Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Diabetes Mellitus
Uploaded by
gibreil0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
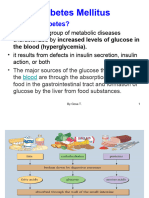
13 views27 pagesThis document summarizes diabetes mellitus, including defining the two main types, their presentations, investigations, treatment options, complications, and management in pregnancy. Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune disorder destroying insulin-producing cells, while type 2 is relative insulin deficiency due to excess adipose tissue. Type 1 tends to present in younger patients with weight loss and ketoacidosis, while type 2 is often found incidentally in middle-aged or older patients. Treatment includes lifestyle changes, oral medications like metformin and sulfonylureas, and insulin. Complications involve damage to various organs and tissues over time if not well-controlled. Gestational diabetes risks are monitored and treated to prevent issues for the mother and baby.
Original Description:
Original Title
DIABETES-MELLITUS
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document summarizes diabetes mellitus, including defining the two main types, their presentations, investigations, treatment options, complications, and management in pregnancy. Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune disorder destroying insulin-producing cells, while type 2 is relative insulin deficiency due to excess adipose tissue. Type 1 tends to present in younger patients with weight loss and ketoacidosis, while type 2 is often found incidentally in middle-aged or older patients. Treatment includes lifestyle changes, oral medications like metformin and sulfonylureas, and insulin. Complications involve damage to various organs and tissues over time if not well-controlled. Gestational diabetes risks are monitored and treated to prevent issues for the mother and baby.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views27 pagesDiabetes Mellitus
Uploaded by
gibreilThis document summarizes diabetes mellitus, including defining the two main types, their presentations, investigations, treatment options, complications, and management in pregnancy. Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune disorder destroying insulin-producing cells, while type 2 is relative insulin deficiency due to excess adipose tissue. Type 1 tends to present in younger patients with weight loss and ketoacidosis, while type 2 is often found incidentally in middle-aged or older patients. Treatment includes lifestyle changes, oral medications like metformin and sulfonylureas, and insulin. Complications involve damage to various organs and tissues over time if not well-controlled. Gestational diabetes risks are monitored and treated to prevent issues for the mother and baby.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 27
DIABETES MELLITUS
DEFINING DIABETES
• Diabetes Mellitus Type 1 : Autoimmune disorder causing
destruction insulin-producing beta cells of the islets of Langerhans
• Diabetes Mellitus: Relative deficiency of insulin due to an excess of
adipose tissue.
HOW DO THEY PRESENT?
Type 1 DM- tend to be younger Type 2 DM
YOUNG PATIENTS MIDDLE AGED OR OLDER
• Weight loss • Incidental finding on routine blood
• Polydipsia tests
• Polyuria • Polydipsia
• May present with DKA • Polyuria
Þ Nausea and vomiting
Þ Abdominal pain
Þ Reduced consciousness level
Investigations: 4 main ways to check Blood Glucose
1. Finger-prick bedside glucose monitor
2. One-off blood glucose: fasting or non-fasting
3. HbA1c: Measures the amount of glycosylated haemoglobin and represents
the average blood glucose over the past 2-3 months
4. Glucose tolerance test.
Þ a fasting blood glucose is taken
Þ Then a 75g glucose load is taken
Þ After 2 hours a second blood glucose reading is then taken
TEST NORMAL IMPAIRED GLUCOSE TOLERANCE DIABETES
75g OGTT <7.8 mmol/L >= 7.8 – 11 mmol/L >11 mmol/L
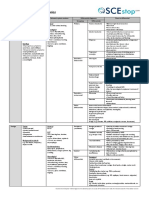
Drug class Mechanism of action Route Main side-effects Contraindication
Insulin Direct replacement SC Hypoglycaemia
Weight gain
Lipodystrophy
Metformin Increases insulin Oral Gastrointestinal upset Low BMI
sensitivity& Lactic acidosis Renal failure
suppresses Weight loss
gluconeogenesis
Sulfonylurea Increase beta cells Oral Hypoglycaemia Patients at risk of
Gliclazide insulin secretion Weight gain hypoglycaemia
Severe hepatic/renal
impairment
Thiazolidinedione Increases fat/muscle glucose Oral Weight gain Heart failure
Pioglitazone uptake Fluid retention
Fractures
DPP-4 inhibitors Increases incretin levels Oral Pancreatitis
(-Gliptins) (hormone released by gut to
e.g. Sitaglipitin increase insulin after food)
SGLT-2 inhibitors Increases urinary glucose Oral UTIs Renal failure
(-Gliflozins) excretion Ketoacidosis
e.g. Dapagliflozin
GLP-1 agonists Incretin (GLP-1) mimetic SC GI upset (n&v) Renal failure
(-tides) Pancreatitis PMH
e.g. Exanetide Weight losss Pancreatitis
Severe GI
disease
INSULIN REGIMENS – TYPE 1 DM
COMPLICTAIONS OF DIABETES
• Cardiovascular disease: Increased risk of Ischaemic Heart disease
• Increased risk for peripheral vascular disease: claudication
• Diabetic neuropathy: polyneuropathy, mono-neuropathy (carpal
tunnel syndrome)
• Nephropathy: kidney damage
• Retinopathy: vision loss
• Poor healing + neuropathy -> Ulcers
DIABETES IN
PREGNANCY
Pregnant patients may have:
1. Pre-existing diabetes: Individuals who have had a
diagnosis of DM prior to pregnancy
2. Gestational diabetes: Those in which diabetes
appears during pregnancy and disappears after
delivery
Risk factors for Gestational diabetes
• BMI > 30
• Previous macroscopic baby
• Previous gestational diabetes
• 1st degree relative with diabetes
• Ethnic groups: south Asian, middle eastern etc.
DIAGNOSTIC THRESHOLDS FOR
GESTATIONAL DIABETES
• Fasting glucose ≥ 5.6 mmol/l
• 2- hour glucose ≥ 7.8 mmol/l
Management of Gestational Diabetes
• Monitoring
Followed up in a joint diabetes and Antenatal clinic weekly
Taught self-monitoring
Fasting target 5.3 mmol/L
1 hr after meals 7.8mmol/L)
• Conservative: Advice on diet and exercise
• Medical:
Þ Metformin
Þ Insulin
• Fasting plasma Glucose <7 mmol/l (126 mg/dl)
Trial of diet and exercise
If glucose targets are not met within 1-2 weeks -> initiate
metformin
If targets are still not met insulin is initiated
• Fasting Plasma Glucose >7 mmol/l (126 mg/dl) at the time of
diagnosis -> insulin should be initiated
USA CLASSIFCATION
PRE-EXISTING DIABETES MANAGEMENT
• Monitoring
Þ Detailed anomaly scan at 20 weeks gestation
Þ Tight glycaemic control to reduce complications
Þ Screen for retinopathy as can worsen during pregnancy
• Conservative
Þ Weight loss if BMI >27
Þ Diet and exercise advice
• Medical
Þ Folic acid 5mg/day form pre-conception to 12 weeks gestation
Þ Stop oral hypoglycaemic apart from metformin
Þ Initiate insulin
Complication of Diabetes in Pregnancy
MATERNAL NEONATAL
Polyhydramnios (foetal polyuria) Macrosomia
Pre-term labour (polyhydramnios) Shoulder dystocia
Small for gestational age
Respiratory distress syndrome
(surfactant)
polycythaemia: neonatal jaundice
CARDIOTOCOGRAPH
Define Risk Low or high
Contractions Record number of contractions in 10 minutes)
Duration
Intensity (felt via examination)
Baseline Rate Average rate in 10 minutes
Normal 110- 150 bpm
Bradycardia, Tachycardia
Variability Normal (at rest 10 – 25bpm)
1. Reassuring >= 5 bpm
2. Non-reassuring <5bpm between 40 -90 minutes
3. Abnormal < 5 bpm > 90 minutes
Accelerations Abrupt increase in baseline heart rate of >15 bpm for >15 seconds
2 accelerations every 15 minutes
Present/Absent
Decelerations Abrupt decrease in baseline heart rate of >15 bpm for >15 seconds.
Overall impression Reassuring, Non-reassuring normal
OTHER RISK FACTORS OBSTETRIC COMPLICATIONS
• Lack of Pre-natal care • Multiple gestation
• Smoking • Postdate gestation
• Drug abuse • Previous caesarean section
• Intrauterine growth restriction
MATERNAL MEDICAL ILLNESS • Premature rupture of membranes
• Gestational diabetes • Congenital malformations
• Hypertension • Induction of labour
• Asthma • Pre-eclampsia
Foetal Tachycardia > 160 bpm Foetal Bradycardia <120 bpm
• Foetal hypoxia Mild 100- 120 bpm
• Chorioamnionitis: Maternal fever • Postdate gestation
• Hyperthyroidism Severe <80 bpm >3 mins
• Foetal or maternal anaemia 1. Prolonged cord compression
2. Cord prolapse
3. Epidural
4. Maternal seizure
5. Rapid foetal decent
DELIVER IMMEDIATELY IF CAUSE
NOT IDENTIFIED AND CORRECTED
Reduced Variability
• Foetal sleeping
• Foetal hypoxia
• Foetal tachycardia
• Prematurity <28 weeks gestation
Early decelerations
• Normal – physiological
• Start when uterine contraction begins and recover when uterine
contraction ends
LATE DECELERATIONS
BEGIN AT PEAK OF UTERINE CONTRACTIONS
RECOVER AFTER CONTRACTION ENDS
PROLONGED DECELERATION
DECELERATION > 2 MINS
IF > 3 MINS ABNORMAL
BOTH REQUIER FOETAL BLOOD SAMPLING =IF ACIDOTIC = EMERGENCY C SECTION
You might also like
- Diabetic Recipes for One and TwoFrom EverandDiabetic Recipes for One and TwoRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Presenter: Dr. P. Usha Rani Resident, ASRAMS, EluruDocument60 pagesPresenter: Dr. P. Usha Rani Resident, ASRAMS, EluruDivya Rekha KolliNo ratings yet
- Diabetic Cooking for One and TwoFrom EverandDiabetic Cooking for One and TwoRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- DiabetesDocument99 pagesDiabetes489226fahimNo ratings yet
- Type 2 Diabetes: How to Eat Better, Lower Blood Sugar, and Manage DiabetesFrom EverandType 2 Diabetes: How to Eat Better, Lower Blood Sugar, and Manage DiabetesNo ratings yet
- Diabetes Mellitus: NZ Diploma in Enrolled NursingDocument38 pagesDiabetes Mellitus: NZ Diploma in Enrolled NursingRegina PunNo ratings yet
- Week4 EndocrineDocument84 pagesWeek4 EndocrineriverabeanicoNo ratings yet
- Diabetes Mellitus in PregnancyDocument55 pagesDiabetes Mellitus in Pregnancyapi-3856051100% (2)
- Hypertensive Disorders in Pregnancy: Department of Obstetrics & Gynecology, Medicine Faculty of UKI JakartaDocument33 pagesHypertensive Disorders in Pregnancy: Department of Obstetrics & Gynecology, Medicine Faculty of UKI JakartaLucy WijayaNo ratings yet
- Preeclampsia and Eclampsia: Regala Bianca Ysabelle M. BSN Ii-B RLE Group 3Document20 pagesPreeclampsia and Eclampsia: Regala Bianca Ysabelle M. BSN Ii-B RLE Group 3Biway RegalaNo ratings yet
- Endo ChecklistDocument39 pagesEndo ChecklistFatin Nurina Mohd NazemiNo ratings yet
- Metabolic Syndrome: Stay Healthy, Live HappilyDocument32 pagesMetabolic Syndrome: Stay Healthy, Live HappilykomalscientistNo ratings yet
- Recovered File 1Document24 pagesRecovered File 1Mao GallardoNo ratings yet
- Diabetes Mellitus Type Ii: HipertensiDocument24 pagesDiabetes Mellitus Type Ii: HipertensinurulNo ratings yet
- Group 3 - Week 2 (Nur192)Document32 pagesGroup 3 - Week 2 (Nur192)Cristine JanolinoNo ratings yet
- Hypertensive Disorders in Pregnancy: Dr. Enricko Siregar, SpogDocument26 pagesHypertensive Disorders in Pregnancy: Dr. Enricko Siregar, SpogEllen SintiaNo ratings yet
- Paeda DMDocument38 pagesPaeda DMAmanuel LemiNo ratings yet
- Hypertensive Disorders in Pregnancy: Dr. Johanes C. Mose, DR, SpogDocument39 pagesHypertensive Disorders in Pregnancy: Dr. Johanes C. Mose, DR, SpogfiskaNo ratings yet
- Diabetes Mellitus: - ClassificationDocument22 pagesDiabetes Mellitus: - ClassificationFernando Junior Parra UchasaraNo ratings yet
- Endo ReviewDocument30 pagesEndo ReviewRiz BorbonNo ratings yet
- Diabetes MellitusDocument44 pagesDiabetes MellitusabdallhNo ratings yet
- Diabetes Mellitus 2021Document61 pagesDiabetes Mellitus 2021Andarge ImperialNo ratings yet
- Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Week 27 Lynn AdamsonDocument6 pagesType 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Week 27 Lynn Adamsondragtoss2No ratings yet
- NOTULENSIDocument100 pagesNOTULENSITasya MRNo ratings yet
- Obs Two Power Point... PreclamciaDocument32 pagesObs Two Power Point... PreclamciaZEMENAY TRUNEHNo ratings yet
- DM in PregDocument32 pagesDM in Pregbryanpei23No ratings yet
- Assessment and Management of Patients With Diabetes MellitusDocument82 pagesAssessment and Management of Patients With Diabetes MellitusMuhidin AeNo ratings yet
- Farmakoterapi Sistem Endokrin: Tim Dosen Farmasi KlinikDocument42 pagesFarmakoterapi Sistem Endokrin: Tim Dosen Farmasi KlinikAnonymous h76WT2cFdkNo ratings yet
- Hypertensive Disorders of PregnancyDocument46 pagesHypertensive Disorders of PregnancyJagadeeswari JayaseelanNo ratings yet
- Less 2 Hrs After Meal: Goals For Blood Glucose Levels During Pregnany: 95 MG/DL or Less Before Meals and 120 MG/DL orDocument6 pagesLess 2 Hrs After Meal: Goals For Blood Glucose Levels During Pregnany: 95 MG/DL or Less Before Meals and 120 MG/DL orspain michaelisNo ratings yet
- NCMB 316 Cu12 EndocrineDocument84 pagesNCMB 316 Cu12 EndocrineJanine Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Diabetes MellitusDocument65 pagesDiabetes MellitusOneTwoNo ratings yet
- Case ADocument2 pagesCase Aapi-26938624No ratings yet
- DIABETES MELLITUS FinalDocument83 pagesDIABETES MELLITUS FinalYuvi Yuvaraj100% (1)
- Diabetes Mellitus: April 2014Document41 pagesDiabetes Mellitus: April 2014Koricho MengistuNo ratings yet
- AH Exam 1 StudyDocument9 pagesAH Exam 1 StudyI KoffiNo ratings yet
- Diabetes MelitusDocument27 pagesDiabetes Melitusana chasanahNo ratings yet
- Assessment - and - Management - of - Patients - With - Diabetes - Mellitus (1) FINALDocument80 pagesAssessment - and - Management - of - Patients - With - Diabetes - Mellitus (1) FINALAMIT MODWALNo ratings yet
- Diabetes Mellitus: Anne Dawnay Biochemical MedicineDocument26 pagesDiabetes Mellitus: Anne Dawnay Biochemical MedicineJoni HermawanNo ratings yet
- Adult 1 - Week 6 (Chapter 48)Document6 pagesAdult 1 - Week 6 (Chapter 48)Sydney SmallNo ratings yet
- Diabetes Mellitus DCM 3Document71 pagesDiabetes Mellitus DCM 3maxwell mafungaNo ratings yet
- CPT CC5Document103 pagesCPT CC5KAYLLIEN DURANNo ratings yet
- Diabetes MellitusDocument26 pagesDiabetes MellitusgosaNo ratings yet
- Referat HDKDocument29 pagesReferat HDKAga Haris100% (1)
- DIABETIC COMA - Clinical Features and ManagementDocument54 pagesDIABETIC COMA - Clinical Features and ManagementRitesh SinghNo ratings yet
- Hypertension in Pregnancy (Pogs-Cpg)Document60 pagesHypertension in Pregnancy (Pogs-Cpg)Ivy Combista Baya100% (1)
- Hyperemesis GravidarumDocument44 pagesHyperemesis GravidarumSharwajit JhaNo ratings yet
- Med - Comp - Slides PDFDocument54 pagesMed - Comp - Slides PDFFiras KNo ratings yet
- Blood GlucoseDocument42 pagesBlood GlucoseShaira De La CruzNo ratings yet
- Diabetes Mellitus CDocument48 pagesDiabetes Mellitus Cjoel david knda mjNo ratings yet
- Gestational Diabetes MellitusDocument31 pagesGestational Diabetes MellitusLidya BintangNo ratings yet
- Curs Studenti StrainiDocument71 pagesCurs Studenti StrainiAlexandru VisanNo ratings yet
- OB - Hypertensive DisordersDocument4 pagesOB - Hypertensive DisordersJasmine Nicole RemetreNo ratings yet
- Hypertensive Disorder in Pregnancy Untuk KuliahDocument78 pagesHypertensive Disorder in Pregnancy Untuk Kuliah404notfoundNo ratings yet
- Lecture - Paediatric Endocrine Emergencies PDFDocument51 pagesLecture - Paediatric Endocrine Emergencies PDFOnSolomonNo ratings yet
- (Belle) Diabetes in PregnancyDocument3 pages(Belle) Diabetes in PregnancyAray Al-AfiqahNo ratings yet
- Diabetes Mellitus: Medical Complications in PregnancyDocument19 pagesDiabetes Mellitus: Medical Complications in PregnancySenopati KhanjieNo ratings yet
- Seminar 5 - DM in PregnancyDocument19 pagesSeminar 5 - DM in PregnancyHakimah K. SuhaimiNo ratings yet
- Topic Discussion DiabetsDocument30 pagesTopic Discussion Diabetsapi-538856946No ratings yet
- Preeclampsia Y Eclampsia: Hospital Materno Infantil Mip Guzmán González Héctor EduardoDocument30 pagesPreeclampsia Y Eclampsia: Hospital Materno Infantil Mip Guzmán González Héctor EduardoHector GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Cerebral HistoriesDocument2 pagesCerebral HistoriesgibreilNo ratings yet
- Galactorrhoea: DR - Abdiaziz Hakiye MBBS AUDocument10 pagesGalactorrhoea: DR - Abdiaziz Hakiye MBBS AUgibreilNo ratings yet
- Fibroadenoma: DR - Abdiaziz Hakiye MBBS AUDocument14 pagesFibroadenoma: DR - Abdiaziz Hakiye MBBS AUgibreilNo ratings yet
- Post Partum HemorrahgeDocument41 pagesPost Partum HemorrahgegibreilNo ratings yet
- Pelvic Pain AcuteDocument144 pagesPelvic Pain AcutegibreilNo ratings yet
- Vaginal Bleeding in Late PregnancyDocument139 pagesVaginal Bleeding in Late PregnancygibreilNo ratings yet
- TraumaDocument12 pagesTraumagibreilNo ratings yet
- Myocarditis.: FFU Medical Faculty July Lectures 2020Document16 pagesMyocarditis.: FFU Medical Faculty July Lectures 2020gibreilNo ratings yet
- Second Trimester Complications 2015Document64 pagesSecond Trimester Complications 2015gibreilNo ratings yet
- Gynae EmerganciesDocument39 pagesGynae EmerganciesgibreilNo ratings yet
- Diseases of The Myocardium.: FFU Medical Faculty July Lectures 2020Document23 pagesDiseases of The Myocardium.: FFU Medical Faculty July Lectures 2020gibreilNo ratings yet
- Hormones of The PlacentaDocument67 pagesHormones of The PlacentagibreilNo ratings yet
- Retained PlacentaDocument15 pagesRetained PlacentagibreilNo ratings yet
- Acynotic Congenital Heart Diseases: FFU May 2020Document14 pagesAcynotic Congenital Heart Diseases: FFU May 2020gibreilNo ratings yet
- Tuberculosis: - Epidemiology of Tuberculosis - General Aspects of Tuberculous Infection and Tuberculosis DiseaseDocument91 pagesTuberculosis: - Epidemiology of Tuberculosis - General Aspects of Tuberculous Infection and Tuberculosis DiseasegibreilNo ratings yet
- Sexually Transmitted Infections: By-Nimco A. MDDocument89 pagesSexually Transmitted Infections: By-Nimco A. MDgibreilNo ratings yet
- Primary Pulmonary Hypertension.: FFU Medical Faculty Pediatric Lecture June 2020Document14 pagesPrimary Pulmonary Hypertension.: FFU Medical Faculty Pediatric Lecture June 2020gibreilNo ratings yet
- Coarctation of The Aorta.: Franz Fanon University Medical Faculty 2020 June Peds. LessonDocument12 pagesCoarctation of The Aorta.: Franz Fanon University Medical Faculty 2020 June Peds. LessongibreilNo ratings yet
- HyperkalemiaDocument4 pagesHyperkalemiagibreilNo ratings yet
- Meningitis: By-Dr Nimco A. MDDocument31 pagesMeningitis: By-Dr Nimco A. MDgibreilNo ratings yet
- RENAL VASCULAR DISEASES UpdatedDocument97 pagesRENAL VASCULAR DISEASES UpdatedgibreilNo ratings yet
- Pneumonia in Adults: 25 Years HIV-related ProblemsDocument35 pagesPneumonia in Adults: 25 Years HIV-related ProblemsgibreilNo ratings yet
- Clinical Manifestations and Diagnosis of Acute Interstitial NephritisDocument37 pagesClinical Manifestations and Diagnosis of Acute Interstitial NephritisgibreilNo ratings yet
- Disease of Adrenal GlandDocument47 pagesDisease of Adrenal GlandgibreilNo ratings yet
- AarticuloDocument6 pagesAarticuloJENNIFER ANDREA OLAYA VARGASNo ratings yet
- (Temperature) Hypothermia Detection in LBWN Using Novel BraceletDocument9 pages(Temperature) Hypothermia Detection in LBWN Using Novel BraceletAnonymous KiraNo ratings yet
- Intestinal Malrotation in Neonates With Nonbilious Emesis: Perinatal/Neonatal Case PresentationDocument3 pagesIntestinal Malrotation in Neonates With Nonbilious Emesis: Perinatal/Neonatal Case PresentationSaurav SultaniaNo ratings yet
- Notions About Child Birth (Natural Birth and Caesarian Section)Document2 pagesNotions About Child Birth (Natural Birth and Caesarian Section)Joseph UkamNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Bone Tissue 2304Document37 pagesChapter 6 Bone Tissue 2304Sav Oli100% (1)
- PATHOPHYSIOLOGY - Placenta PreviaDocument5 pagesPATHOPHYSIOLOGY - Placenta PreviaFretzgine Lou Manuel100% (2)
- Design and DevelopmentDocument66 pagesDesign and DevelopmentAhmedSaadNo ratings yet
- Respiration PHYSIODocument23 pagesRespiration PHYSIOTauseef AfridiNo ratings yet
- Maternal and Child Care Nursing Module 1Document90 pagesMaternal and Child Care Nursing Module 1Andrea Monique R. Galasinao100% (1)
- Hormonal Imbalances and Its Causes in Young FemalesDocument6 pagesHormonal Imbalances and Its Causes in Young FemalesElizafarfan124No ratings yet
- Extremely Low Birth Weight (ELBW) InfantDocument48 pagesExtremely Low Birth Weight (ELBW) InfanthannanyusofNo ratings yet
- Prevalence, Nature and Determinants of Postpartum Mental HealthDocument14 pagesPrevalence, Nature and Determinants of Postpartum Mental HealthBidan Riska AmaliaNo ratings yet
- Preterm LaborDocument10 pagesPreterm Laborfathima AlfasNo ratings yet
- 11+12 Lecture Normal Labor & Birth ProcessesDocument41 pages11+12 Lecture Normal Labor & Birth Processesزياد- 90No ratings yet
- Pre-Eclampsia, Eclampsia and HELLP SyndromeDocument15 pagesPre-Eclampsia, Eclampsia and HELLP SyndromehendraNo ratings yet
- Ante NatalDocument8 pagesAnte NatalRevathi DadamNo ratings yet
- Foundation of Human Skills Fy BMSDocument10 pagesFoundation of Human Skills Fy BMSAmit AmitNo ratings yet
- HUMASIS Products Brochure - 2020Document32 pagesHUMASIS Products Brochure - 2020Quan NguyenngocNo ratings yet
- Short ETHICS CASE STUDIES With QuestionsDocument3 pagesShort ETHICS CASE STUDIES With QuestionsRahman AsifNo ratings yet
- HCG Card Pregnancy Test: RAPU01C040Document7 pagesHCG Card Pregnancy Test: RAPU01C040Anusha SebastianNo ratings yet
- Presentation On: Kgmu College of NursingDocument42 pagesPresentation On: Kgmu College of NursingSweety YadavNo ratings yet
- Clinical Study of Infants of Diabetic MotherDocument112 pagesClinical Study of Infants of Diabetic Mothervighnaharta Online ServicesNo ratings yet
- NeonatalresuscitationDocument67 pagesNeonatalresuscitationfidaNo ratings yet
- NCM 106 Module 5FDocument22 pagesNCM 106 Module 5FMega SoundNo ratings yet
- Aberrant Liquor VolumeDocument37 pagesAberrant Liquor VolumeDoaaNo ratings yet
- Infertility NilDocument16 pagesInfertility NilNilakshi Barik MandalNo ratings yet
- Lack of Parental Guidance - Brian Jomes PortfolioDocument2 pagesLack of Parental Guidance - Brian Jomes PortfolioGaspar GuedesNo ratings yet
- RAD RLE MCN 6 Case StudyDocument9 pagesRAD RLE MCN 6 Case StudyCathleen Nasis Forrosuelo100% (2)
- Literature ReviewDocument13 pagesLiterature ReviewMaxine VirayNo ratings yet
- E Learning NCM 107 NotesDocument47 pagesE Learning NCM 107 NotesSophia TomasNo ratings yet