100% found this document useful (1 vote)
151 views13 pagesFastener Design: Bolts and Nuts Bolts Nuts
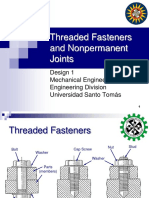
The document discusses fasteners such as bolts and nuts. It defines tensile stress area and provides formulas for calculating tensile and torsional stress. It also covers power screw applications and the strength of bolts. Additionally, it examines preloaded fasteners in tension by modeling clamped material as a spring. Key formulas show that preloading allows the bolt to support a fraction of the total load, reducing stresses on both the bolt and clamped material.
Uploaded by
Adam PrasetyaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
100% found this document useful (1 vote)
151 views13 pagesFastener Design: Bolts and Nuts Bolts Nuts
The document discusses fasteners such as bolts and nuts. It defines tensile stress area and provides formulas for calculating tensile and torsional stress. It also covers power screw applications and the strength of bolts. Additionally, it examines preloaded fasteners in tension by modeling clamped material as a spring. Key formulas show that preloading allows the bolt to support a fraction of the total load, reducing stresses on both the bolt and clamped material.
Uploaded by
Adam PrasetyaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd