0% found this document useful (0 votes)
701 views22 pagesBusiness Statistics for MBA Students
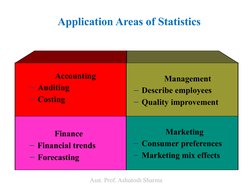
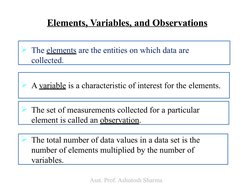
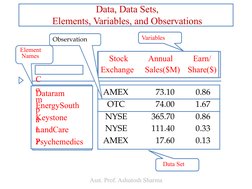
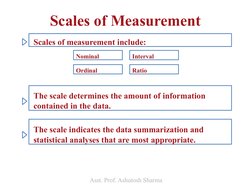
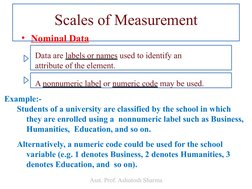
The document is a lecture on business statistics and analytics for MBA students presented by Assistant Professor Ashutosh Sharma. It covers key topics in statistics including definitions of statistics and related terms, applications of statistics in business and economics, data sources and types of data, scales of measurement, descriptive and inferential statistics. It provides examples and explanations of these fundamental statistical concepts.
Uploaded by
Sohail KhanCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
701 views22 pagesBusiness Statistics for MBA Students
The document is a lecture on business statistics and analytics for MBA students presented by Assistant Professor Ashutosh Sharma. It covers key topics in statistics including definitions of statistics and related terms, applications of statistics in business and economics, data sources and types of data, scales of measurement, descriptive and inferential statistics. It provides examples and explanations of these fundamental statistical concepts.
Uploaded by
Sohail KhanCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd