0% found this document useful (0 votes)
48 views13 pagesSigma-Delta ADC for Engineers
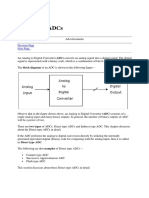
The document discusses Delta-Sigma (Sigma-Delta) analog-to-digital converters (ADCs). It explains that Delta-Sigma ADCs use comparators and integrators in their circuit design, which allows them to achieve high resolution with low cost by integrating both analog and digital circuitry on a single chip. It also provides block diagrams and explanations of the operational principles and components of Delta-Sigma ADCs.
Uploaded by
mhd kdaimatiCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
48 views13 pagesSigma-Delta ADC for Engineers
The document discusses Delta-Sigma (Sigma-Delta) analog-to-digital converters (ADCs). It explains that Delta-Sigma ADCs use comparators and integrators in their circuit design, which allows them to achieve high resolution with low cost by integrating both analog and digital circuitry on a single chip. It also provides block diagrams and explanations of the operational principles and components of Delta-Sigma ADCs.
Uploaded by
mhd kdaimatiCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd