0% found this document useful (0 votes)
82 views41 pagesCSE 333 Computer Peripherals & Interfacing
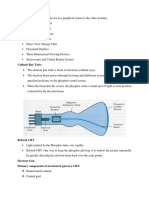
The document discusses video display systems including CRT, LCD, and LED displays. It describes how CRT displays work using an electron gun and phosphor coating to generate images. Raster scan and random scan display methods are also covered. Character generation for CRT displays is then explained through the use of dot matrices and memory buffers.
Uploaded by
hossain shuvoCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
82 views41 pagesCSE 333 Computer Peripherals & Interfacing
The document discusses video display systems including CRT, LCD, and LED displays. It describes how CRT displays work using an electron gun and phosphor coating to generate images. Raster scan and random scan display methods are also covered. Character generation for CRT displays is then explained through the use of dot matrices and memory buffers.
Uploaded by
hossain shuvoCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd