0% found this document useful (0 votes)
176 views14 pagesClarifier Mechanism and Principles
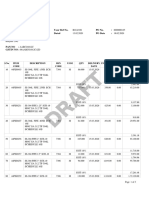
The document discusses clarifiers, which are used to separate suspended solids from liquids like raw water or sewage water. Clarifiers work through the principles of particle settling, where particles are acted upon by forces like gravity, fluid drag, and buoyancy that determine their settling velocity. Key factors that influence clarifier performance include the surface overflow rate, the clarifier surface area, and its depth. Clarifiers contain mechanisms to remove settled solids that are durable and efficient with benefits like flexible configurations and low maintenance costs.
Uploaded by
yv singlaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
176 views14 pagesClarifier Mechanism and Principles
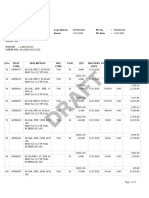
The document discusses clarifiers, which are used to separate suspended solids from liquids like raw water or sewage water. Clarifiers work through the principles of particle settling, where particles are acted upon by forces like gravity, fluid drag, and buoyancy that determine their settling velocity. Key factors that influence clarifier performance include the surface overflow rate, the clarifier surface area, and its depth. Clarifiers contain mechanisms to remove settled solids that are durable and efficient with benefits like flexible configurations and low maintenance costs.
Uploaded by
yv singlaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
- About Clarifier
- Principles of Settling