Professional Documents
Culture Documents
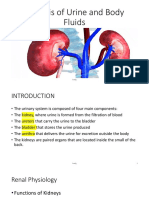
Chapter 18
Uploaded by
serena0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views35 pagesNorquest ANPH 1001/1002
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentNorquest ANPH 1001/1002
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views35 pagesChapter 18
Uploaded by
serenaNorquest ANPH 1001/1002
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 35
PowerPoint Presentation to Accompany
© 2010 Delmar, Cengage Learning
1
Chapter 18
The Urinary System
© 2010 Delmar, Cengage Learning
2
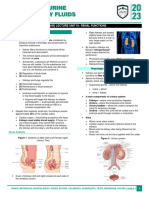
Introduction
• Maintains homeostasis
– Removes and restores solutes and fluids
• Organs
– Two kidneys: main filtering organs, produce
urine
– Two ureters
– One bladder
– One urethra
© 2010 Delmar, Cengage Learning
3 3
Introduction (cont’d.)
© 2010 Delmar, Cengage Learning
4 4
Functions of the Urinary
System
© 2010 Delmar, Cengage Learning
5 5
Functions of the Urinary System
(cont’d.)
• Excretion: nitrogenous, drugs and toxins
• Maintaining blood volume and
concentration
– Balance of water and dissolved salts
• pH regulation
– Balance of hydrogen ions
© 2010 Delmar, Cengage Learning
6
Functions of the Urinary System
(cont’d.)
• Blood pressure maintenance
– Renin
• Erythrocyte concentration
– Erythropoietin: stimulates red blood cell
production
• Vitamin D production
– Calciferol
© 2010 Delmar, Cengage Learning
7
The External Anatomy of the
Kidneys
© 2010 Delmar, Cengage Learning
8
The External Anatomy of the
Kidneys (cont’d.)
• Paired organs that are reddish in color
• About the size of a closed fist
• Located just above waist
– Between parietal peritoneum and posterior
wall of abdomen
• Referred to as retroperitoneal
© 2010 Delmar, Cengage Learning
9
The External Anatomy of the
Kidneys (cont’d.)
• Hilum: passage area for ureters, vessels,
nerves
• Surrounding layers
– Renal capsule: innermost, barrier
– Adipose capsule: middle, protection
– Renal fascia: outer, anchors kidney
© 2010 Delmar, Cengage Learning
10
The Internal Anatomy of the
Kidneys
© 2010 Delmar, Cengage Learning
11
The Internal Anatomy of the
Kidneys (cont’d.)
© 2010 Delmar, Cengage Learning
12
The Internal Anatomy of the
Kidneys (cont’d.)
• Medulla: inner area
– Renal pyramids: tips point inward
• Cortex: outer area
– Cortical material between pyramids
– Cortex and renal pyramids contain nephrons
© 2010 Delmar, Cengage Learning
13
The Internal Anatomy of the
Kidneys (cont’d.)
• Nephrons: functional units of the kidney
• Minor calyx
– Funnel shaped, collects urine from pyramid
ducts
• Major calyces: formed from minor calyces
– Join to form renal pelvis
– Renal pelvis narrows to form ureter
© 2010 Delmar, Cengage Learning
14
The Anatomy of the Nephrons
© 2010 Delmar, Cengage Learning
15
The Anatomy of the Nephrons
(cont’d.)
• Nephron: microscopic renal tubule
• Bowman’s glomerular capsule: double-
walled globe
– Podocytes: innermost layer
– Parietal layer: outermost layer
• Endothelial-capsular membrane: filter
© 2010 Delmar, Cengage Learning
16
The Anatomy of the Nephrons
(cont’d.)
• Renal tubule
– Proximal convoluted tubule
– Descending limb, loop and ascending limb of
Henle
– Distal convoluted tubule
• Collecting ducts
© 2010 Delmar, Cengage Learning
17
Blood and Nerve Supply to the
Nephrons
© 2010 Delmar, Cengage Learning
18
Blood and Nerve Supply to the
Nephrons (cont’d.)
© 2010 Delmar, Cengage Learning
19
Blood and Nerve Supply to the
Nephrons (cont’d.)
• Renal arteries: transport 1200 mL of blood
per minute
• Interlobar arteries
• Arcuate arteries
• Interlobular arteries
• Afferent arterioles divide into glomerular
capillaries
© 2010 Delmar, Cengage Learning
20
Blood and Nerve Supply to the
Nephrons (cont’d.)
• Efferent arterioles
• Peritubular capillaries
• Interlobular veins drain into arcuate vein
• Interlobar veins
• Renal veins
© 2010 Delmar, Cengage Learning
21
Physiology of the Nephrons
© 2010 Delmar, Cengage Learning
22
Physiology of the Nephrons
(cont’d.)
• Functions
– Control blood concentration and volume
– Regulate blood pH
– Remove toxins from blood
– Stimulate red blood cell production
© 2010 Delmar, Cengage Learning
23
Physiology of the Nephrons
(cont’d.)
• Urine formation
– Glomerular filtration
– Tubular reabsorption
– Tubular secretion
• Urine: 95% water, urea, uric acid,
electrolytes
– 56 mL an hour is normal
– 30 mL an hour indicates possible kidney failure
© 2010 Delmar, Cengage Learning
24
The Ureters: Anatomy and
Function
© 2010 Delmar, Cengage Learning
25
The Ureters: Anatomy and Function
(cont’d.)
• Extensions of the renal pelvis
• Connect to urinary bladder
• Function: transport urine to urinary bladder
• Urine movement
– Peristalsis, gravity, hydrostatic pressure
© 2010 Delmar, Cengage Learning
26
The Urinary Bladder and the
Micturition Reflex
© 2010 Delmar, Cengage Learning
27
The Urinary Bladder and the
Micturition Reflex (cont’d.)
• Urinary bladder held in position by
peritoneum
• Trigone: region between openings of
ureters and urethra
• Detrusor muscle: three-layered smooth
muscle
• Internal urinary sphincter: involuntary
control
© 2010 Delmar, Cengage Learning
28
The Urinary Bladder and the
Micturition Reflex (cont’d.)
• Micturition: expulsion of urine from bladder
• External urinary sphincter: voluntary
control
• Bladder capacity
– 700-800 mL
– 200-400 mL: conscious of need to urinate
• Stretch receptors initiate micturition reflex
© 2010 Delmar, Cengage Learning
29
The Urinary Bladder and the
Micturition Reflex (cont’d.)
• During urination
– Detrusor muscle contracts
– Muscles of pelvic floor and abdominal wall
contract
– External urinary sphincter relaxes and urine
moves from bladder to the outside
© 2010 Delmar, Cengage Learning
30
The Urethra: Male and
Female Positions
© 2010 Delmar, Cengage Learning
31
The Urethra: Male and Female
Positions (cont’d.)
• Urethra: connects bladder to the outside
• Females
– Lies directly posterior to pubic symphysis
– Located in wall of vagina
– 3.8 cm long
– Between clitoris and vaginal opening
© 2010 Delmar, Cengage Learning
32
The Urethra: Male and Female
Positions (cont’d.)
• Males
– 20 cm long
– Passes through prostate gland and penis
– Opens at tip of penis
– Transports urine and semen
© 2010 Delmar, Cengage Learning
33
Animation – Urine Formation
• This animation presents an overview of how urine is formed
Click Here to Play Urine Formation Animation
© 2010 Delmar, Cengage Learning
34
Summary
• Discussed the functions of the urinary
system
• Described the internal and external
anatomy of the kidney
• Discussed the structure and function of the
nephron
• Discussed micturition and the role of the
ureters and urinary bladder
© 2010 Delmar, Cengage Learning
35
You might also like
- HARVARD MEDICAL Improving Sleep - A Guide To A Good Nights Rest PDFDocument53 pagesHARVARD MEDICAL Improving Sleep - A Guide To A Good Nights Rest PDFdarioarrus79% (14)
- Always Breathe Correctly E Book PDFDocument62 pagesAlways Breathe Correctly E Book PDFFilipe Boiler100% (1)
- Biological Basis of Human BehaviorDocument44 pagesBiological Basis of Human BehaviorDr. Jayesh Patidar100% (5)
- Frog Dissection GuideDocument16 pagesFrog Dissection GuideGabrielle PortillasNo ratings yet
- Chapter 16Document35 pagesChapter 16serenaNo ratings yet
- Powerpoint Presentation To Accompany: © 2010 Delmar, Cengage LearningDocument32 pagesPowerpoint Presentation To Accompany: © 2010 Delmar, Cengage LearningserenaNo ratings yet
- Bio 208 Urinary SystemDocument121 pagesBio 208 Urinary SystemNazir RabiuNo ratings yet
- Powerpoint Presentation To Accompany: © 2010 Delmar, Cengage LearningDocument59 pagesPowerpoint Presentation To Accompany: © 2010 Delmar, Cengage LearningserenaNo ratings yet
- 1-Renal Physiology 1 (Renal Functions & Basic Concepts)Document33 pages1-Renal Physiology 1 (Renal Functions & Basic Concepts)dgcwbbwhqjNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10Document34 pagesChapter 10serenaNo ratings yet
- Powerpoint Presentation To Accompany: © 2010 Delmar, Cengage LearningDocument54 pagesPowerpoint Presentation To Accompany: © 2010 Delmar, Cengage LearningserenaNo ratings yet
- Kidney PhysiologyDocument144 pagesKidney PhysiologySilasNo ratings yet
- SEHH2234 2021 S2 Ch16 Urinary System StudentsDocument58 pagesSEHH2234 2021 S2 Ch16 Urinary System Studentsmiki leeNo ratings yet
- Kidney Function Lecture NotesDocument80 pagesKidney Function Lecture NotesNomel JonesNo ratings yet
- Excretory System: Ramesh Balayar (ZRB) IOM-2015Document26 pagesExcretory System: Ramesh Balayar (ZRB) IOM-2015AbhishekNo ratings yet
- The Urinary System Functions of The Urinary System: © 2018 Pearson Education, Ltd. 1Document13 pagesThe Urinary System Functions of The Urinary System: © 2018 Pearson Education, Ltd. 1lourd nabNo ratings yet
- The Urinary System Functions of The Urinary System: © 2018 Pearson Education, Inc. 1Document13 pagesThe Urinary System Functions of The Urinary System: © 2018 Pearson Education, Inc. 1Stef FieNo ratings yet
- Chapter 17Document35 pagesChapter 17serenaNo ratings yet
- Urinary SystemDocument55 pagesUrinary SystemChristian UdaundoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11Document40 pagesChapter 11serenaNo ratings yet
- The Excretory/ Urinary System: Lecture By: Marri Jmelou M. Roldan, MSCDocument29 pagesThe Excretory/ Urinary System: Lecture By: Marri Jmelou M. Roldan, MSCHeaven SolNo ratings yet
- Chapter 15 The Urinary SystemDocument18 pagesChapter 15 The Urinary SystemYeshia InocencioNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument37 pagesAnatomy and PhysiologyJamesMarcoMNo ratings yet
- PPT@Renal System4PC (2022)Document88 pagesPPT@Renal System4PC (2022)ademabdella38No ratings yet
- Urinary System SummaryDocument94 pagesUrinary System SummaryRhyza Marie LopezNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 - Excretory SystemsDocument57 pagesChapter 12 - Excretory Systemsnokate konkoorNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Patients With Renal Disorders Management of Urinary Tract DisordersDocument16 pagesAssessment of Patients With Renal Disorders Management of Urinary Tract DisordersJhosita Flora LarocoNo ratings yet
- Urinary System: Human Anatomy & Physiology (Biol 20025)Document21 pagesUrinary System: Human Anatomy & Physiology (Biol 20025)Aila Grace PeriodicoNo ratings yet
- Unit 6-Urinary System (Slides)Document71 pagesUnit 6-Urinary System (Slides)alan tangNo ratings yet
- Excretory System Lecture 1 JUWDocument12 pagesExcretory System Lecture 1 JUWamjad.46987No ratings yet
- 11 Biology Notes ch19 Excretory Products and Their Elimination PDFDocument3 pages11 Biology Notes ch19 Excretory Products and Their Elimination PDFRamachandranPerumalNo ratings yet
- Powerpoint Presentation To Accompany: © 2010 Delmar, Cengage LearningDocument25 pagesPowerpoint Presentation To Accompany: © 2010 Delmar, Cengage LearningserenaNo ratings yet
- Urogenital Guide Notes PDFDocument26 pagesUrogenital Guide Notes PDFJoryn LimNo ratings yet
- Latu - Urinary System - New 2023Document50 pagesLatu - Urinary System - New 2023oppongphilomina6No ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of Urinary SystemDocument53 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of Urinary SystemArathy KalathingalNo ratings yet
- Aubf Prelim 1Document59 pagesAubf Prelim 1Kat JornadalNo ratings yet
- Lecture 8 Urinary SystemDocument46 pagesLecture 8 Urinary SystemKang MonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 - ExcretionDocument46 pagesChapter 11 - Excretionapi-372850875% (4)
- Apy 121 Urinary SystemDocument45 pagesApy 121 Urinary SystemSANDIE SORELLENo ratings yet
- KidneyDocument85 pagesKidneyIshita SinghNo ratings yet
- Urinary SystemDocument4 pagesUrinary SystemMohammed Keyarul IslamNo ratings yet
- Excretory SystemDocument37 pagesExcretory SystemBlister CountNo ratings yet
- Aubf LecDocument97 pagesAubf Lechinata shoyoNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Urinary System, Educational PlatformDocument45 pagesUnit 2 Urinary System, Educational Platformneedo707070No ratings yet
- Vipin Sir Biology 19. Excretory Products and Their EliminationDocument55 pagesVipin Sir Biology 19. Excretory Products and Their EliminationvanshpatelssisNo ratings yet
- ExcretionDocument56 pagesExcretionChinmaya SNo ratings yet
- Chapter 15Document32 pagesChapter 15serenaNo ratings yet
- Urinary LectureDocument12 pagesUrinary Lectureastraia celesteNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Urinary SystemDocument7 pagesLesson 1 Urinary SystemJulio De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Powerpoint Presentation To Accompany: © 2010 Delmar, Cengage LearningDocument38 pagesPowerpoint Presentation To Accompany: © 2010 Delmar, Cengage LearningserenaNo ratings yet
- Moderator: Mr. Ram Singh (Lecturer) Deptt. of Radio-Diagnosis & Imaging, PGIMER, ChandigarhDocument119 pagesModerator: Mr. Ram Singh (Lecturer) Deptt. of Radio-Diagnosis & Imaging, PGIMER, ChandigarhMunish DograNo ratings yet
- The Urinary SystemDocument34 pagesThe Urinary Systemaarti HingeNo ratings yet
- QUIAMBAO - Urinary System Reviewer - AnaPhy LecDocument8 pagesQUIAMBAO - Urinary System Reviewer - AnaPhy LecqlouisamarieNo ratings yet
- ExcertionDocument39 pagesExcertionMuhammad UsmanNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Urinary SystemDocument43 pagesAnatomy of Urinary SystemIrfan Ali JunejoNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology RenalDocument5 pagesAnatomy and Physiology RenalMaryGeneville Opeña AbitNo ratings yet
- Physiology OF Renal SYSTEMDocument24 pagesPhysiology OF Renal SYSTEMsam bossaNo ratings yet
- Lect 4 Urinary SystemDocument42 pagesLect 4 Urinary Systemnightter4No ratings yet
- The Urinary System Overview of Kidney FunctionsDocument9 pagesThe Urinary System Overview of Kidney FunctionsLALRINTLUANGI CHHAKCHHUAKNo ratings yet
- RenalSystem Part 1 (Spring2020)Document49 pagesRenalSystem Part 1 (Spring2020)Sahil ParikhNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13Document26 pagesChapter 13serenaNo ratings yet
- Hhis221 Lab - Urinary SystemDocument48 pagesHhis221 Lab - Urinary SystemNel TinduganiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 17Document35 pagesChapter 17serenaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13Document26 pagesChapter 13serenaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 15Document32 pagesChapter 15serenaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14Document43 pagesChapter 14serenaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12Document32 pagesChapter 12serenaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11Document40 pagesChapter 11serenaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10Document34 pagesChapter 10serenaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document29 pagesChapter 6serenaNo ratings yet
- Powerpoint Presentation To Accompany: © 2010 Delmar, Cengage LearningDocument23 pagesPowerpoint Presentation To Accompany: © 2010 Delmar, Cengage LearningserenaNo ratings yet
- Powerpoint Presentation To Accompany: © 2010 Delmar, Cengage LearningDocument25 pagesPowerpoint Presentation To Accompany: © 2010 Delmar, Cengage LearningserenaNo ratings yet
- Powerpoint Presentation To Accompany: © 2010 Delmar, Cengage LearningDocument54 pagesPowerpoint Presentation To Accompany: © 2010 Delmar, Cengage LearningserenaNo ratings yet
- Powerpoint Presentation To Accompany: © 2010 Delmar, Cengage LearningDocument38 pagesPowerpoint Presentation To Accompany: © 2010 Delmar, Cengage LearningserenaNo ratings yet
- Powerpoint Presentation To Accompany: © 2010 Delmar, Cengage LearningDocument38 pagesPowerpoint Presentation To Accompany: © 2010 Delmar, Cengage LearningserenaNo ratings yet
- Powerpoint Presentation To Accompany: © 2010 Delmar, Cengage LearningDocument35 pagesPowerpoint Presentation To Accompany: © 2010 Delmar, Cengage LearningserenaNo ratings yet
- Las Science4 q2w2Document2 pagesLas Science4 q2w2Annabelle Poniente HertezNo ratings yet
- Thrombosis: Thrombus Is Blood That Has Clotted in The Heart or A Blood VesselDocument53 pagesThrombosis: Thrombus Is Blood That Has Clotted in The Heart or A Blood VesselhjjhNo ratings yet
- Chapter 42 Study QuestionsDocument8 pagesChapter 42 Study QuestionsGabriel FreschNo ratings yet
- Distribution CellDocument4 pagesDistribution CellJhonathan RodríguezNo ratings yet
- Las-Science 6 Quarter 2 Week 1Document4 pagesLas-Science 6 Quarter 2 Week 1EvelynMartinezNo ratings yet
- Week 10 Lab Activity Respiratory SystemDocument5 pagesWeek 10 Lab Activity Respiratory SystemSophia Nicole RosalesNo ratings yet
- Avian Circulatory SystemDocument27 pagesAvian Circulatory SystemCarlBuscato100% (4)
- Percakapan BHS Ingg 1-5 - OciDocument30 pagesPercakapan BHS Ingg 1-5 - OciYetty LasmiNo ratings yet
- Circulation and Gas ExchangeDocument164 pagesCirculation and Gas ExchangeZuliyanto ZakariaNo ratings yet
- Long Quiz Hema Lec 2021 MergedDocument49 pagesLong Quiz Hema Lec 2021 MergedAngela ReyesNo ratings yet
- Vital SgnsDocument58 pagesVital SgnsKANT JAMES D. MAHANNo ratings yet
- Workbook ActivityDocument2 pagesWorkbook ActivityRisciella 18No ratings yet
- Lymphatic System and Immune SystemDocument4 pagesLymphatic System and Immune SystemKyle Labor100% (1)
- Breathing and Exchange: of GasesDocument10 pagesBreathing and Exchange: of GaseshellohelloworldNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document4 pagesChapter 2Mariane NajeNo ratings yet
- Anatomy - Cardiovascular System - Part IIIDocument12 pagesAnatomy - Cardiovascular System - Part IIIVăn ĐứcNo ratings yet
- Laporan Kinerja Lab Per Pasien Pemeriksaan 2022-10-09 S - D 2022-10-09Document72 pagesLaporan Kinerja Lab Per Pasien Pemeriksaan 2022-10-09 S - D 2022-10-09LaboratoriumNo ratings yet
- Haematology Question BankDocument3 pagesHaematology Question BankNIHAR UTHALE100% (1)
- Red Blood Cell Phenotyping of Blood Donors in Islamabad, PakistanDocument5 pagesRed Blood Cell Phenotyping of Blood Donors in Islamabad, PakistanAHNS123No ratings yet
- Evaluation #6: A. B. C. DDocument12 pagesEvaluation #6: A. B. C. DFrancia Martinez RepatacodoNo ratings yet
- Rabbit RespirationDocument5 pagesRabbit RespirationshajehanNo ratings yet
- Brown2012 SleepWakefulnessReviewDocument101 pagesBrown2012 SleepWakefulnessReviewvkasNo ratings yet
- CH 10 Test BankDocument25 pagesCH 10 Test BankBiano, Fortune JayneNo ratings yet
- Measuring Lung CapacityDocument15 pagesMeasuring Lung CapacitySthephen MarquezNo ratings yet
- Blood GroupingDocument8 pagesBlood GroupingdevarajNo ratings yet
- Blood Cells and Its Types With FunctionsDocument5 pagesBlood Cells and Its Types With Functionskaleb16_2No ratings yet