Professional Documents
Culture Documents
What Is A MOSFET and How Does It Work?
Uploaded by
marv hartiganOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
What Is A MOSFET and How Does It Work?
Uploaded by
marv hartiganCopyright:
Available Formats
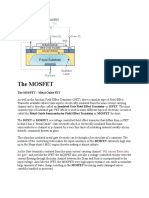
What is a MOSFET and How does it work?
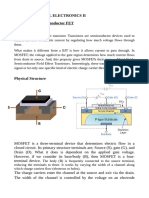
MOSFET, in short, is a metal oxide semiconductor field-effect
transistor used to switch or amplify voltages in circuits. Being part of
the field-effect transistor family, it is a current-controlled device that is
constructed with 3 terminals;
• Source
• Gate
• Drain
The purpose of a MOSFET transistor is essentially to control
voltage/current flow between the source and the drain.
The working principle differs based on the type of MOSFET.
Working Principle of MOSFET
To understand how MOSFET transistors work, we’ll take a look at
a typical circuit diagram as follows:
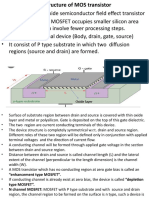
A block, also known as a substrate of p-type semiconductor acts
as the base for MOSFET
Two sides on this p-type substrate are made highly doped with
an n-type impurity (marked as n+)
The drain terminals (Source and Drain) are then brought out
from these two end regions
The entire surface of the substrate is coated with a layer of
silicon dioxide
Silicon dioxide acts as insulation
Working Principle of MOSFET
A thin insulated metallic plate is then placed on top of the silicon dioxide,
acting as a capacitor plate
The gate terminal is then brought out from the thin metallic plate
A DC circuit is then formed by connecting a voltage source between these
two n-type regions (marked in red in the image)
When voltage is applied at the gate, it generates an electrical field that
changes the width of the channel region, where the electrons flow. The
wider the channel region, the better conductivity of a device will be.
Types of MOSFET and functions
There are two classes of MOSFETS;
• Depletion Mode, and
• Enhancement mode.
Each class is available as n-channel or p-channel, tallying up to four
types of MOSFETs in total!
Here are its explanation, alongside the working principle:
Depletion Mode:
•Depletion mode tends to be referred to as a normally closed switch
• It states that when there’s no voltage applied at the gate,
channel conductance is at its maximum
• When voltage is applied at the gate, The conductivity of the
device decreases
Types of MOSFET and functions
Enhancement Mode:
•Enhancement mode tends to be referred to as a normally open switch, where for conductance to occur,
voltage is needed to pass-through
• When there’s no voltage applied at the gate, there’s no conductance
• When voltage is applied at the gate, the conductivity of the device increases
N-Channel MOSFET:
•The drain and the source are doped with n+ impurity while the substrate is in p-type
•The current flows through the P-channel MOSFET
•When a positive voltage is applied on the gate, the electrons from the n+ source and the drain region are
attracted towards it, forming an electron reach channel
P-Channel MOSFET:
•Unlike the N-channel, the drain and the source are doped with p+ impurity while the substrate is in n-
type
•The current flows through the P-channel MOSFET
•When a negative voltage is applied on the gate, the electrons underneath the sulfur oxide respond to the
flow of current and get pushed downwards into the substrate
You might also like
- Merzbacher 3rd EdDocument670 pagesMerzbacher 3rd Edpirafafita4100% (2)
- Mosfet PDFDocument26 pagesMosfet PDFkhaledNo ratings yet
- Mosfet PDFDocument19 pagesMosfet PDFAditya MadhusudhanNo ratings yet
- Zeeman EffectDocument4 pagesZeeman Effectss626100% (1)
- Vacuum Energy An Electric SystemsDocument3 pagesVacuum Energy An Electric SystemsMarcus ReidNo ratings yet
- Quantum Physics 1Document42 pagesQuantum Physics 1kasun1237459No ratings yet
- Journey To The Edge of ReasonDocument337 pagesJourney To The Edge of ReasonFrancesco CavinaNo ratings yet
- Working Principles of Depletion and Enhancement MOSFET EditedDocument19 pagesWorking Principles of Depletion and Enhancement MOSFET EditedJust for funNo ratings yet
- B.E.LDocument18 pagesB.E.LJust for funNo ratings yet
- Module 2-18EE53Document59 pagesModule 2-18EE53AshwiniNo ratings yet
- MOS Logic FamilyDocument35 pagesMOS Logic Familyvinayak mastaNo ratings yet
- Mosfet: Presented by Vivek Krishna Kannan Siddarth Ram Mohan ArunDocument15 pagesMosfet: Presented by Vivek Krishna Kannan Siddarth Ram Mohan ArunfdfdfNo ratings yet
- Mosfet: Presented by Vivek Krishna Kannan Siddarth Ram Mohan ArunDocument15 pagesMosfet: Presented by Vivek Krishna Kannan Siddarth Ram Mohan ArunVictor TolentinoNo ratings yet
- Team4 Mosfet PDFDocument15 pagesTeam4 Mosfet PDFharishgokulNo ratings yet
- Mosfet 103Document15 pagesMosfet 103Victor TolentinoNo ratings yet
- Mosfet 105Document15 pagesMosfet 105Victor TolentinoNo ratings yet
- Mosfet: Presented by Vivek Krishna Kannan Siddarth Ram Mohan ArunDocument15 pagesMosfet: Presented by Vivek Krishna Kannan Siddarth Ram Mohan ArunMushaim AfreenNo ratings yet
- Mosfet: Presented by Vivek Krishna Kannan Siddarth Ram Mohan ArunDocument15 pagesMosfet: Presented by Vivek Krishna Kannan Siddarth Ram Mohan ArunVictor TolentinoNo ratings yet
- Mosfet 101Document15 pagesMosfet 101Victor TolentinoNo ratings yet
- Bee - FetDocument7 pagesBee - Fetwaheedarbab9302No ratings yet
- Lecture 1 - BJTs and MOSFETsDocument12 pagesLecture 1 - BJTs and MOSFETsGhostNo ratings yet
- MosfetDocument23 pagesMosfetgopikrishna yarlagaddaNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Introduction To Mos TechnologyDocument57 pagesUnit 2 Introduction To Mos Technologykshitiz vNo ratings yet
- Debre Markos University Institute of Technology School of Electrical and Computer Engineering Computer Engineering (PG)Document10 pagesDebre Markos University Institute of Technology School of Electrical and Computer Engineering Computer Engineering (PG)enidegNo ratings yet
- ETI 2203 Lesson 7Document10 pagesETI 2203 Lesson 7amash.emillyNo ratings yet
- Mini ProjectDocument25 pagesMini Projectcharan524No ratings yet
- Channel MOSFETDocument3 pagesChannel MOSFETRamulu VeesamNo ratings yet
- Untitled 4Document13 pagesUntitled 4maria.rehmanNo ratings yet
- 04 Transistor MOSFETDocument18 pages04 Transistor MOSFETNatalie mirelesNo ratings yet
- Mosfet and JfetDocument5 pagesMosfet and JfetJonarc Joseph VasquezNo ratings yet
- Mosfet: A Seminar Report OnDocument11 pagesMosfet: A Seminar Report OnFrancisNo ratings yet
- MOSFETDocument18 pagesMOSFETAditya PriyadarshiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 (Mosfet Transistor)Document22 pagesChapter 4 (Mosfet Transistor)Muriel MeyouNo ratings yet
- MOSFETDocument4 pagesMOSFETelen19111036 KFUEITNo ratings yet
- Principles and Applications of MOSFET and JFET MosfetDocument5 pagesPrinciples and Applications of MOSFET and JFET MosfetKim KimNo ratings yet
- Mosfet: Transistor (MOSFET, MOS-FET, or MOS FET) Is ADocument21 pagesMosfet: Transistor (MOSFET, MOS-FET, or MOS FET) Is AthesumitsinghNo ratings yet
- FetDocument17 pagesFetSagar SabharwalNo ratings yet
- Presented: Presentation On Jfet & MosfetDocument19 pagesPresented: Presentation On Jfet & MosfetManik MiaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document39 pagesLecture 1Nuniwal JyotiNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 NotesDocument9 pagesUnit 5 NotesShashikant PandeyNo ratings yet
- L2 Ivlsi 11012019Document31 pagesL2 Ivlsi 11012019naman mathurNo ratings yet
- Industrial Electronics Lecture-3 MosfetDocument13 pagesIndustrial Electronics Lecture-3 MosfetHamza TariqNo ratings yet
- SECA1503Document149 pagesSECA1503Thabasum Aara SNo ratings yet
- ProjestDocument2 pagesProjestdevilsking578No ratings yet
- ECE221 MOSFETs-I SRMAP PDFDocument30 pagesECE221 MOSFETs-I SRMAP PDFRajeshNo ratings yet
- Lecture11!11!12284 MosfetDocument28 pagesLecture11!11!12284 Mosfetshivali.vannarathNo ratings yet
- New Microsoft Word Document-1Document4 pagesNew Microsoft Word Document-1Agaba SamuelNo ratings yet
- Back To Basics Introduction To BJTs JFETs MESFETs and MOSFETsDocument28 pagesBack To Basics Introduction To BJTs JFETs MESFETs and MOSFETssonitha alvaNo ratings yet
- Unit III Jfet, MosfetDocument22 pagesUnit III Jfet, MosfetDevendra BansalNo ratings yet
- Lect 4,5,6,7 MOSFET Construction, Working Principle SND ChsrscteridticsDocument26 pagesLect 4,5,6,7 MOSFET Construction, Working Principle SND Chsrscteridticsshashikala kotiNo ratings yet
- The MOSFET - Metal Oxide FET: "NO Current Flows Into The Gate"Document11 pagesThe MOSFET - Metal Oxide FET: "NO Current Flows Into The Gate"Aan BeckhsNo ratings yet
- FALLSEM2022-23 BEEE102L TH VL2022230105984 Reference Material I 19-01-2023 003 MOSFETDocument22 pagesFALLSEM2022-23 BEEE102L TH VL2022230105984 Reference Material I 19-01-2023 003 MOSFETvishwadeepNo ratings yet
- Mosfet: MOS-FET, or MOS FET) Is A Transistor Used For Amplifying orDocument22 pagesMosfet: MOS-FET, or MOS FET) Is A Transistor Used For Amplifying ordadadabababaNo ratings yet
- What Is A MOSFET - Basics, Working Principle & ApplicationsDocument3 pagesWhat Is A MOSFET - Basics, Working Principle & ApplicationsKimberly Camacho CatubigNo ratings yet
- Mosfet DC Analysis: Semiconductor Field Effect Transistor or MOSFET For ShortDocument41 pagesMosfet DC Analysis: Semiconductor Field Effect Transistor or MOSFET For ShortSaley SaeedNo ratings yet
- Metal Oxide Semiconductor Field Effect Transisitor AssignmentDocument20 pagesMetal Oxide Semiconductor Field Effect Transisitor AssignmentSokoine Hamad DenisNo ratings yet
- The Mosfet: Home TransistorsDocument10 pagesThe Mosfet: Home TransistorsPrabashaNo ratings yet
- Power TransistorsDocument58 pagesPower Transistorssree haritha pNo ratings yet
- Unit I Cmos Technology An MOS (Metal-Oxide-Silicon) Structure Is Created by Superimposing Several Layers of ConductingDocument2 pagesUnit I Cmos Technology An MOS (Metal-Oxide-Silicon) Structure Is Created by Superimposing Several Layers of ConductingIshita AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Course Name: Basic Electronics Engineering Course Code: EC101 Metal Oxide Semiconductor Field Effect Transistor (MOSFET)Document37 pagesCourse Name: Basic Electronics Engineering Course Code: EC101 Metal Oxide Semiconductor Field Effect Transistor (MOSFET)Dr Sunipa RoyNo ratings yet
- 7.1 The MOSFET - Introduction: 7.1.1 Basic Structure and Principle of OperationDocument4 pages7.1 The MOSFET - Introduction: 7.1.1 Basic Structure and Principle of OperationManoj VatsNo ratings yet
- 510.22E - Lecture - 7Document12 pages510.22E - Lecture - 7SantosNo ratings yet
- UNIT II (Part 2) PDFDocument7 pagesUNIT II (Part 2) PDFZulkifl KhairoowalaNo ratings yet
- StudentDocument2 pagesStudentmarv hartiganNo ratings yet
- FinaldoneDocument18 pagesFinaldonemarv hartiganNo ratings yet
- Final PPT TreesDocument18 pagesFinal PPT Treesmarv hartiganNo ratings yet
- FinaldoneDocument18 pagesFinaldonemarv hartiganNo ratings yet
- Tes 2Document2 pagesTes 2marv hartiganNo ratings yet
- FinaldoneDocument18 pagesFinaldonemarv hartiganNo ratings yet
- TreesDocument10 pagesTreesmarv hartiganNo ratings yet
- Canva PPT TestDocument2 pagesCanva PPT Testmarv hartiganNo ratings yet
- Final PPT TreesDocument18 pagesFinal PPT Treesmarv hartiganNo ratings yet
- Classic - Vitals Report 3 - 5 - 2023Document40 pagesClassic - Vitals Report 3 - 5 - 2023marv hartiganNo ratings yet
- Software EngineeringDocument25 pagesSoftware Engineeringmarv hartiganNo ratings yet
- Dbms PPT Glen and DeepakDocument12 pagesDbms PPT Glen and Deepakmarv hartiganNo ratings yet
- Math TPDocument7 pagesMath TPmarv hartiganNo ratings yet
- Quantum MechanicsDocument31 pagesQuantum MechanicsMuhammad SaadNo ratings yet
- Universality of Quantum Gates: Markus SchmassmannDocument22 pagesUniversality of Quantum Gates: Markus SchmassmannDaattavyaNo ratings yet
- DFT Prediction of Band Gap in Organic-Inorganic Metal Halide PerovskitesDocument23 pagesDFT Prediction of Band Gap in Organic-Inorganic Metal Halide PerovskitesRakhshan JavaidNo ratings yet
- PN Junction Diode - MergedDocument55 pagesPN Junction Diode - MergedPrasanth. SNo ratings yet
- Introduction of Electron ConfigurationDocument26 pagesIntroduction of Electron ConfigurationKram M RazatlabNo ratings yet
- 7.solid State Physics - GATE 2010 - 2013Document12 pages7.solid State Physics - GATE 2010 - 2013Abhishek UpadhyayNo ratings yet
- What We Can Learn About Quantum Physics From A Single Qubit: Wolfgang - Duer@uibk - Ac.at Stefan - Heusler@uni-Muenster - deDocument15 pagesWhat We Can Learn About Quantum Physics From A Single Qubit: Wolfgang - Duer@uibk - Ac.at Stefan - Heusler@uni-Muenster - deAdrian CamachoNo ratings yet
- Item # Manufacturer Ref Des Qty MFG Part #: XXXX XXXX XXXXX Xxpcs Bom (Sample Bill of Materials)Document3 pagesItem # Manufacturer Ref Des Qty MFG Part #: XXXX XXXX XXXXX Xxpcs Bom (Sample Bill of Materials)KenrickNo ratings yet
- Gtifs - Is - I: Joruicmnufl, LDocument40 pagesGtifs - Is - I: Joruicmnufl, LAugustoAzeredoSilvaNo ratings yet
- Sakurai Solutions 1-1 1-4 1-8Document4 pagesSakurai Solutions 1-1 1-4 1-8Mario Mede RiteNo ratings yet
- Assignment3Document3 pagesAssignment3Ashwin IndwarNo ratings yet
- Chemistry IX M PART 1 PDFDocument80 pagesChemistry IX M PART 1 PDFAkhil s kumarNo ratings yet
- Elecs Circuit and Devices Chapter 1Document25 pagesElecs Circuit and Devices Chapter 1vhinzsanguinaryNo ratings yet
- SynthesisDocument22 pagesSynthesispiyush_chawla18No ratings yet
- What Is Zener Diode?Document4 pagesWhat Is Zener Diode?Riaz IsraniNo ratings yet
- CH 08Document16 pagesCH 08HanaTrianaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To The Keldysh Formalism: Alex KamenevDocument34 pagesIntroduction To The Keldysh Formalism: Alex KamenevvanalexbluesNo ratings yet
- Lab V. Light Emitting Diodes: 1. ObjectiveDocument8 pagesLab V. Light Emitting Diodes: 1. ObjectiveMeenakshi SuryavanshiNo ratings yet
- Jason Ho - Spinor-BEC and Multi-Component Quantum GasesDocument134 pagesJason Ho - Spinor-BEC and Multi-Component Quantum GasesPomac232No ratings yet
- Ez Dyson ManualDocument30 pagesEz Dyson ManualploploNo ratings yet
- Soluciones A Problemas de Mecaninca CuanticaDocument7 pagesSoluciones A Problemas de Mecaninca CuanticaIván GarcíaNo ratings yet
- Semiconductor Cheat Sheet Ver 1Document18 pagesSemiconductor Cheat Sheet Ver 1testerJesterNo ratings yet
- Auger Electron Spectroscopy - 97-2003Document5 pagesAuger Electron Spectroscopy - 97-2003Kannan BaskarNo ratings yet
- ECE111 - Analog Electronics: Sandeep Saini Gaurav ChatterjeeDocument21 pagesECE111 - Analog Electronics: Sandeep Saini Gaurav ChatterjeeAAYUSH SHUKLANo ratings yet
- STP 80 NF 70Document13 pagesSTP 80 NF 70Ikhwan SyafariNo ratings yet
- CH101 Lecture 3Document52 pagesCH101 Lecture 3api-3819150No ratings yet