Professional Documents
Culture Documents
National Income Concepts
Uploaded by
Data Analyst0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
17 views22 pagesThis document discusses different methods of measuring a nation's income, including the product method, income method, and expenditure method. It also defines key macroeconomic terms like gross domestic product (GDP), gross national product (GNP), net national product (NNP), national income, personal income, and disposable personal income. GDP is the total market value of all final goods and services produced within a country in a given period of time.
Original Description:
Original Title
National_income_concepts
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses different methods of measuring a nation's income, including the product method, income method, and expenditure method. It also defines key macroeconomic terms like gross domestic product (GDP), gross national product (GNP), net national product (NNP), national income, personal income, and disposable personal income. GDP is the total market value of all final goods and services produced within a country in a given period of time.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
17 views22 pagesNational Income Concepts
Uploaded by
Data AnalystThis document discusses different methods of measuring a nation's income, including the product method, income method, and expenditure method. It also defines key macroeconomic terms like gross domestic product (GDP), gross national product (GNP), net national product (NNP), national income, personal income, and disposable personal income. GDP is the total market value of all final goods and services produced within a country in a given period of time.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 22
Unit-III
Measuring a Nation’s Income
Microeconomics is the study of how
individual households and firms make
decisions and how they interact with
one another in markets.
Macroeconomics is the study of the
economy as a whole.
Itsgoal is to explain the economic changes
that affect many households, firms, and
markets at once.
Macroeconomics
• Macroeconomics answers questions like
the following:
Why is average income high in some countries and
low in others?
Why do prices rise rapidly in some time periods
while they are more stable in others?
Why do production and employment expand in
some years and contract in others?
Economic activities vs. Non-economic
activities
• Economic Activities: All activities which create
goods and services that can be valued at
market price. Like: Production by farmers,
businessman etc.
• Non-economic Activities: All activities which
create goods and services that do not have
any market value. Like: Services of Housewife.
The Economy’s
Income and Expenditure
When judging whether the economy is doing
well or poorly, it is natural to look at the total
income that everyone in the economy is
earning.
For an economy as a whole, income must equal
expenditure because:
Every transaction has a buyer and a seller.
Every Rupee of spending by some buyer is a
Rupee of income for some seller.
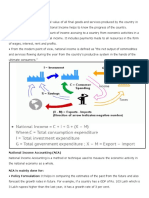
The Circular-Flow Diagram
Revenue Spending
Market for
Goods
Goods & Goods &
Services sold and Services
Services bought
Firms
Households
Inputs for Labor, land, and
production Market for capital
Factors
Wages, rent, and of Production Income
profit
Methods of Measuring National Income
Three different angles:
1) Aggregate of productive units of different sector.
Net Product method: Aggregate of productions.
2) Combination of individuals and households’
different factors of production. Factor-income
method: Combination of Factor-owners and users.
3) Collection of consuming, saving and investment.
Expenditure Method: Collection of spending units.
Product method/ Net Product
method/Value added Method
1) Estimate gross value of domestic output in
various branches of production
2) Determine cost of inputs and depreciation
3) Deducting these costs & depreciation from
gross value.
It gives us Net Value added.
This procedure is also called value added or
income product.
Income Method/Factor share method
National income= Rent+ Wages + Interest +
profit
These are grouped under three categories:
1) Labour Incomes
2) Capital Incomes
3) Mixed Incomes
Expenditure Method
1) All the money expenditure at market prices are
computed and added.
a) Pvt. Consumption. b) direct tax payments
c) Payment to organisations. d) Pvt. Savings.
2) Value of all the products finally disposed off are
computed and added up.
b) Pvt. Consumer goods & services. b) Pvt.
investment goods. c) Public goods & services. d)
Net investment.
Choosing the method
• Depends upon data availability
• Purpose of the national income analysis
• No single method is accurate.
• Countries often adopt more than two methods to
measure national income.
Most common method is product method.
In India, product method is adopted. CSO (Central Statistical
Organization) estimates NY.
Product method is used for Agriculture and manufacturing
sector. For service sector Income method is adopted.
Some terms: Gross Domestic Product
• Gross domestic product (GDP) is a
measure of the income and
expenditures of an economy.
• It is the total market value of all final
goods and services produced within a
country in a given period of time.
The Measurement of GDP
• Output is valued at market prices.
• It records only the value of final goods, not
intermediate goods (the value is counted only once).
• It includes both tangible goods (food, clothing, cars)
and intangible services (haircuts, housecleaning, doctor
visits).
• It includes goods and services currently produced, not
transactions involving goods produced in the past.
• It measures the value of production within the
geographic confines of a country.
The Measurement of GDP
• It measures the value of production that
takes place within a specific interval of
time, usually a year or a quarter (three
months).
What Is Counted and not counted in GDP?
GDP includes all items produced in the
economy and sold legally in markets.
GDP excludes most items that are
produced and consumed at home and
that never enter the marketplace.
It excludes items produced and sold
illicitly, such as illegal drugs.
Other Measures of Income
• Gross National Product (GNP)
• Net National Product (NNP)
• National Income
• Personal Income
• Disposable Personal Income
Gross National Product
• Gross national product (GNP) is the total
income earned by a nation’s permanent
residents (called nationals).
• It differs from GDP by including income that
our citizens earn abroad and excluding
income that foreigners earn here.
Net National Product (NNP)
• Net National Product (NNP) is the total
income of the nation’s residents (GNP)
minus losses from depreciation.
• Depreciation is the wear and tear on the
economy’s stock of equipment and
structures.
National Income
• National Income is the total income earned
by a nation’s residents in the production of
goods and services.
• It differs from NNP by excluding indirect
business taxes (such as sales taxes) and
including business subsidies.
Personal Income
• Personal income is the income that households
and noncorporate businesses receive.
• Unlike national income, it excludes retained
earnings, which is income that corporations
have earned but have not paid out to their
owners.
• In addition, it includes household’s interest
income and government transfers.
Disposable Personal Income
• Disposable personal income is the income
that household and noncorporate
businesses have left after satisfying all their
obligations to the government.
• It equals personal income minus personal
taxes and certain nontax payments.
Prices
• GDP, GNP, NNP, etc can be measured at
Current prices and constant prices.
• For comparisons purposes and research
mostly GDP or GNP at constant prices are
used.
• Some indicators are measured at factor cost.
• GDP@Factor cost = GDP@market price-
Indirect tax + subsidies.
You might also like
- CWI - Part A Fundamentals Examination (Full) PDFDocument43 pagesCWI - Part A Fundamentals Examination (Full) PDFJulian Ramirez Ospina100% (4)
- National Income and Occupational Structure in IndiaDocument45 pagesNational Income and Occupational Structure in IndiaakshatNo ratings yet
- Switchword PairsDocument6 pagesSwitchword PairsLaleKulahli100% (7)
- National in Come in IndiaDocument41 pagesNational in Come in IndiaSunil SunitaNo ratings yet
- Lecture2.1.Natl IncomeAndGrowth.ilkkaracan2024Document54 pagesLecture2.1.Natl IncomeAndGrowth.ilkkaracan2024Mehmet Emre AYDEMİRNo ratings yet
- NI Acounting - FDocument33 pagesNI Acounting - Fmonalishas_1No ratings yet
- Module - 4 National IncomeDocument64 pagesModule - 4 National Incomelakshmi dileepNo ratings yet
- Lecture 12 Methods To Measure National IncomeDocument28 pagesLecture 12 Methods To Measure National IncomeDevyansh GuptaNo ratings yet
- National IncomeDocument16 pagesNational IncomeSamia Irshad ullahNo ratings yet
- Principles of Economics 4Document51 pagesPrinciples of Economics 4reda gadNo ratings yet
- Mee - 2 - Data of Macro (2013) - ClassDocument60 pagesMee - 2 - Data of Macro (2013) - Classsnata92No ratings yet
- National Income Accounting: Economics, 7 Edition Boyes and Melvin Houghton Mifflin Company, 2008Document26 pagesNational Income Accounting: Economics, 7 Edition Boyes and Melvin Houghton Mifflin Company, 2008Asad NaseerNo ratings yet
- ch-7 NewDocument16 pagesch-7 NewSAKIB MD SHAFIUDDINNo ratings yet
- Measuring A Nation's IncomeDocument76 pagesMeasuring A Nation's Incomeمدرسة حوارة الاساسيةNo ratings yet
- CH 6 Fundamental Concepts of MacroeconomicsDocument52 pagesCH 6 Fundamental Concepts of MacroeconomicsabelNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 & 3: Measuring Macroeconomic PerformanceDocument34 pagesLecture 2 & 3: Measuring Macroeconomic PerformanceAli zizoNo ratings yet
- PGDM (2019-21) Term 2 (September-December) : Dr. Kalpana TokasDocument30 pagesPGDM (2019-21) Term 2 (September-December) : Dr. Kalpana Tokasv_amyNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Circular FlowDocument62 pagesUnit 2 Circular Flowk pradeepaNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Circular FlowDocument62 pagesUnit 2 Circular FlowAnshumaan PatroNo ratings yet
- GDP:two Measures of National Product Flow of Product Approach. Earning and Cost ApproachDocument53 pagesGDP:two Measures of National Product Flow of Product Approach. Earning and Cost ApproachUmer Farooq MirzaNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 NewDocument94 pagesUnit 5 NewrajapatnaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 11 National IncomeDocument38 pagesLecture 11 National IncomeDevyansh GuptaNo ratings yet
- BUS 404 Chapter 3Document17 pagesBUS 404 Chapter 3R-540 Mahmud Hasan Batch-105-CNo ratings yet
- Intro to Macroeconomics GDP, Inflation, Business Cycles (Ch.23Document36 pagesIntro to Macroeconomics GDP, Inflation, Business Cycles (Ch.23jawadzaheerNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 NewDocument94 pagesUnit 5 NewrajapatnaNo ratings yet
- Understanding GDP and Its ComponentsDocument71 pagesUnderstanding GDP and Its ComponentsSidharth RainaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 20: The Measurement of National Income: National Output and Value AddedDocument4 pagesChapter 20: The Measurement of National Income: National Output and Value AddedSaaki GaneshNo ratings yet
- PBD Module 1 NotesDocument13 pagesPBD Module 1 Notesafshots422No ratings yet
- Theory of National IncomeDocument72 pagesTheory of National IncomeAlex RockNo ratings yet
- Measuring GDP and Economic Growth: Chapter 21, Michael ParkinDocument21 pagesMeasuring GDP and Economic Growth: Chapter 21, Michael ParkinOyon Nur newazNo ratings yet
- ECON1102 Complete NotesDocument60 pagesECON1102 Complete NotesJustin100% (1)
- Macroeconomic Analysis For Management 1 - Chapter 3Document21 pagesMacroeconomic Analysis For Management 1 - Chapter 3dawsonNo ratings yet
- Module 2Document70 pagesModule 2PriyankaNo ratings yet
- Nationalincome 141209072252 Conversion Gate02Document37 pagesNationalincome 141209072252 Conversion Gate02Simmi KhuranaNo ratings yet
- The International Economic Environment: Chapter - 3Document29 pagesThe International Economic Environment: Chapter - 3Tasnim IslamNo ratings yet
- Gross Domestic ProductDocument18 pagesGross Domestic ProductABBAS ANo ratings yet
- Chapter Two: National Income AccountingDocument18 pagesChapter Two: National Income AccountingMenna ElmeslhyNo ratings yet
- Managerial Economics National Income PDFDocument9 pagesManagerial Economics National Income PDFSanjeev KumarNo ratings yet
- Nations WealthDocument49 pagesNations WealthwomabaNo ratings yet
- Measuring National Income: Concepts and MethodsDocument17 pagesMeasuring National Income: Concepts and MethodsPradeep RaviNo ratings yet
- National Income Accounting (NIA)Document8 pagesNational Income Accounting (NIA)Mamta VermaNo ratings yet
- What Is Macroeconomics? Its OriginDocument55 pagesWhat Is Macroeconomics? Its OriginAman Singh RajputNo ratings yet
- National IncomeDocument18 pagesNational Incomepankajpatidar7440No ratings yet
- Macroeconomics: Why is national income accounting importantDocument40 pagesMacroeconomics: Why is national income accounting importantDigvijay SinghNo ratings yet
- Session 3Document19 pagesSession 3Ramji TripathyNo ratings yet
- Chap - 22.measuring A Nation's IncomeDocument55 pagesChap - 22.measuring A Nation's IncomeellieNo ratings yet
- National Income-1Document17 pagesNational Income-1Ms. Vandana MohantyNo ratings yet
- National Income ConceptsDocument34 pagesNational Income ConceptsQammer ShahzadNo ratings yet
- Macroeconomics S2 (Pertemuan 2.1)Document30 pagesMacroeconomics S2 (Pertemuan 2.1)Muhammad Faizal AkbarNo ratings yet
- Ofp 015Document51 pagesOfp 015abdul ahmad kilimaNo ratings yet
- National Income: By-Roopak Malik & Raneesh ChoudharyDocument18 pagesNational Income: By-Roopak Malik & Raneesh Choudharyemin4No ratings yet
- National IncomeDocument29 pagesNational IncomegipaworldNo ratings yet
- National IncomeDocument47 pagesNational IncomeJannat MalhotraNo ratings yet
- Economics IDocument34 pagesEconomics IKevin kayNo ratings yet
- GDP Explained: Measuring a Nation's Economic OutputDocument52 pagesGDP Explained: Measuring a Nation's Economic OutputShahzod OltiboyevNo ratings yet
- Macroeconomic IndicatorsDocument27 pagesMacroeconomic Indicatorsanjali mishraNo ratings yet
- National Income AccountingDocument36 pagesNational Income AccountingMharck AtienzaNo ratings yet
- Measuring A Nation's Income: Microeconomics MacroeconomicsDocument5 pagesMeasuring A Nation's Income: Microeconomics MacroeconomicsMuhammad DawoodNo ratings yet
- Concepts and Measurement of National IncomeDocument66 pagesConcepts and Measurement of National IncomesubramanianNo ratings yet
- The National Income Accounting 1Document15 pagesThe National Income Accounting 1Kyle Kenneth GarciaNo ratings yet
- Unit-V Managerial EconomicsDocument34 pagesUnit-V Managerial Economicsatulkumar.rise1No ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Business Economics Study Resource: CIMA Study ResourcesFrom EverandFundamentals of Business Economics Study Resource: CIMA Study ResourcesNo ratings yet
- Inflation Causes and Effects RevisionDocument26 pagesInflation Causes and Effects RevisionData AnalystNo ratings yet
- Inflation DeflationDocument18 pagesInflation DeflationData AnalystNo ratings yet
- InflationDocument10 pagesInflationData AnalystNo ratings yet
- InterestDocument14 pagesInterestData AnalystNo ratings yet
- Networking: - Computer NetworkDocument32 pagesNetworking: - Computer NetworkCaunan Joanna PaulineNo ratings yet
- Web Chapter - How Documents Transfer Across InternetDocument102 pagesWeb Chapter - How Documents Transfer Across InternetData AnalystNo ratings yet
- Acc Gr11 May 2009 PaperDocument13 pagesAcc Gr11 May 2009 PaperSam ChristieNo ratings yet
- IGO Operations Manual PDFDocument2,251 pagesIGO Operations Manual PDFMardi Wirengkoso100% (1)
- Resume Dianne Ostrander 4-27-06-09Document2 pagesResume Dianne Ostrander 4-27-06-09api-12400587No ratings yet
- Solution Map For Mining ppt3952 PDFDocument29 pagesSolution Map For Mining ppt3952 PDFHans AcainNo ratings yet
- Personal SWOT AnalysisDocument8 pagesPersonal SWOT AnalysisNamNo ratings yet
- Prenatal DevelopmentDocument23 pagesPrenatal DevelopmentLF90No ratings yet
- UT Dallas Syllabus For Se2370.501 05s Taught by Weichen Wong (Wew021000)Document1 pageUT Dallas Syllabus For Se2370.501 05s Taught by Weichen Wong (Wew021000)UT Dallas Provost's Technology GroupNo ratings yet
- LMV Tyre SafetyDocument19 pagesLMV Tyre SafetykarvadNo ratings yet
- Negros IslandDocument18 pagesNegros IslandGrace AmaganNo ratings yet
- EnrollNOLA Daily Seat Availability ReportDocument2 pagesEnrollNOLA Daily Seat Availability ReportAdvocateOnlineNo ratings yet
- Final CBLMDocument66 pagesFinal CBLMRanilyn UrbiztundoNo ratings yet
- PreciControl CMV IgG Avidity - Ms - 05942322190.V4.EnDocument2 pagesPreciControl CMV IgG Avidity - Ms - 05942322190.V4.EnARIF AHAMMED PNo ratings yet
- Manual THT70 PDFDocument54 pagesManual THT70 PDFwerterNo ratings yet
- Wind Energy Services Brochure 4696 3 Da en PDFDocument62 pagesWind Energy Services Brochure 4696 3 Da en PDFghadasaudiNo ratings yet
- Energy Performance of Hot, DryDocument128 pagesEnergy Performance of Hot, DrySrinu ReddyNo ratings yet
- 4 McdonaldizationDocument17 pages4 McdonaldizationAngelica AlejandroNo ratings yet
- Customer Status Update Report 27th January 2015 ColourDocument20 pagesCustomer Status Update Report 27th January 2015 ColourmaryNo ratings yet
- 2Tafseer2019Sep4 17 24oc1 8 29nov5 262020jan7 21F11 18 25Document96 pages2Tafseer2019Sep4 17 24oc1 8 29nov5 262020jan7 21F11 18 25Aroob YaseenNo ratings yet
- Cardio Fitt Pin PostersDocument5 pagesCardio Fitt Pin Postersapi-385952225No ratings yet
- Aspen Separation Unit-OpsDocument25 pagesAspen Separation Unit-Opsedwin dableoNo ratings yet
- Underwater vessels, sensors, weapons and control systemsDocument1 pageUnderwater vessels, sensors, weapons and control systemsNguyễn ThaoNo ratings yet
- Cucs 016 13 PDFDocument16 pagesCucs 016 13 PDFAnonymous SlyvspdBNo ratings yet
- Eriopon R LiqDocument4 pagesEriopon R LiqsaskoNo ratings yet
- Multiple PDP Contexts User Guide Rev1Document16 pagesMultiple PDP Contexts User Guide Rev1ajit_balyan2003No ratings yet
- Prepare Egg Dishes GuideDocument5 pagesPrepare Egg Dishes GuideRuth CesistaNo ratings yet
- NHW Upper Intermediate 4e Wordlist HungarianDocument34 pagesNHW Upper Intermediate 4e Wordlist HungarianpcdmisNo ratings yet
- PhotosynthesisDocument30 pagesPhotosynthesisAngela CanlasNo ratings yet
- Paratech Brochures RSSDocument12 pagesParatech Brochures RSSTatiana Andrea Carvajal GutierrezNo ratings yet