0% found this document useful (0 votes)
740 views17 pagesATOMISM
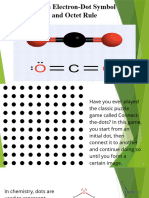
Atomism originated with ancient Greek philosophers Leucippus and Democritus, who theorized that all matter is made up of fundamental indivisible particles called atoms. They proposed that atoms come in different shapes and sizes and combine in various arrangements to form all substances. In the early 1800s, chemist John Dalton revived the concept of atoms to explain chemical reactions, proposing that atoms are the basic units of elements and cannot be created or destroyed in chemical reactions. Aristotle was an influential ancient Greek philosopher and scientist who made seminal contributions across many fields and is credited with establishing the foundations of modern science through empirical observation and systematic experimentation.
Uploaded by
Jobelle ManalangCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
740 views17 pagesATOMISM
Atomism originated with ancient Greek philosophers Leucippus and Democritus, who theorized that all matter is made up of fundamental indivisible particles called atoms. They proposed that atoms come in different shapes and sizes and combine in various arrangements to form all substances. In the early 1800s, chemist John Dalton revived the concept of atoms to explain chemical reactions, proposing that atoms are the basic units of elements and cannot be created or destroyed in chemical reactions. Aristotle was an influential ancient Greek philosopher and scientist who made seminal contributions across many fields and is credited with establishing the foundations of modern science through empirical observation and systematic experimentation.
Uploaded by
Jobelle ManalangCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd