Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Unit 3: Lesson 2 The Periodic Table
Uploaded by
Salah Ibrahim0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views14 pagesOriginal Title
14591151
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views14 pagesUnit 3: Lesson 2 The Periodic Table
Uploaded by
Salah IbrahimCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 14
Unit 3 Lesson 2 The Periodic Table
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
Unit 3 Lesson 2 The Periodic Table
Get Organized!
What are elements?
• It was once believed that fire, wind, earth, and
water, in various combinations, made up all
objects.
• By the 1860s, scientists considered there to be at
least 60 different basic substances, or elements.
• Scientists found that many of these elements have
similar properties and began classifying them.
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
Unit 3 Lesson 2 The Periodic Table
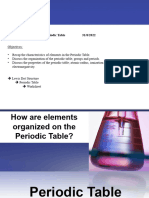
How are the elements organized?
• Dmitri Mendeleev first organized the elements by
arranging them in order of increasing atomic
mass.
• He observed that the properties of those elements
were in a periodic, or regularly repeating, pattern.
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
Unit 3 Lesson 2 The Periodic Table
How are the elements organized?
• Mendeleev’s arrangement of the elements became
known as the periodic table.
• Henry Moseley reorganized Mendeleev’s periodic
table in order of increasing number of protons, or
atomic number.
• The periodic table is useful because it makes clear
many patterns among the elements’ properties.
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
Unit 3 Lesson 2 The Periodic Table
How are the elements organized?
• What can you learn about an element from the
periodic table?
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
Unit 3 Lesson 2 The Periodic Table
Making Arrangements
What information is contained in each
square on the periodic table?
• Each square contains an element’s chemical
name, atomic number, chemical symbol, and
average atomic mass.
• The atomic number is placed at the top of each
square.
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
Unit 3 Lesson 2 The Periodic Table
What information is contained in each
square on the periodic table?
• The chemical symbol is an abbreviation for the
element’s name.
• The first letter of the chemical symbol is always
capitalized, and any other letter is lowercase.
• The name of the element is written under the
symbol.
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
Unit 3 Lesson 2 The Periodic Table
What information is contained in each
square on the periodic table?
• All atoms of an element have the same number of
protons, but the number of neutrons can vary.
• The average atomic mass of an atom is the
weighted average of the masses of all the
naturally occurring isotopes of that element.
• Average atomic mass is reported in atomic mass
units (u).
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
Unit 3 Lesson 2 The Periodic Table
How are the elements arranged on the
periodic table?
• A zigzag line on the periodic table divides the
three major categories of elements: metals,
nonmetals, and metalloids.
• Metals are elements that are shiny and conduct
heat and electricity well.
• Elements to the left of the zigzag line are metals,
except for hydrogen.
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
Unit 3 Lesson 2 The Periodic Table
How are the elements arranged on the
periodic table?
• The elements to the right of the zigzag line are
nonmetals.
• Nonmetals are poor conductors of heat and
electricity, and are often dull and brittle.
• Metalloids are elements that have some
properties of metals and nonmetals. They border
the zigzag line.
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
Unit 3 Lesson 2 The Periodic Table
How are the elements arranged on the
periodic table?
• List three metals, nonmetals, and metalloids.
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
Unit 3 Lesson 2 The Periodic Table
How are the elements arranged on the
periodic table?
• Each vertical column of elements on the periodic
table is called a group, or family.
• Elements in a group are similar because their
atoms have the same number of valence
electrons.
• Valence electrons participate in chemical bonding.
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
Unit 3 Lesson 2 The Periodic Table
How are the elements arranged on the
periodic table?
• Each horizontal row of elements on the periodic
table is called a period.
• Physical and chemical properties of elements
change in predictable ways from one end of the
period to the other.
• Atomic size decreases as you move from left to
right across a period.
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
Unit 3 Lesson 2 The Periodic Table
How are the elements arranged on the
periodic table?
• Elements in the middle of a period are the most
dense.
• As you move from left to right within a period, the
atomic number of each element increases by 1.
• The lanthanides and actinides are placed below
the table to allow the table to be narrower.
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
You might also like
- IGCSE 14 MomentumDocument39 pagesIGCSE 14 MomentumHakim Abbas Ali Phalasiya36% (11)
- Class 11 Chemistry NCERT Textbook Chapter 3 Classification of Elements and Periodicity in Properties PDFDocument31 pagesClass 11 Chemistry NCERT Textbook Chapter 3 Classification of Elements and Periodicity in Properties PDFSaketh VuppalapatiNo ratings yet
- Fatigue of Bolted ConnectionsDocument19 pagesFatigue of Bolted Connectionsz2aliNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Lesson 2Document9 pagesChemistry Lesson 2Vinod Varadan SNo ratings yet
- The Ultimate Mathematics of The QuranDocument188 pagesThe Ultimate Mathematics of The Quranindiapower19No ratings yet
- Biols102 All ChaptersDocument617 pagesBiols102 All ChaptersmariamNo ratings yet
- Theory of Flow Fracture NadaiDocument611 pagesTheory of Flow Fracture Nadaimarc53042100% (1)
- Lecture 5 The Periodic TableDocument56 pagesLecture 5 The Periodic TableSherlyn PedidaNo ratings yet
- The Chemistry of the Metallic Elements: The Commonwealth and International Library: Intermediate Chemistry DivisionFrom EverandThe Chemistry of the Metallic Elements: The Commonwealth and International Library: Intermediate Chemistry DivisionNo ratings yet
- 6-8H Cnlaepn693408 U03l02Document12 pages6-8H Cnlaepn693408 U03l02Its ya BoiiNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 - L1, L2, L3Document44 pagesUnit 2 - L1, L2, L3Rawan YounisNo ratings yet
- Hint Hint Hint Hint: Key ConceptsDocument1 pageHint Hint Hint Hint: Key ConceptsjankaleighNo ratings yet
- History of Periodic TableDocument94 pagesHistory of Periodic TableMUHAMMAD SYAFI BIN ABDUL MALIK / UPMNo ratings yet
- The Modern Periodic Table Chemistry PresentationDocument15 pagesThe Modern Periodic Table Chemistry PresentationShee YingNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of General Organic and Biological Chemistry With Masteringchemistry 7th Edition Mcmurry Solutions ManualDocument36 pagesFundamentals of General Organic and Biological Chemistry With Masteringchemistry 7th Edition Mcmurry Solutions Manualslapperboatbill49x100% (21)
- Class Powerpoint Lesson On The Periodic TableDocument22 pagesClass Powerpoint Lesson On The Periodic TableTrudy- Ann CaineNo ratings yet
- Year 10 ChemistryDocument26 pagesYear 10 ChemistryBigDaddy GNo ratings yet
- 2.1 Composition of Matter: Chapter 2: Chemistry of LifeDocument15 pages2.1 Composition of Matter: Chapter 2: Chemistry of Lifeapi-520057338No ratings yet
- Science 7 WEEK 3Document58 pagesScience 7 WEEK 3Rochel MarasiganNo ratings yet
- Ncert ch3 Chemistry Class 11Document26 pagesNcert ch3 Chemistry Class 11Karan ManglaNo ratings yet
- Periodic Table and Periodicity of Properties: Major ConceptsDocument14 pagesPeriodic Table and Periodicity of Properties: Major ConceptsAbdullah AdeelNo ratings yet
- The Development of The Periodic TableDocument95 pagesThe Development of The Periodic TableSherren NalaNo ratings yet
- Periodic Table: Oakland Schools Chemistry Resource UnitDocument42 pagesPeriodic Table: Oakland Schools Chemistry Resource UnitAnum TauqirNo ratings yet
- 3 Ways To Study The Chemical and Physical Properties of Atoms in The Periodic TableDocument4 pages3 Ways To Study The Chemical and Physical Properties of Atoms in The Periodic TableHuma AasimNo ratings yet
- Classification of Elements and Periodicity in Properties: Unit 3Document26 pagesClassification of Elements and Periodicity in Properties: Unit 3Nithin Bharadwaj KummamuruNo ratings yet
- Science 8 Quarter3 Module 4Document15 pagesScience 8 Quarter3 Module 4Noeh PiedadNo ratings yet
- Worksheet On PTDocument3 pagesWorksheet On PTAlexander MalvarNo ratings yet
- Biology Basis of LifeDocument71 pagesBiology Basis of LifeAhmed BazzyNo ratings yet
- General ScienceDocument42 pagesGeneral SciencenypupNo ratings yet
- 6-8H Cnlaepn693408 U03l01Document16 pages6-8H Cnlaepn693408 U03l01Its ya BoiiNo ratings yet
- Periodic Trends CompleteDocument51 pagesPeriodic Trends CompleteZal Fildan DuomaNo ratings yet
- Periodic Table of ElementsDocument32 pagesPeriodic Table of ElementsKamilah Caitlyn AmansecNo ratings yet
- Elements and The PeriodicDocument45 pagesElements and The PeriodicRenata AlvesNo ratings yet
- CHM 105 INORGANIC CHEMISTRY I (Autosaved)Document59 pagesCHM 105 INORGANIC CHEMISTRY I (Autosaved)Daniel DominicNo ratings yet
- 1 of 20 1 of 36: © Boardworks LTD 2004 © Boardworks LTD 2005Document19 pages1 of 20 1 of 36: © Boardworks LTD 2004 © Boardworks LTD 2005MindOfPrinceNo ratings yet
- ATOMIC MODEL and PERIODIC TABLEDocument67 pagesATOMIC MODEL and PERIODIC TABLEkimsioco02No ratings yet
- Periodic TableDocument41 pagesPeriodic TableMahmoud AladdasiNo ratings yet
- Periodic Properties Chemistry Class 11Document32 pagesPeriodic Properties Chemistry Class 11Ravinder singhNo ratings yet
- Misconceptions in The Periodic TableDocument3 pagesMisconceptions in The Periodic TableEdcademiaNo ratings yet
- The Periodic Classification of Elements From Mendeleev To ModernDocument8 pagesThe Periodic Classification of Elements From Mendeleev To Modernfarhatomar1477No ratings yet
- Chapter 02 Skeletal NotesDocument27 pagesChapter 02 Skeletal NotesElizabeth WoodNo ratings yet
- Week 3 3rd QuarterDocument55 pagesWeek 3 3rd QuarterCirille AgpaoaNo ratings yet
- Periodic TableDocument6 pagesPeriodic TableAgriyae JainNo ratings yet
- National Open University of Nigeria: School of Science and TechnologyDocument136 pagesNational Open University of Nigeria: School of Science and TechnologyDrema PatricklaNo ratings yet
- CHM 111 PDFDocument136 pagesCHM 111 PDFSreenivasuluNo ratings yet
- General Science and Environment MKT-125 (3 Credits)Document43 pagesGeneral Science and Environment MKT-125 (3 Credits)World EducationNo ratings yet
- MT633 - Unit 1 Chemical Foundations ForDocument109 pagesMT633 - Unit 1 Chemical Foundations ForTia MallariNo ratings yet
- 11 Physics Ncert ChapterDocument26 pages11 Physics Ncert ChapterBhumika DNo ratings yet
- General Science and Environment MKT-125 (3 Credits) : Course TeacherDocument42 pagesGeneral Science and Environment MKT-125 (3 Credits) : Course TeacherWorld EducationNo ratings yet
- DS-4, English MediumDocument56 pagesDS-4, English MediumRashini AnneNo ratings yet
- Introduction To The Modern Periodic TableDocument10 pagesIntroduction To The Modern Periodic Tablefrankycoc667No ratings yet
- Elements, Atoms, and The Atomic Theory: Type of AtomDocument7 pagesElements, Atoms, and The Atomic Theory: Type of AtomSasikumar MadhavanNo ratings yet
- Reviewer For 1st Monthly Examination (SCIENCE)Document4 pagesReviewer For 1st Monthly Examination (SCIENCE)Marco Antonio MatanguihanNo ratings yet
- Organization of The Periodic: Open Chemical Building Blocks Book To Page 85. Get Chalkboards, Chalk, and EraserDocument39 pagesOrganization of The Periodic: Open Chemical Building Blocks Book To Page 85. Get Chalkboards, Chalk, and EraserJackie ChristoffelNo ratings yet
- Chemitry Tarea InglesDocument1 pageChemitry Tarea InglesDIEGO LUNANo ratings yet
- History of The PeriodicTableDocument50 pagesHistory of The PeriodicTablePscf CarmonaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2. Atomic StructureDocument24 pagesChapter 2. Atomic StructuremohansaiNo ratings yet
- Kech 103Document26 pagesKech 103Jonel C. FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Periodic TableDocument34 pagesPeriodic TableSarah Francisco HerviasNo ratings yet
- Stem Quimica enDocument20 pagesStem Quimica enHelliana SmithNo ratings yet
- Chemistry of the Non-Metallic Elements: The Commonwealth and International Library: Intermediate Chemistry DivisionFrom EverandChemistry of the Non-Metallic Elements: The Commonwealth and International Library: Intermediate Chemistry DivisionNo ratings yet
- Do You Know How Much Energy Your Body NeedDocument6 pagesDo You Know How Much Energy Your Body NeedSalah IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Unit 3: Lesson 3 Electrons and Chemical BondingDocument13 pagesUnit 3: Lesson 3 Electrons and Chemical BondingSalah IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 Pure Substances and Mixtures: Unit 1Document21 pagesLesson 4 Pure Substances and Mixtures: Unit 1Salah IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Essential Question:: How Do Particles in Solids, Liquids, and Gases Move?Document11 pagesUnit 1 Essential Question:: How Do Particles in Solids, Liquids, and Gases Move?Salah IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Lesson 2 WeatheringDocument15 pagesUnit 1 Lesson 2 WeatheringSalah IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Concept 3 - Light & SightDocument7 pagesConcept 3 - Light & SightSalah IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Report 2 SMDocument11 pagesReport 2 SMDulanjaya NayanajithNo ratings yet
- Salt AnalysisDocument17 pagesSalt Analysisvijaylakshmi0727No ratings yet
- Stoichiometry Final Test BankDocument140 pagesStoichiometry Final Test BankFatmaNo ratings yet
- BCG Report2020 3Document3 pagesBCG Report2020 3Green MichaelsNo ratings yet
- TGA DSC Reading MaterialDocument58 pagesTGA DSC Reading MaterialSaurabh ShashankNo ratings yet
- Astm d6730 AppDocument5 pagesAstm d6730 AppRuồi SữaNo ratings yet
- Determination of Abamectin in Citrus Fruits by LiquidDocument9 pagesDetermination of Abamectin in Citrus Fruits by LiquidAW EmeNo ratings yet
- Saved RecsDocument77 pagesSaved RecsCarlos PeñaNo ratings yet
- BHN Ball Impression ValueDocument5 pagesBHN Ball Impression ValueJAFFERNo ratings yet
- Fuji TimerDocument4 pagesFuji Timertimbrant9129No ratings yet
- Boundary Conditions E and HDocument3 pagesBoundary Conditions E and HAamod ShankerNo ratings yet
- CiVentiChem India Presentation - 2012Document60 pagesCiVentiChem India Presentation - 2012Venugopal Rao VeeramaneniNo ratings yet
- Automotive High Heat Paint: Technical Data ATO-15Document2 pagesAutomotive High Heat Paint: Technical Data ATO-15HillNo ratings yet
- Mixing: The Benefit of Vacuum Mixing: Jian-Sheng WangDocument6 pagesMixing: The Benefit of Vacuum Mixing: Jian-Sheng WangpriftifNo ratings yet
- Amendment DEIA Chemical Use 2012 enDocument103 pagesAmendment DEIA Chemical Use 2012 enbqdianzNo ratings yet
- Science 7Document5 pagesScience 7katherine bacallaNo ratings yet
- A Critical Review of Friction Measurement of Textile MaterialsDocument10 pagesA Critical Review of Friction Measurement of Textile MaterialsNilavan MuthuNo ratings yet
- PLUG VALVE - Full Bore - Technical BulletinDocument28 pagesPLUG VALVE - Full Bore - Technical BulletinRenzo Conde Montenegro100% (1)
- Complete Guide On Online HWG ID Registration PDFDocument11 pagesComplete Guide On Online HWG ID Registration PDFNehru Valdenarro ValeraNo ratings yet
- MA 3000 NIC 600 2233 01 Simplified Operation ManualDocument10 pagesMA 3000 NIC 600 2233 01 Simplified Operation ManualPaul PlimNo ratings yet
- 24carat Alloy1Document10 pages24carat Alloy1NileshhkNo ratings yet
- Lab Report Experiment 1Document12 pagesLab Report Experiment 1afifiNo ratings yet
- Proximate Analysis of The Analysis Sample of Coal and Coke by Instrumental ProceduresDocument5 pagesProximate Analysis of The Analysis Sample of Coal and Coke by Instrumental ProceduresGerónimo PerazzoNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 - EntropyDocument37 pagesUnit 2 - EntropyDeepank SachdevNo ratings yet
- FM200 Beta - Gamma ManualDocument102 pagesFM200 Beta - Gamma ManualFi ND100% (1)
- Catalogo Dixon Oil&GAS Conexoes PDFDocument60 pagesCatalogo Dixon Oil&GAS Conexoes PDFCarlos SopasNo ratings yet