0% found this document useful (0 votes)
165 views39 pagesTelecommunication Network Overview
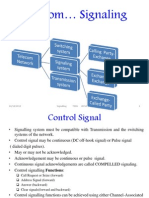
This document provides an overview of telecommunication networks and No. 7 signaling. It discusses the components and functions of telecommunication networks including terminals, switching systems, transmission networks and access networks. It also describes signaling concepts and the No. 7 signaling network architecture with signaling end points, signaling transfer points and signaling links. Finally, it outlines the No. 7 protocol structure used for communication between network elements.
Uploaded by
Mohamed TatouCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
165 views39 pagesTelecommunication Network Overview
This document provides an overview of telecommunication networks and No. 7 signaling. It discusses the components and functions of telecommunication networks including terminals, switching systems, transmission networks and access networks. It also describes signaling concepts and the No. 7 signaling network architecture with signaling end points, signaling transfer points and signaling links. Finally, it outlines the No. 7 protocol structure used for communication between network elements.
Uploaded by
Mohamed TatouCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
- Manual TOC
- Components and Function of Telecommunication Network
- Concepts of Signaling
- Overview of SPC Switch Technique
- No.7 Signaling Network
- No.7 Protocol Structure
- Closing