging markets that have adequate
functionality at a low cost
Potential Risks of
International Expansion
1. Political risk - potential threat to a firm‘s operations in a
country due to ineffectiveness of the domestic political
system.
2. Economic risk - potential threat to a firm‘s
operations in a country due to economic policies and
conditions, including property rights laws and
enforcement of those laws.
3. Counterfeiting - selling of trademarked goods
without the consent of the trademark holder.
4. Currency risk - potential threat to a firm‘s operations
in a country due to fluctuations in the local currency‘s
exchange rate.
5. Management - risk potential threat to a firm‘s
operations in a country due to the problems that
managers have making decisions in the context of
foreign markets.
You might also like
- International Business ManagementDocument42 pagesInternational Business ManagementMihir BansalNo ratings yet
- International Business and TradeDocument4 pagesInternational Business and TradeAutum Leondale100% (4)
- Algorithms (Complete Course) :-Btech CSE: TopicsDocument4 pagesAlgorithms (Complete Course) :-Btech CSE: TopicsRahul SinghNo ratings yet
- Csec It Mock ExamDocument10 pagesCsec It Mock Examvidur_talreja100% (1)
- Lesson 11 International Aspects of Corporate FinanceDocument17 pagesLesson 11 International Aspects of Corporate Financeman ibe0% (1)
- Strategies For Global MarketsDocument43 pagesStrategies For Global MarketsRia Sarkar50% (2)
- International MarketingDocument59 pagesInternational MarketingRahul Singh100% (3)
- LC - Gunk SqueezesDocument5 pagesLC - Gunk SqueezesHeris SitompulNo ratings yet
- Probability Distributions Summary - Exam PDocument1 pageProbability Distributions Summary - Exam Proy_gettyNo ratings yet
- Lump Sum Contract NotesDocument1 pageLump Sum Contract NotesamrkiplNo ratings yet
- University of Hargeisa GIT Pharmacology Review Questions: Name:aniisa Muse Ahmed Faculty:midwifery ID:1716642 Class:3ADocument4 pagesUniversity of Hargeisa GIT Pharmacology Review Questions: Name:aniisa Muse Ahmed Faculty:midwifery ID:1716642 Class:3AAniza Mouse100% (1)
- Global StrategyDocument16 pagesGlobal StrategyDINHSYHOAN1No ratings yet
- Static Var CompensatorDocument29 pagesStatic Var CompensatorCarlos Fabian GallardoNo ratings yet
- International MarketingDocument77 pagesInternational MarketingSaki HussainNo ratings yet
- IM Answer KeyDocument12 pagesIM Answer KeySupriya sNo ratings yet
- IBT Lesson 1-2Document9 pagesIBT Lesson 1-2runerudesuNo ratings yet
- BBA - GGS Indraprastha University BBA-308 INTERNATIONAL Business ManagementDocument4 pagesBBA - GGS Indraprastha University BBA-308 INTERNATIONAL Business ManagementKunal KalraNo ratings yet
- IBPS Notes Part 1Document16 pagesIBPS Notes Part 1Yash PatelNo ratings yet
- International Strategy 2Document17 pagesInternational Strategy 2starshine.jimenezNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document6 pagesChapter 7Crusher asadonNo ratings yet
- IBPS Full NotesDocument35 pagesIBPS Full NotesYash PatelNo ratings yet
- International BusinessDocument29 pagesInternational BusinesskaranvishweshsharmaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Internal StrategyDocument3 pagesChapter 7 Internal StrategyivyNo ratings yet
- SEM 3rd IBDocument26 pagesSEM 3rd IBSmile For Kids TVNo ratings yet
- Designing and Managing Global Marketing StrategiesDocument23 pagesDesigning and Managing Global Marketing StrategiesShreekānth DāngiNo ratings yet
- Unit I Introduction To International MarketingDocument11 pagesUnit I Introduction To International MarketingCharushilaNo ratings yet
- Mkt506 Dossa As1Document10 pagesMkt506 Dossa As1Shaharyar Nasim BaqarNo ratings yet
- International Marketing 1Document11 pagesInternational Marketing 1Irfana Mubarak100% (1)
- International ManagementDocument17 pagesInternational ManagementMartina Clarke GarciaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8: Tapping Into Global Markets: Deciding Which Markets To EnterDocument29 pagesChapter 8: Tapping Into Global Markets: Deciding Which Markets To Entersurprise MF100% (1)
- Ibm ImpDocument3 pagesIbm ImpAastha KohliNo ratings yet
- Topic 10Document15 pagesTopic 10AliNo ratings yet
- Expanding A Business Internationally Can Offer Several BenefitsDocument1 pageExpanding A Business Internationally Can Offer Several BenefitsPriya deyNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Gloal MarketingDocument8 pagesUnit 2 Gloal MarketingHariharan EKSNo ratings yet
- Global Market CompetitionDocument3 pagesGlobal Market CompetitionFAMULERAS, Irene, AbanadorNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document2 pagesChapter 2CASAQUIT, IRA LORAINENo ratings yet
- International Marketing StrategyDocument21 pagesInternational Marketing StrategyDehan Annafi MawansyahNo ratings yet
- Velammal Engineering College, CHENNAI - 600 066: Department of Management Sciences Questions & AnswersDocument50 pagesVelammal Engineering College, CHENNAI - 600 066: Department of Management Sciences Questions & AnswerscowgaNo ratings yet
- 04 Intl Biz Globalisation Session 7 & 8Document19 pages04 Intl Biz Globalisation Session 7 & 8shashankNo ratings yet
- Global Business Environment FINALDocument41 pagesGlobal Business Environment FINALSanthosh KrishnaNo ratings yet
- 05 Intl Biz Globalisation Session 7 & 8Document21 pages05 Intl Biz Globalisation Session 7 & 8Kapil PrabhuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 SumaryDocument3 pagesChapter 8 SumarydskjbfNo ratings yet
- DefinitionsDocument5 pagesDefinitionscgureayaNo ratings yet
- MBS 3rd Semester International BusinessDocument135 pagesMBS 3rd Semester International BusinessfierceaadarshaNo ratings yet
- According To Kedia & Mukherji (1999) (Wortzel, 1991)Document21 pagesAccording To Kedia & Mukherji (1999) (Wortzel, 1991)Maliha ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- International MarketingDocument13 pagesInternational MarketingBiniyam GizawNo ratings yet
- Unit 7: Global Aspects of EntrepreneurshipDocument14 pagesUnit 7: Global Aspects of EntrepreneurshipAngela Inesoria INo ratings yet
- Business Policy & StrategyDocument10 pagesBusiness Policy & StrategyCaptain Jellyfish MasterNo ratings yet
- INBUSTRADE - Topic5 The Global MarketplaceDocument46 pagesINBUSTRADE - Topic5 The Global MarketplaceSapphire LayNo ratings yet
- Module 1Document8 pagesModule 1AdityaNo ratings yet
- Chapter One InternationalDocument11 pagesChapter One InternationalAbdu YaYa AbeshaNo ratings yet
- Topics - International Business - Definition - Internationalizing Business-AdvantagesDocument157 pagesTopics - International Business - Definition - Internationalizing Business-AdvantagesPravitha SajeeNo ratings yet
- UNIT 7 - Global Aspects of Entrepreneurship 1Document15 pagesUNIT 7 - Global Aspects of Entrepreneurship 1Altaire Gabrieli DayritNo ratings yet
- Ibm Notes For ReferenceDocument156 pagesIbm Notes For ReferencePravitha SajeeNo ratings yet
- 5 Global Business IssuesDocument12 pages5 Global Business IssuesLayar KayarNo ratings yet
- Module - 1 Introduction To International Business: Rock Salt (From Pakistan Rs 20/KG)Document12 pagesModule - 1 Introduction To International Business: Rock Salt (From Pakistan Rs 20/KG)RITIKA SINHANo ratings yet
- Unit - I Introduction To International BusinessDocument53 pagesUnit - I Introduction To International BusinessChandhini RNo ratings yet
- International Business Management: Unit-1Document5 pagesInternational Business Management: Unit-1Chandrasekar IdumbanNo ratings yet
- Course Note For Class 22Document41 pagesCourse Note For Class 22박서희No ratings yet
- International BusinessDocument113 pagesInternational BusinessPallavi NaikNo ratings yet
- Report (International Business)Document15 pagesReport (International Business)fizza kashifNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document10 pagesUnit 1Mohd SuhailNo ratings yet
- MGT 430 Review Questions For Midterm Exam Spring 2016Document5 pagesMGT 430 Review Questions For Midterm Exam Spring 2016AmandaNo ratings yet
- Globalisation Strategies Prof Bharat NadkarniDocument15 pagesGlobalisation Strategies Prof Bharat NadkarniRajat ShettyNo ratings yet
- Management of International BusinessDocument100 pagesManagement of International BusinessSantosh AdhikariNo ratings yet
- 2021 Holiday Consumer Protection GuideDocument61 pages2021 Holiday Consumer Protection GuidePeterBurkeNo ratings yet
- LP Grade 8 MolaveDocument19 pagesLP Grade 8 MolaveBlessing Shielo VicenteNo ratings yet
- Multi Car ParkingDocument33 pagesMulti Car ParkingTanvi KhuranaNo ratings yet
- Ch. 30 Basic MacroeconomicsDocument38 pagesCh. 30 Basic MacroeconomicsFatmahNo ratings yet
- FTL20.pdf Ultrasonic SondeDocument20 pagesFTL20.pdf Ultrasonic SondeJaroslav BiresNo ratings yet
- Telecom - MA - Update 2019 - vFINALDocument11 pagesTelecom - MA - Update 2019 - vFINALYandhi SuryaNo ratings yet
- Health Related Fitness and NutritionDocument4 pagesHealth Related Fitness and NutritionKarol RydloNo ratings yet
- OpenScapeBusiness V1 R2.1.0 Release Note V1.2.10 ExternDocument14 pagesOpenScapeBusiness V1 R2.1.0 Release Note V1.2.10 Externjan2No ratings yet
- Application Form Safety Program Pg1Document1 pageApplication Form Safety Program Pg1Mark Jayson GarciaNo ratings yet
- Javascript: Case Study To Be Used For Hands-On SessionsDocument14 pagesJavascript: Case Study To Be Used For Hands-On SessionsSettiNagarajuNo ratings yet
- Choose The Best Answer From The Four Options (Marked A, B, C, or D) To Complete The Sentences. Exercise 1Document6 pagesChoose The Best Answer From The Four Options (Marked A, B, C, or D) To Complete The Sentences. Exercise 1Van AnhNo ratings yet
- Latihan SoalDocument7 pagesLatihan SoaljuliaNo ratings yet
- Epidemiological Study of Ostrich Diseases and Its Management in The Ostrich Farm of NepalDocument13 pagesEpidemiological Study of Ostrich Diseases and Its Management in The Ostrich Farm of NepalKarki KedarNo ratings yet
- Bioshock Audio DiariesDocument6 pagesBioshock Audio DiariesGeorge CuriosoNo ratings yet
- Module 5 Advanced MechanicsDocument60 pagesModule 5 Advanced Mechanicsiknowvictoriassecret49No ratings yet
- Josef Suk-BagatellaDocument6 pagesJosef Suk-BagatellaAlessandro CaspaniNo ratings yet
- Tele BRANCHES 01.06.2021Document23 pagesTele BRANCHES 01.06.2021Abhishek BarwalNo ratings yet
- P.E 12 AquaticsDocument5 pagesP.E 12 Aquaticsabrenicaraniel05No ratings yet
- DFX8 WebDocument2 pagesDFX8 Websamer8saifNo ratings yet
- QuestionsDocument3 pagesQuestionsRajani NairNo ratings yet
- NWPC Annual Report 2014Document56 pagesNWPC Annual Report 2014lupethe3No ratings yet
- MSYS-1 0 11-ChangesDocument3 pagesMSYS-1 0 11-ChangesCyril BerthelotNo ratings yet
- Financial Statement Analysis at Sangam Dairy: by TurnitinDocument116 pagesFinancial Statement Analysis at Sangam Dairy: by TurnitinHarry SaiNo ratings yet