0% found this document useful (0 votes)
407 views26 pagesExperiment - 5
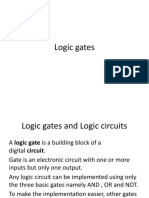
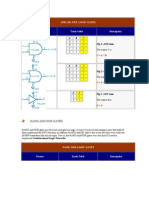
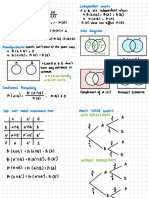
Logic gates are basic electronic circuits that use Boolean algebra to produce an output from one or more inputs. The document describes the common logic gates (NOT, AND, OR, XOR, NAND, NOR) and their truth tables. It explains that NAND and NOR gates are "universal gates" that can be combined with other gates of the same type to perform the logic of any other gate, allowing more complex circuits to be implemented using fewer integrated circuits.
Uploaded by
Dilip GangopadhyayCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
407 views26 pagesExperiment - 5
Logic gates are basic electronic circuits that use Boolean algebra to produce an output from one or more inputs. The document describes the common logic gates (NOT, AND, OR, XOR, NAND, NOR) and their truth tables. It explains that NAND and NOR gates are "universal gates" that can be combined with other gates of the same type to perform the logic of any other gate, allowing more complex circuits to be implemented using fewer integrated circuits.
Uploaded by
Dilip GangopadhyayCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd