100% found this document useful (1 vote)
260 views22 pagesUnderstanding Soft Tissue Injuries
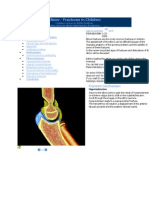
Soft tissue injuries include contusions, sprains, strains, tendinitis, bursitis, and stress injuries. Contusions are bruises caused by blunt force trauma that damages muscle fibers and blood vessels. Sprains involve tearing ligaments around joints from sudden movements. Strains tear muscles or tendons from overexertion. Tendinitis is inflammation of tendons, often from repetitive motions. Bursitis inflames fluid-filled sacs that cushion bones. Stress injuries result from repetitive impacts or prolonged fixed positions. All are generally treated with RICE (rest, ice, compression, and elevation) and avoiding re-injury through heat, alcohol, running, or massage.
Uploaded by
Yan Zhe ChanCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
100% found this document useful (1 vote)
260 views22 pagesUnderstanding Soft Tissue Injuries
Soft tissue injuries include contusions, sprains, strains, tendinitis, bursitis, and stress injuries. Contusions are bruises caused by blunt force trauma that damages muscle fibers and blood vessels. Sprains involve tearing ligaments around joints from sudden movements. Strains tear muscles or tendons from overexertion. Tendinitis is inflammation of tendons, often from repetitive motions. Bursitis inflames fluid-filled sacs that cushion bones. Stress injuries result from repetitive impacts or prolonged fixed positions. All are generally treated with RICE (rest, ice, compression, and elevation) and avoiding re-injury through heat, alcohol, running, or massage.
Uploaded by
Yan Zhe ChanCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd