Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Limit Increment Derivative and Continuity
Uploaded by
Bhaskar Joshi0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views26 pagesThis file provides you the knowledge of theory related to limits, continuity and derivatives.
Original Title
LIMIT-INCREMENT-DERIVATIVE-AND-CONTINUITY
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis file provides you the knowledge of theory related to limits, continuity and derivatives.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views26 pagesLimit Increment Derivative and Continuity
Uploaded by
Bhaskar JoshiThis file provides you the knowledge of theory related to limits, continuity and derivatives.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 26
LIMIT, INCREMENT, DERIVATIVE
Limit: When the successive values of a
variable x approach nearer and nearer a
fixed value a, in such a way that the
difference x — a becomes small and
remains as small as we please, the value a
is called the limit of the variable x.
LIMIT, INCREMENT, DERIVATIVE
Basics of limit
•
Proof of Squeeze Theorem
Verification
Homework
Prove that the right hand limit converges to e as n tends to infinity.
This quantity e is the base of the Napierian logarithm.
Hint: Use Binomial Theorem
Infinite limits
From graph we see
that as the x tends
to infinity(negative
or positive), the
function y is
approaching to zero.
Also, we see that
the x axis is
asymptote to the
curve.
Limits
LIMITS
Increments
• An increment of a variable quantity is any
addition to its value, and is denoted by the
symbol ∆ written before the quantity. Thus ∆x
denotes an increment of x, ∆y, an increment
of y.
Continuity
Illustration
Example
Example
Derivative
• The derivative of a function may be defined as
the limiting value of the ratio of the increment
of the function to the increment of the
variable, as the latter increment approaches
zero.
• It is to be noticed that dy/dx is not defined as
as a fraction, but a single symbol denoting the
limit of the fraction ∆y/∆x
Derivative
Understanding derivative of x squared
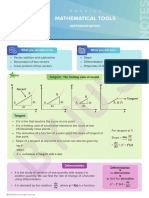
Physical/Geometrical
meaning/interpretation of derivative
• Derivative of a function at any point
represents the slope of the tangent to the
curve drawn at that point.
• At this point, the chord and the tangent
become coincident.
Derivative and Integral
You might also like
- An Introduction to Lebesgue Integration and Fourier SeriesFrom EverandAn Introduction to Lebesgue Integration and Fourier SeriesNo ratings yet
- The Definite Integral: Limits of Riemann SumsDocument10 pagesThe Definite Integral: Limits of Riemann SumsPablo NortonNo ratings yet
- Limits and Continuity (Calculus) Engineering Entrance Exams Question BankFrom EverandLimits and Continuity (Calculus) Engineering Entrance Exams Question BankNo ratings yet
- Differentiation of Algebraic FunctionsDocument32 pagesDifferentiation of Algebraic FunctionsIan Jay AntipuestoNo ratings yet
- DerivativeDocument18 pagesDerivativeHerdianto ArifienNo ratings yet
- Derivative: Differentiation and The DerivativeDocument16 pagesDerivative: Differentiation and The DerivativeJaime Eduardo Sttivend VelezNo ratings yet
- Derivatives, Rate of Change, Relationship Between A-1Document10 pagesDerivatives, Rate of Change, Relationship Between A-1lemankhanimNo ratings yet
- Maxima and Minima 2024Document8 pagesMaxima and Minima 2024Vince Leo Panoncillon GonzalesNo ratings yet
- LimitsDocument24 pagesLimitsVenkat GowdaNo ratings yet
- Geometrical Meaning of Differentiation: Douglas Arnold Here HereDocument1 pageGeometrical Meaning of Differentiation: Douglas Arnold Here Hereapi-240156957No ratings yet
- Differential CalculusDocument30 pagesDifferential CalculusRahul DubeyNo ratings yet
- Consu Bit (Numerical and Statistical) 1Document2 pagesConsu Bit (Numerical and Statistical) 1SreejithNo ratings yet
- CALCULUSDocument28 pagesCALCULUSaron zigglerNo ratings yet
- G6 Polynomial CurvesDocument13 pagesG6 Polynomial CurvesMaxine AsuncionNo ratings yet
- RegressionDocument25 pagesRegressionABY MOTTY RMCAA20-23No ratings yet
- 12 4 CurvatureDocument7 pages12 4 CurvatureVenu GeorgeNo ratings yet
- Maths For EconomicsDocument32 pagesMaths For Economicsnurul azna abd majid (BG)No ratings yet
- Differentiation: Group MembersDocument32 pagesDifferentiation: Group MembersAnkit PokhrelNo ratings yet
- Differentiation & IntegrationDocument12 pagesDifferentiation & IntegrationSIVARANJANI PNo ratings yet
- My Understanding of DerivativeDocument1 pageMy Understanding of DerivativewaliNo ratings yet
- Limit and ContinuityDocument4 pagesLimit and Continuityapi-1274662850% (1)
- DifferentiationDocument11 pagesDifferentiationVidhan SinghNo ratings yet
- LIMITSDocument2 pagesLIMITSDIACHEL AMANTENo ratings yet
- Sample ConceptsDocument4 pagesSample Conceptskimdaniel2006No ratings yet
- Derivative, TXTDocument169 pagesDerivative, TXTSamuel ParkNo ratings yet
- Gradient of A VectorDocument8 pagesGradient of A Vectordwarika2006No ratings yet
- Differential Calculus: Limit and ContinuityDocument4 pagesDifferential Calculus: Limit and Continuityapi-127466285No ratings yet
- Lesson 1.1 The Limit of A FunctionDocument18 pagesLesson 1.1 The Limit of A FunctiontalatayodjasminesNo ratings yet
- CH 6Document42 pagesCH 6Mikiyas MulunehNo ratings yet
- Limits Are The Backbone of CalculusDocument4 pagesLimits Are The Backbone of CalculusShiela Mae LegaspiNo ratings yet
- Limits at Infinity: Basic Calculus Grade 12Document21 pagesLimits at Infinity: Basic Calculus Grade 12hedge hogNo ratings yet
- ACTIVIDAD DE BILINGÜISMO (1) CompletoDocument2 pagesACTIVIDAD DE BILINGÜISMO (1) CompletoKatia PadillaNo ratings yet
- Derivatives: A Physics 100 TutorialDocument18 pagesDerivatives: A Physics 100 TutorialJust SleepingNo ratings yet
- Reviewer BSEE (Calculus)Document13 pagesReviewer BSEE (Calculus)Ronalyn ManzanoNo ratings yet
- Regression Analysis Using SPSS: DR Somesh K SinhaDocument17 pagesRegression Analysis Using SPSS: DR Somesh K SinhaSomesh100% (1)
- Differentiation & Maxima & MinimaDocument30 pagesDifferentiation & Maxima & Minimaakki2511No ratings yet
- Chapter One 1. LimitDocument10 pagesChapter One 1. LimitBetsegaw DemekeNo ratings yet
- Correlation and Simple RegressionDocument5 pagesCorrelation and Simple RegressionMarjorie HouNo ratings yet
- Limits: F, Find The Area Between The Graph of F and The Interval (A, B) On The X-AxisDocument8 pagesLimits: F, Find The Area Between The Graph of F and The Interval (A, B) On The X-AxisKainat Komal KhanNo ratings yet
- Chapter Three: Applications of The DerivativeDocument60 pagesChapter Three: Applications of The DerivativeSabir AliNo ratings yet
- RegressionDocument24 pagesRegressionVaruni GuptaNo ratings yet
- Gradient Descent - Xiaowei HuangDocument53 pagesGradient Descent - Xiaowei HuangHuy PhamNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 BDocument9 pagesChapter 2 BBiplove PokhrelNo ratings yet
- Project On Concept of Limit: A Project Report Submitted To Kist Secondary School Kathmandu, Nepal Date: .Document19 pagesProject On Concept of Limit: A Project Report Submitted To Kist Secondary School Kathmandu, Nepal Date: .Agrima AryalNo ratings yet
- Advanced Functions GlossaryDocument9 pagesAdvanced Functions GlossaryKnoll711No ratings yet
- Limits and ContinuityDocument18 pagesLimits and ContinuityMelchor Jaramilla OronosNo ratings yet
- 4 4 Limits To InfinityDocument21 pages4 4 Limits To InfinityEd Angelo T.CirunarysNo ratings yet
- Math Week 6 NotesDocument3 pagesMath Week 6 Notesapi-490233660No ratings yet
- Q1 Vocabulary. AP Calculus: LimitsDocument1 pageQ1 Vocabulary. AP Calculus: LimitsEsther EnriquezNo ratings yet
- Pearson and Spearman Correlation SPSSDocument46 pagesPearson and Spearman Correlation SPSSGALIH PRAHISTYANo ratings yet
- Maths Chapter 2Document298 pagesMaths Chapter 2Tinsae MathewosNo ratings yet
- 2nd Sem MathDocument15 pages2nd Sem MathJayesh khachaneNo ratings yet
- Econ 303 Section 2.1Document30 pagesEcon 303 Section 2.1Mary Catherine Almonte - EmbateNo ratings yet
- MACHINE LEARNING ALGORITHM Unit-IIDocument115 pagesMACHINE LEARNING ALGORITHM Unit-IIakash chandankarNo ratings yet
- Limit and ContinuityDocument17 pagesLimit and ContinuityAyash JainNo ratings yet
- LIMITSDocument2 pagesLIMITSDIACHEL AMANTENo ratings yet
- Regression Lecture SummaryDocument31 pagesRegression Lecture Summaryabrham abagedaNo ratings yet
- Limits and Continuity: Thu Mai, Michelle Wong, Tam VuDocument17 pagesLimits and Continuity: Thu Mai, Michelle Wong, Tam VusampritcNo ratings yet
- GeomderivativeofsinxDocument1 pageGeomderivativeofsinxvaxifeb809No ratings yet
- AP Calculus AB - Ultimate Guide Notes - KnowtDocument29 pagesAP Calculus AB - Ultimate Guide Notes - Knowtcondyerhaze1No ratings yet