0% found this document useful (0 votes)
222 views16 pages5.4 Trignometric Leveling
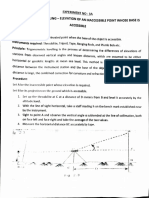
Here are the steps to calculate the reduced level of the top of the tower:
1. Vertical angle (θ) measured from station A = ?
2. Horizontal distance (AB) = 50 m
3. Given: RL of BM at A = 100 m
4. Using the formula: h = AB tanθ
5. As all points are in same vertical plane, no correction is required.
6. Therefore, RL of top of tower = RL of BM at A + h
= 100 + 50tanθ
So the reduced level of the top of the tower can be calculated by substituting the measured vertical angle in the formula: RL of top of tower = 100 + 50tanθ
Uploaded by
Sumit Kumar SinhaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
222 views16 pages5.4 Trignometric Leveling
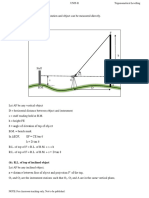
Here are the steps to calculate the reduced level of the top of the tower:
1. Vertical angle (θ) measured from station A = ?
2. Horizontal distance (AB) = 50 m
3. Given: RL of BM at A = 100 m
4. Using the formula: h = AB tanθ
5. As all points are in same vertical plane, no correction is required.
6. Therefore, RL of top of tower = RL of BM at A + h
= 100 + 50tanθ
So the reduced level of the top of the tower can be calculated by substituting the measured vertical angle in the formula: RL of top of tower = 100 + 50tanθ
Uploaded by
Sumit Kumar SinhaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd