Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Fascioloza
Uploaded by
Larisa Elena0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
27 views10 pagesFascioloza is a parasitic disease caused by Fasciola hepatica and Fasciola gigantica. The life cycle begins when eggs are excreted and release miracidia in water. The miracidia infect snail intermediate hosts and undergo development through sporocyst and cercariae stages. The cercariae encyst on aquatic plants as metacercariae. Humans and pigs become infected by ingesting metacercariae, which excyst in the intestine and migrate to the liver to mature over 3 months into flukes 20-75mm long attached to the intestinal wall.
Original Description:
Original Title
Fascioloza by Medtorrents.com
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentFascioloza is a parasitic disease caused by Fasciola hepatica and Fasciola gigantica. The life cycle begins when eggs are excreted and release miracidia in water. The miracidia infect snail intermediate hosts and undergo development through sporocyst and cercariae stages. The cercariae encyst on aquatic plants as metacercariae. Humans and pigs become infected by ingesting metacercariae, which excyst in the intestine and migrate to the liver to mature over 3 months into flukes 20-75mm long attached to the intestinal wall.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
27 views10 pagesFascioloza
Uploaded by
Larisa ElenaFascioloza is a parasitic disease caused by Fasciola hepatica and Fasciola gigantica. The life cycle begins when eggs are excreted and release miracidia in water. The miracidia infect snail intermediate hosts and undergo development through sporocyst and cercariae stages. The cercariae encyst on aquatic plants as metacercariae. Humans and pigs become infected by ingesting metacercariae, which excyst in the intestine and migrate to the liver to mature over 3 months into flukes 20-75mm long attached to the intestinal wall.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 10
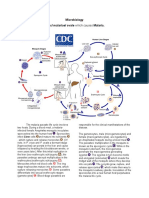
Fascioloza
Immature eggs are discharged into the intestine and stool .
Eggs become embryonated in water , eggs release miracidia ,
which invade a suitable snail intermediate host . In the snail the
parasites undergo several developmental stages (sporocysts ,
rediae , and cercariae ). The cercariae are released from the
snail and encyst as metacercariae on aquatic plants . The
mammalian hosts become infected by ingesting metacercariae on
the aquatic plants. After ingestion, the metacercariae excyst in
the duodenum and attach to the intestinal wall. There they
develop into adult flukes (20 to 75 mm by 8 to 20 mm) in
approximately 3 months, attached to the intestinal wall of the
mammalian hosts (humans and pigs) . The adults have a life
span of about one year.
Fasciola hepatica (ou)
Fasciola hepatica (femela)
Adult fluke of Fasciolopsis buski.
The adult flukes range in size: 20 to 75 mm by 8 to 20 mm.
Fascioliasis.
Section of liver showing
adult worm
of Fasciola hepatica
lying within a bile duct.
duct
Fasciolopsis Buski adult;
approximate length = 50 mm
Measuring up to 75 mm in
length, it is one of the largest
trematodes found in humans
You might also like
- Victorian Toadstools and Mushrooms: A Key and Descriptive Notes to 120 Different Gilled Fungi (Family Agaricaceae) , with Remarks on Several Other Families of the Higher FungiFrom EverandVictorian Toadstools and Mushrooms: A Key and Descriptive Notes to 120 Different Gilled Fungi (Family Agaricaceae) , with Remarks on Several Other Families of the Higher FungiNo ratings yet
- CDC - Fasciola - BiologyDocument2 pagesCDC - Fasciola - BiologypecopecochanNo ratings yet
- F Buski 111003095909 Phpapp01Document15 pagesF Buski 111003095909 Phpapp01Ashik MajumdarNo ratings yet
- F BuskiDocument15 pagesF BuskiArisia No AliceNo ratings yet
- L:6 Parasitology: Prof. Dr. Nada KhazalDocument18 pagesL:6 Parasitology: Prof. Dr. Nada KhazalMasar ElfNo ratings yet
- Intestinal TrematodesDocument3 pagesIntestinal TrematodesMORDENO, JOHN GABRIEL O. SCINo ratings yet
- Microbiology Plasmodium Vivax/ Malariae/ Ovale Which Causes Malaria. Life CycleDocument4 pagesMicrobiology Plasmodium Vivax/ Malariae/ Ovale Which Causes Malaria. Life CycleKrysny MontebonNo ratings yet
- (Ancylostoma Braziliense) (Ancylostoma Caninum) (Ancylostoma Duodenale) (Necator Americanus)Document8 pages(Ancylostoma Braziliense) (Ancylostoma Caninum) (Ancylostoma Duodenale) (Necator Americanus)ŘŷØoo TЯyNo ratings yet
- Fascioliasis: (Assignment)Document6 pagesFascioliasis: (Assignment)adeelNo ratings yet
- Liver Flukes Fasciola Hepatica.: Fasciolopsis BuskiDocument3 pagesLiver Flukes Fasciola Hepatica.: Fasciolopsis BuskiOtuko JoshuaNo ratings yet
- Answers:: 1) Why Does Fasciola Hepatica Produce Cyst?Document4 pagesAnswers:: 1) Why Does Fasciola Hepatica Produce Cyst?afshinNo ratings yet
- Trypanosoma: Viannia Subgenus in The Midgut For Organisms in The Leishmania Subgenus), and MigrateDocument3 pagesTrypanosoma: Viannia Subgenus in The Midgut For Organisms in The Leishmania Subgenus), and MigratebimtolaNo ratings yet
- AscaridiozaDocument25 pagesAscaridiozaLarisa ElenaNo ratings yet
- Post Lab MidtermsDocument18 pagesPost Lab MidtermsRaven TolentinoNo ratings yet
- FInal Laboratory Activity Microbiology LABESORESDocument10 pagesFInal Laboratory Activity Microbiology LABESORESJAN ELMER L. LABESORESNo ratings yet
- HelminthsDocument190 pagesHelminthsSarhan AliNo ratings yet
- Schistosomes: Diecious TrematodesDocument6 pagesSchistosomes: Diecious TrematodesShivanshi KNo ratings yet
- Ascaris Lumbricoides: MorphologyDocument7 pagesAscaris Lumbricoides: MorphologyIntan HaddadNo ratings yet
- BELIZARIO VY Et Al Medical Parasitology in The Philippines 3e 158 226Document69 pagesBELIZARIO VY Et Al Medical Parasitology in The Philippines 3e 158 226Sharon Agor0% (1)
- BELIZARIO VY Et Al Medical Parasitology in The Philippines 3e 158 226Document69 pagesBELIZARIO VY Et Al Medical Parasitology in The Philippines 3e 158 226Sharon Agor100% (1)
- Pathophysiology Schistosomiasis: Table in New WindowDocument7 pagesPathophysiology Schistosomiasis: Table in New WindowKaren Leigh MagsinoNo ratings yet
- General Parasitology L2Document27 pagesGeneral Parasitology L2kayse abtidoonNo ratings yet
- Fasciolopsis Buski - Intestinal FlukeDocument3 pagesFasciolopsis Buski - Intestinal FlukeOtuko JoshuaNo ratings yet
- Ascaris Lumbricoides: I. MorphologyDocument6 pagesAscaris Lumbricoides: I. MorphologyJoseline SorianoNo ratings yet
- Lab Activity - FecalysisDocument2 pagesLab Activity - FecalysisARRWEN DOMINIQUE YZABELLE TUAZONNo ratings yet
- Fasciola HepaticaDocument4 pagesFasciola Hepaticam1ha1davidNo ratings yet
- Other Trematodes (Intestinal, Liver and Pancreatic Flukes) : Fasciolopsis BuskiDocument5 pagesOther Trematodes (Intestinal, Liver and Pancreatic Flukes) : Fasciolopsis BuskiChristine BuenNo ratings yet
- Practical - Larval Stages of Taenia Solium - DR Roopa SamalDocument6 pagesPractical - Larval Stages of Taenia Solium - DR Roopa SamalAmishee SoodNo ratings yet
- Bovine Meat Inspection-Parasites of Cattle PDFDocument21 pagesBovine Meat Inspection-Parasites of Cattle PDFJanice Li100% (1)
- SchistosomiasisDocument12 pagesSchistosomiasisHarold Jake ArguellesNo ratings yet
- Ascari As IsDocument16 pagesAscari As IsCici Novelia ManurungNo ratings yet
- Intestinal Nematodes Life CycleDocument7 pagesIntestinal Nematodes Life CyclealianaNo ratings yet
- Schistosomiasis & FascioliosisDocument40 pagesSchistosomiasis & FascioliosisWahyudi YusmanNo ratings yet
- Cleanup Run Me FirstDocument12 pagesCleanup Run Me FirstJesus BerriosNo ratings yet
- Fasciola HepaticaDocument38 pagesFasciola HepaticaDeni Susanto100% (1)
- Askariasis Sebagai Penyakit Cacing Yang Perlu Diingat KembaliDocument4 pagesAskariasis Sebagai Penyakit Cacing Yang Perlu Diingat KembaliRina Paramita UtamiNo ratings yet
- Cology of Parasites: Part 2: Problems and Obstacles Parasite AdaptationsDocument50 pagesCology of Parasites: Part 2: Problems and Obstacles Parasite AdaptationsMusfeera KhanNo ratings yet
- PARASITOLOGYDocument57 pagesPARASITOLOGYChellie GualbertoNo ratings yet
- Mlec Life Cycle of NematodesDocument22 pagesMlec Life Cycle of Nematodess.labita.sherynejoelNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes On FasciolidaeDocument7 pagesLecture Notes On FasciolidaeGaniu MustaphaNo ratings yet
- Parasitology Lab Study ChartDocument2 pagesParasitology Lab Study ChartnoneyabuNo ratings yet
- Rebecca Hebner Humbio 153 Parasites and Pestilence Parasite: Schistosoma MekongiDocument32 pagesRebecca Hebner Humbio 153 Parasites and Pestilence Parasite: Schistosoma MekongiJan DielNo ratings yet
- Fasciola HepaticaDocument19 pagesFasciola HepaticaNaila NawazNo ratings yet
- Nematoda UsusDocument35 pagesNematoda Ususamanda fairuzNo ratings yet
- 6b. Nematode AnatDocument5 pages6b. Nematode AnatsenjicsNo ratings yet
- INTESTINAL NEMATODES Hand Out 10 - 11Document6 pagesINTESTINAL NEMATODES Hand Out 10 - 11microperadeniyaNo ratings yet
- Para Lec 4Document24 pagesPara Lec 4stpaulafamilyNo ratings yet
- Intestinal FlukesDocument24 pagesIntestinal Flukesroy mata88% (8)
- Parasitology - Trematodes - Intestinal & Liver FlukesDocument76 pagesParasitology - Trematodes - Intestinal & Liver FlukesNicole ManogNo ratings yet
- "Helminths and SanitationDocument12 pages"Helminths and SanitationSyed Ali Akbar BokhariNo ratings yet
- Introduction of Helminthology UpdatesDocument44 pagesIntroduction of Helminthology Updatespurnama bakti0% (1)
- Introduction of Helminthology: Parasitology DepartementDocument44 pagesIntroduction of Helminthology: Parasitology DepartementmunjiNo ratings yet
- COMMON WORM INFESTATION DrASBDocument54 pagesCOMMON WORM INFESTATION DrASBDr AMAL S BABUNo ratings yet
- HelmenthsDocument38 pagesHelmenthsKarwanNo ratings yet
- AscariasisDocument50 pagesAscariasisAnaleah MalayaoNo ratings yet
- Intestinal Nematodes: Dr. Devika DdawelaDocument127 pagesIntestinal Nematodes: Dr. Devika DdawelaPraveenKumarNo ratings yet
- Gastrodiscoides HominisDocument7 pagesGastrodiscoides HominisRahmah MartiyasihNo ratings yet
- Mass Drug Administration For Soil Transmitted Helmenthiasis: Maria Fe Viviane S. Sespeñe, M.D.,MPHDocument25 pagesMass Drug Administration For Soil Transmitted Helmenthiasis: Maria Fe Viviane S. Sespeñe, M.D.,MPHMelcanieNo ratings yet
- Helminths: NematodesDocument17 pagesHelminths: NematodesNicolle PanchoNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument27 pagesUntitledLarisa ElenaNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument26 pagesUntitledLarisa ElenaNo ratings yet
- AscaridiozaDocument25 pagesAscaridiozaLarisa ElenaNo ratings yet
- RetinaDocument3 pagesRetinaLarisa ElenaNo ratings yet
- nd1 PDFDocument220 pagesnd1 PDFLarisa ElenaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Vol-I Vishram SinghDocument345 pagesAnatomy Vol-I Vishram Singhleena lost84% (55)
- nd1 PDFDocument220 pagesnd1 PDFLarisa ElenaNo ratings yet