Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Kuliah Penis & Scrotum
Uploaded by
Aditya Prambudhi0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views13 pagesThis document discusses various disorders of the male genital organs including the penis, scrotum, testis and spermatic cord. It covers congenital anomalies such as hypospadias, acquired conditions like Peyronie's disease, tumors, and infections. Specific attention is given to classifications of hypospadias, types of hydrocele, locations of cryptorchidism, and precancerous lesions and cancers of the penis.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses various disorders of the male genital organs including the penis, scrotum, testis and spermatic cord. It covers congenital anomalies such as hypospadias, acquired conditions like Peyronie's disease, tumors, and infections. Specific attention is given to classifications of hypospadias, types of hydrocele, locations of cryptorchidism, and precancerous lesions and cancers of the penis.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views13 pagesKuliah Penis & Scrotum
Uploaded by
Aditya PrambudhiThis document discusses various disorders of the male genital organs including the penis, scrotum, testis and spermatic cord. It covers congenital anomalies such as hypospadias, acquired conditions like Peyronie's disease, tumors, and infections. Specific attention is given to classifications of hypospadias, types of hydrocele, locations of cryptorchidism, and precancerous lesions and cancers of the penis.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 13
Disorders of the Penis, Scrotum,
Testis & Spermatic Cord
Dr.M.Galuh Richata, SpU
Disorders of the Penis &
Male Urethra
Congenital Anomalies of the Penis
- Apenia (very rare)
- Megalopenis (increased testosterone)
- Micropenis (more common)
- Adult Penile Size
Disorders of the Penis &
Male Urethra
Congenital Anomalies of the Urethra
- Urethral Stricture (most common site: fossa
naviculare, membranous)
- Posterior Urethral Valve
- Anterior Urethral Valve
- Urethrorectal & Vesicorectal Fistulas
- Hypospadia
- Epispadia
- Chordee without Hypospadia
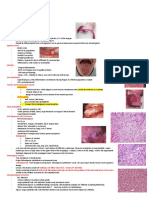
Hypospadia
Classification, according the location:
Glandular
Coronal (70%)
Penile Shaft
Penoscrotal
Perineal
Disorders of the Penis &
Male Urethra
Acquired Disease/Disorders
Priapism
Peyronie Disease
Phimosis
Paraphimosis
Urethral Stricture
Urethral Condyloma Acuminata (warts)
Stenosis of the Urethral Meatus
Disorders of the Scrotum, Testis &
Spermatic Cord
Ectopic Testis & Cryptorchidism
- superficial inguinal (most common site)
- perineal
- femoral or crural
- penile
- transverse or paradoxic descent
- pelvic
Disorders of the Scrotum, Testis &
Spermatic Cord
Spermatocele (cyst of epididymis)
Varicocele (dilatation of pampiniformis plexus)
Hydrocele
Torsion of the spermatic cord (torsio testis)
Scrotal Abscess
Hernial Scrotalis
Disorders of the Scrotum, Testis &
Spermatic Cord
Hydrocele
Disorders of the Scrotum, Testis &
Spermatic Cord
Hydrocele
Disorders of the Scrotum, Testis &
Spermatic Cord
Hydrocele
Tumor of the Genital
Tumors of the Testis
Germ Cell (90-95%): Seminoma and NonSeminoma
Non Germinal Cells: Leydig cell, Sertoli cell,
gonadoblastoma)
Tumor of the Genital
Tumor of the Penis
Most commonly in the 6th decade of life
Etiologic factor: poor hygiene (smegma accumulation
under the phimotic foreskin results in chronic
inflammation leading to carcinoma), viral infection.
Tumor of the Penis : Pathology
A. Precancerous Dermatologic Lesions:
Leukoplakia
Balanitis Xerotica Obliterans
Giant condyloma acuminata
B. Carcinoma in situ:
Bowen disease
Erythroplasia of Queyrat
C. Invasive Ca of the penis (Squamous cell Ca)
You might also like
- Sexual Reproductive HealthDocument29 pagesSexual Reproductive HealthAlen VukosavljevicNo ratings yet
- Sexual Reproductive Health - 3rd Ed'Document141 pagesSexual Reproductive Health - 3rd Ed'Phạm Ngọc HânNo ratings yet
- NbmeDocument5 pagesNbmeRahul ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Sex at The Anatomical LevelDocument46 pagesSex at The Anatomical LevelkavehNo ratings yet
- Sexual Reproductive Health - 4th EdDocument164 pagesSexual Reproductive Health - 4th EdKaptan Tsubasa FanNo ratings yet
- Male Reproductive System FinalDocument5 pagesMale Reproductive System FinalJohn Dale Lulu CruzNo ratings yet
- Nada's GI Path ReviewDocument44 pagesNada's GI Path ReviewNada Much100% (2)
- Benign and Malignant Ovarian Tumors (Gynaecology)Document70 pagesBenign and Malignant Ovarian Tumors (Gynaecology)Dr Ali MehdiNo ratings yet
- Lecture 23 - Ovarian TumoursDocument89 pagesLecture 23 - Ovarian TumoursAnonymous 0XqZUl06Pm67% (3)
- Diseases and Disorders of The Male Reproductive SystemDocument2 pagesDiseases and Disorders of The Male Reproductive SystemRichard Bueta100% (1)
- Assessing The Male Genitourinary SystemDocument46 pagesAssessing The Male Genitourinary SystemJonah nyachae100% (1)
- Kuliah Penis & Scrotum RevisiDocument13 pagesKuliah Penis & Scrotum Revisianisamaya0% (1)
- Kuliah Penis & Scrotum RevisiDocument13 pagesKuliah Penis & Scrotum Revisiranz ibonkNo ratings yet
- Kuliah Penis & ScrotumDocument13 pagesKuliah Penis & ScrotumagilNo ratings yet
- Kuliah Penis & ScrotumDocument13 pagesKuliah Penis & ScrotumEmallia Phypiet FitrianiNo ratings yet
- Morpho Lectures Merged Reproductive System PDFDocument204 pagesMorpho Lectures Merged Reproductive System PDFapNo ratings yet
- Scrotal Sonography Us אשכיםDocument116 pagesScrotal Sonography Us אשכיםOded YanaNo ratings yet
- Sexual Reproductive Health Notes (Optimized)Document237 pagesSexual Reproductive Health Notes (Optimized)pranjal shahNo ratings yet
- MTI Notes InfertilityDocument14 pagesMTI Notes InfertilityMahmoud KhelfaNo ratings yet
- Testicular TumorDocument56 pagesTesticular TumorMuhammad MakkiNo ratings yet
- SEXH - Infertility (2p)Document2 pagesSEXH - Infertility (2p)Omar HamwiNo ratings yet
- Finalcaprostate 180114163813 PDFDocument124 pagesFinalcaprostate 180114163813 PDFAlchemi ANo ratings yet
- Pemicu 4 "Air Seni Tidak Memancar Lurus": Adrian Pratama - 405100018Document34 pagesPemicu 4 "Air Seni Tidak Memancar Lurus": Adrian Pratama - 405100018Charles FerdinandNo ratings yet
- Alekls 0102Document50 pagesAlekls 0102tomas.cingel3No ratings yet
- Tumor Saluran Kemih (Tumors/Malignancy of Urinary Tract) : Dr.M.Galuh Richata, SpuDocument22 pagesTumor Saluran Kemih (Tumors/Malignancy of Urinary Tract) : Dr.M.Galuh Richata, SpuAditya PrambudhiNo ratings yet
- Tumor Saluran Kemih (Tumors/Malignancy of Urinary Tract) : Dr.M.Galuh Richata, SpuDocument22 pagesTumor Saluran Kemih (Tumors/Malignancy of Urinary Tract) : Dr.M.Galuh Richata, SpuLuthfiAhmadNo ratings yet
- Student'S Gynaecology Notes: For Students, by StudentsDocument45 pagesStudent'S Gynaecology Notes: For Students, by StudentsAdli IsmailNo ratings yet
- Path Exam 4Document18 pagesPath Exam 4sumiti_kumarNo ratings yet
- Embryo Finals 1Document4 pagesEmbryo Finals 1VenzNo ratings yet
- Thediagnosisand Managementof Scrotalmasses: Jeffrey S. Montgomery,, David A. BloomDocument10 pagesThediagnosisand Managementof Scrotalmasses: Jeffrey S. Montgomery,, David A. BloomLyka MahrNo ratings yet
- Sexual Reproductive HealthDocument162 pagesSexual Reproductive HealthBinod BinodNo ratings yet
- Tumor Saluran Kemih (Tumors/Malignancy of Urinary Tract) : Dr.M.Galuh Richata, SpuDocument22 pagesTumor Saluran Kemih (Tumors/Malignancy of Urinary Tract) : Dr.M.Galuh Richata, SpuNadia IndriNo ratings yet
- Repro CorrDocument67 pagesRepro CorrsrhmdNo ratings yet
- Lower: Urinary TractDocument143 pagesLower: Urinary TractLouis FortunatoNo ratings yet
- Male Reproductive System: Professor John SimpsonDocument11 pagesMale Reproductive System: Professor John SimpsonAndika TansirNo ratings yet
- Infertility: by Kenbon SDocument58 pagesInfertility: by Kenbon SgimNo ratings yet
- Pathology of The AdnexaDocument59 pagesPathology of The AdnexaArnella HutagalungNo ratings yet
- Abnormalities of The Testes and ScrotumDocument34 pagesAbnormalities of The Testes and ScrotumIma MoriNo ratings yet
- Jantan-1 2017Document63 pagesJantan-1 2017Jefri naldiNo ratings yet
- EM Male Genital Tract RGDocument25 pagesEM Male Genital Tract RGPrakashNo ratings yet
- DR Mohamed Saber DR Jeremy Jones: Testicular MicrolithiasisDocument5 pagesDR Mohamed Saber DR Jeremy Jones: Testicular MicrolithiasisJean NgNo ratings yet
- PATH DR - Hameed Male Reproductive System Lec 1Document35 pagesPATH DR - Hameed Male Reproductive System Lec 1Cosplay AccountNo ratings yet
- AMENORRHOEADocument13 pagesAMENORRHOEAsuleiman AbdullahiNo ratings yet
- Male Reproductive System 1mittalDocument23 pagesMale Reproductive System 1mittalSAYMABANUNo ratings yet
- Disorders of The Male Genitourinary SystemDocument30 pagesDisorders of The Male Genitourinary SystemDua'a Al-HamdanNo ratings yet
- Solid Tumors in Children-2012Document59 pagesSolid Tumors in Children-2012Marga KouryNo ratings yet
- Ovarian Tumours PresentationDocument49 pagesOvarian Tumours PresentationChoden JamyangNo ratings yet
- Marfan's Syndrome Examination (Seated)Document4 pagesMarfan's Syndrome Examination (Seated)Aldi SetyoNo ratings yet
- Ovarian DisordersDocument5 pagesOvarian DisordersNada MuchNo ratings yet
- Benign Ovarian Tumors - Unilateral, 99% Cystic, MobileDocument9 pagesBenign Ovarian Tumors - Unilateral, 99% Cystic, MobileSolomon Seth SallforsNo ratings yet
- Maia Gregoire, Gracia Merlo-Grammaire Progressive Du Francais Avec 400 Exercices - Niveau Debutant-Cle International (1997)Document30 pagesMaia Gregoire, Gracia Merlo-Grammaire Progressive Du Francais Avec 400 Exercices - Niveau Debutant-Cle International (1997)assssssNo ratings yet
- 2021 HID Repro Unit Recap 1 - FinalDocument63 pages2021 HID Repro Unit Recap 1 - Finalf3er3No ratings yet
- Neoplasm of Kidney and Urinary TractDocument49 pagesNeoplasm of Kidney and Urinary TractYama Piniel FrimantamaNo ratings yet
- $12. Urinary Tract Infections 2015Document39 pages$12. Urinary Tract Infections 2015Sindhu BabuNo ratings yet
- Scrotal Masses Testicular CancerDocument34 pagesScrotal Masses Testicular CancerAnas HamadNo ratings yet
- Sexual Determination DX: LH Elevated E ElevatedDocument28 pagesSexual Determination DX: LH Elevated E Elevatedsamantha_schnei9354No ratings yet
- Ferrets Oncology-MainDocument26 pagesFerrets Oncology-MainJOAQUINALONZOPEREIRANo ratings yet
- Kuliah Tumor RevisiDocument22 pagesKuliah Tumor Revisiranz ibonkNo ratings yet
- Male Genital Organs Clinical Marija DjuricDocument31 pagesMale Genital Organs Clinical Marija DjuricНемосјановић ЋудмилаNo ratings yet