Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Financial Reporting
Uploaded by
AR Ananth Rohith Bhat0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views10 pagesOriginal Title
FINANCIAL REPORTING
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views10 pagesFinancial Reporting
Uploaded by
AR Ananth Rohith BhatCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 10
Examples of Indirect Taxes
5. Cascade tax
This is where tax is taken at each stage of production and is a business cost
because no refunds are provided by local government.
6. Value added tax (VAT)
VAT is charged each time a component or product is sold but the government
allows businesses to claim back all the tax they have paid(input tax).
The entire tax burden is passed to the final consumer.
The VAT system is used by almost all countries in the world.
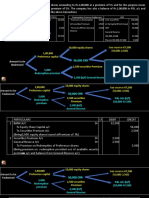
Value Added Tax
VAT payable = output tax – input tax
Output tax – VAT charged on sales to customers
Input tax – VAT paid on purchases
VAT aims to tax most business transactions which are referred to as taxable supplies.
Therefore, supplies could be:
Standard Rated – Taxed at the standard rate of VAT
Higher Rated – Taxed at a higher rate
Zero Rated – Taxed at a rate of 0% (Basic food, e.g. bread)
Exempt – Not subject to VAT
Value Added Tax
In the UK, supplies such as food, children’s clothing and exports are zero rated for
the purpose of VAT. Businesses who sell zero rated sales are allowed to claim back
input VAT on purchases.
Alternatively, in the UK, supplies such as finance and insurance are exempt for the
purpose of VAT. Businesses who make exempt sales cannot claim back input VAT
on purchases.
If the inclusive price is given VAT is calculated by:
Inclusive price × tax rate
100 + tax rate
Value Added Tax
VAT registration is required by a taxable person making a taxable supply.
A taxable person can be an individual or a company.
A taxable supply can zero, standard or higher rated sales.
They will be required to register for VAT when their taxable turnover
(zero, standard or higher rated sales) reach a certain limit (this will vary
from tax year to tax year).
Impact of employee taxation
Employees are taxed on their earnings under income tax. Earnings can
include-
salaries, bonuses, commissions and benefits in kind.
Benefits in kind are non-cash benefits in lieu of further cash payments such
as:
company cars
living accommodation
loans
private medical insurance
Impact of employee taxation
The basis of assessment is based on the individual country:
France – amount earned in previous year
Switzerland – average of previous two years’ earnings
UK – amount actually received in the current tax year
Employees can deduct certain expenses which are wholly, exclusively and
necessary for employment, such as business travel, contributions to pension
plans, donations to charity through a payroll deduction scheme and professional
subscriptions.
Pay-As-You-Earn (PAYE).
Most governments expect enterprises to withhold tax on employees’ salaries and
report earnings to the tax authorities. In the UK, this tax system is referred to as
Pay-As-You-Earn (PAYE).
The benefits of having a PAYE system are:
Tax is collected at source, hence taxpayers are less likely to default payment.
Tax authorities receive regular payments from employers – helps to budget
cash flows for the government.
The tax authority only has to deal with the employer, rather than a number of
individuals.
Most of the administration costs are borne by the employer, instead of the
government.
Impact of employee taxation
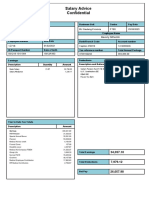
The standard pro-forma for calculating employee tax would be as follows:
$
Salary X
Plus: bonus, commission, benefits X
Less: subscriptions (X)
Less: pension contributions (X)
Less: charity donations (X)
Less: personal allowances (X)
Taxable income X
Administration
Enterprises need to keep records to satisfy tax requirements for the following taxes:
Corporate income tax
Sales tax
Overseas subsidiaries
Employee tax
Minimum retention of records
Payment of tax
Power of tax authorities
The revenue authorities have various powers to impose penalties and
interest on late payment of tax. In addition, they have the power to:
Review and query filed returns.
Request special reports if they believe inaccurate information has been
submitted.
Examine records of previous years (in the US, tax authorities can go
back 20 years).
Enter and search the entity's premises and seize documents.
Pass on information to foreign tax authorities.
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (894)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Salary Slip TemplateDocument1 pageSalary Slip TemplateAnissuzira Othman100% (1)
- Module1: Amalgamation and AbsorptionDocument12 pagesModule1: Amalgamation and AbsorptionAR Ananth Rohith BhatNo ratings yet
- Chapter - I Operating System: Functions of OSDocument7 pagesChapter - I Operating System: Functions of OSAR Ananth Rohith BhatNo ratings yet
- Certificate of APPRECIATION: Dr. Gerald Santhosh DsouzaDocument2 pagesCertificate of APPRECIATION: Dr. Gerald Santhosh DsouzaAR Ananth Rohith BhatNo ratings yet
- Internal AuditDocument9 pagesInternal AuditAR Ananth Rohith BhatNo ratings yet
- Working CapitalDocument39 pagesWorking CapitalAR Ananth Rohith BhatNo ratings yet
- Preference Redemption ProblemsDocument27 pagesPreference Redemption ProblemsAR Ananth Rohith BhatNo ratings yet
- InnovactDocument6 pagesInnovactAR Ananth Rohith BhatNo ratings yet
- TYPES OF GST UNDER INDIAN CONSTITUTIONDocument8 pagesTYPES OF GST UNDER INDIAN CONSTITUTIONAR Ananth Rohith BhatNo ratings yet
- Corporate Accounting 1: III Semester BBADocument57 pagesCorporate Accounting 1: III Semester BBAAR Ananth Rohith BhatNo ratings yet
- Negotiable InstrumentDocument6 pagesNegotiable InstrumentAR Ananth Rohith BhatNo ratings yet
- New Education Policy: Union Cabinet of India National Policy On Education, 1986Document6 pagesNew Education Policy: Union Cabinet of India National Policy On Education, 1986AR Ananth Rohith BhatNo ratings yet
- Basic Concepts of Cost ACCOUNTING - (Part 1)Document9 pagesBasic Concepts of Cost ACCOUNTING - (Part 1)AR Ananth Rohith BhatNo ratings yet
- Ii B.com - 3 Sem-Cost-TheoryDocument19 pagesIi B.com - 3 Sem-Cost-TheoryAR Ananth Rohith BhatNo ratings yet
- Contract CostingDocument3 pagesContract CostingAR Ananth Rohith BhatNo ratings yet
- B.B.M-V Semester-Cost and Management Accounting-I (Practical)Document1 pageB.B.M-V Semester-Cost and Management Accounting-I (Practical)AR Ananth Rohith BhatNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1-Job and Batch Costing: Ref: Cost & Management Accounting by K.S.AdigaDocument14 pagesChapter 1-Job and Batch Costing: Ref: Cost & Management Accounting by K.S.AdigaAR Ananth Rohith BhatNo ratings yet
- Cost - Vi SemDocument18 pagesCost - Vi SemAR Ananth Rohith BhatNo ratings yet
- Auditing essentials for proper oversightDocument18 pagesAuditing essentials for proper oversightAR Ananth Rohith BhatNo ratings yet
- Section BDocument1 pageSection BAR Ananth Rohith BhatNo ratings yet
- New Microsoft PowerPoint PresentationDocument19 pagesNew Microsoft PowerPoint PresentationAR Ananth Rohith BhatNo ratings yet
- Literature Review On Online AdvertisingDocument6 pagesLiterature Review On Online AdvertisingAR Ananth Rohith BhatNo ratings yet
- Fin Account-Sole Trading AnswersDocument10 pagesFin Account-Sole Trading AnswersAR Ananth Rohith BhatNo ratings yet
- Fin Account-Sole Trading AnswersDocument9 pagesFin Account-Sole Trading AnswersAR Ananth Rohith BhatNo ratings yet
- AuditDocument70 pagesAuditAR Ananth Rohith BhatNo ratings yet
- Purchase ConsiderationDocument5 pagesPurchase ConsiderationAR Ananth Rohith BhatNo ratings yet
- Purchase ConsiderationDocument5 pagesPurchase ConsiderationAR Ananth Rohith BhatNo ratings yet
- Capital StructureDocument18 pagesCapital StructureAR Ananth Rohith BhatNo ratings yet
- MMDocument6 pagesMMAR Ananth Rohith BhatNo ratings yet
- HRD Concepts, Objectives and NeedsDocument1 pageHRD Concepts, Objectives and NeedsAR Ananth Rohith BhatNo ratings yet
- Wa0027.Document2 pagesWa0027.chagusahoo170No ratings yet
- Tax Invoice: Billed To: Invoice DetailsDocument1 pageTax Invoice: Billed To: Invoice Detailsbipin jainNo ratings yet
- PansDocument1 pagePansVee-kay Vicky KatekaniNo ratings yet
- Itrv Sarath 21-22Document1 pageItrv Sarath 21-22bindu mathaiNo ratings yet
- Property Tax Revision - NoticeDocument1 pageProperty Tax Revision - NoticeBenedict DavidNo ratings yet
- Moving to Ireland | Tax guideDocument20 pagesMoving to Ireland | Tax guideAbhilash SahooNo ratings yet
- STATEMENTDocument3 pagesSTATEMENTncrgurukripaNo ratings yet
- Dasnac Arc Price & PaymentDocument1 pageDasnac Arc Price & PaymentZUK GamingNo ratings yet
- Welcome To Greater Chennai CorporationDocument1 pageWelcome To Greater Chennai CorporationStella-JebasNo ratings yet
- TAX INVOICE FOR MARIYIL ENTERPRISESDocument1 pageTAX INVOICE FOR MARIYIL ENTERPRISESSamsung KumarNo ratings yet
- LectureDocument3 pagesLectureJimmy RecedeNo ratings yet
- Tax Invoice for HP Laptop with 18% IGSTDocument1 pageTax Invoice for HP Laptop with 18% IGSTThirumal K SNo ratings yet
- Details of Receiver (Billed To) Details of Consignee (Shipped To)Document1 pageDetails of Receiver (Billed To) Details of Consignee (Shipped To)VESTIGE JVRATNAMNo ratings yet
- AutoInvoice Execution ReportDocument6 pagesAutoInvoice Execution ReportabduskhanNo ratings yet
- Rto MardanDocument2 pagesRto Mardanjanbahadur393100% (1)
- FILING STATUS (Check One)Document3 pagesFILING STATUS (Check One)hypnotix-2000No ratings yet
- Invoice #3793: Qloudin Technologies PVT LTDDocument1 pageInvoice #3793: Qloudin Technologies PVT LTDRandi RonaNo ratings yet
- Bill To / Ship To:: Qty Gross Amount Discount Other Charges Taxable Amount CGST SGST/ Ugst Igst Cess Total AmountDocument1 pageBill To / Ship To:: Qty Gross Amount Discount Other Charges Taxable Amount CGST SGST/ Ugst Igst Cess Total AmountAbhi ShNo ratings yet
- Add: CGST Add: SGST Total Tax Amount: Total Amount Including Tax: Total Amount Excluding TaxDocument2 pagesAdd: CGST Add: SGST Total Tax Amount: Total Amount Including Tax: Total Amount Excluding TaxHajrabi ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Scenario (Problem) : Empid Firstname Middlename Lastname Position Sex Civ - Status Birthdate Date Hired Yrs. in Service AgeDocument3 pagesScenario (Problem) : Empid Firstname Middlename Lastname Position Sex Civ - Status Birthdate Date Hired Yrs. in Service AgeMadonna LuisNo ratings yet
- Tax Q and A 2Document2 pagesTax Q and A 2Marivie UyNo ratings yet
- Comparison of Old Tax Law and Train LawDocument3 pagesComparison of Old Tax Law and Train LawSyed Almendras IINo ratings yet
- FORM 16 DETAILSDocument2 pagesFORM 16 DETAILSKushal MalhotraNo ratings yet
- Review Materials: Prepared By: Junior Philippine Institute of Accountants UC-Banilad Chapter F.Y. 2019-2020Document33 pagesReview Materials: Prepared By: Junior Philippine Institute of Accountants UC-Banilad Chapter F.Y. 2019-2020AB CloydNo ratings yet
- NIRC Vs TRAIN ComparisonDocument3 pagesNIRC Vs TRAIN ComparisonAngeli PaulineNo ratings yet
- Turnover Declaration Letter - de RegistrationDocument4 pagesTurnover Declaration Letter - de RegistrationGeraldJadeLazaroNo ratings yet
- TPS - Tax Forms Done Tax ReturnDocument42 pagesTPS - Tax Forms Done Tax ReturnLuis Castro100% (1)
- TaskDocument1 pageTaskPawan KeswaniNo ratings yet
- Inter Tech 3Document3 pagesInter Tech 3Harsh DiwakerNo ratings yet