0% found this document useful (0 votes)
115 views17 pagesLinear Induction Motor
The document summarizes a linear induction motor (LIM). Key points:
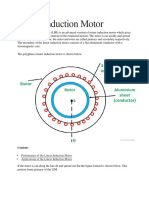
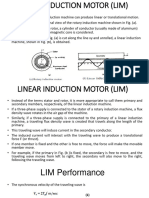
1) A LIM produces linear motion rather than rotary motion like a conventional induction motor due to its open air gap design.
2) LIMs can be classified as short primary single sided, short secondary single sided, or double sided primary based on their construction.
3) LIMs experience end effects due to their open ended design which can impact efficiency.
4) LIMs have advantages over conventional motors like low cost and maintenance but also disadvantages like low power factor and efficiency.
5) Common applications of LIMs include traction motors, conveyor belts, sliding doors, and
Uploaded by
Mani Balaji TCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
115 views17 pagesLinear Induction Motor
The document summarizes a linear induction motor (LIM). Key points:
1) A LIM produces linear motion rather than rotary motion like a conventional induction motor due to its open air gap design.
2) LIMs can be classified as short primary single sided, short secondary single sided, or double sided primary based on their construction.
3) LIMs experience end effects due to their open ended design which can impact efficiency.
4) LIMs have advantages over conventional motors like low cost and maintenance but also disadvantages like low power factor and efficiency.
5) Common applications of LIMs include traction motors, conveyor belts, sliding doors, and
Uploaded by
Mani Balaji TCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd